Summary
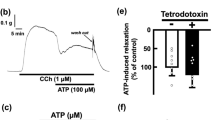
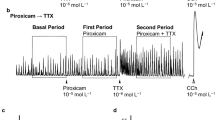
The participation of substance P in the noncholinergic contraction induced by transmural stimulation (TMS) of the carp intestinal bulb was examined. In the presence of atropine, substance P caused the contraction of carp intestinal bulb smooth muscle in a concentration dependent manner (1 nmol/1 − 1 μmol/l). The EC50 value was 28 ± 7 nmol/l (n = 6). Substance P-induced desensitization (1 μmol/l for 15 min), decreased the response to substance P and the atropine-resistant contraction induced by TMS (20 Hz) selectively. In contrast, in the absence of atropine, the contraction induced by TMS (20 Hz) was slightly attenuated with the substance P-induced desensitization. The acid extract obtained from the carp intestinal bulb contained a smooth muscle excitatory material whose pharmacological properties were consistent with those of substance P. The present results indicate that a substance P-like peptide is present in the carp intestinal bulb which is involved in the non-cholinergic contraction induced by TMS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baron SA, Jaffe BM, Gintzler AR (1983) Release of substance P from the enteric nervous system: direct quantitation and characterization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 227:365–368
Burnstock G (1972) Purinergic nerves. Pharmacol Rev 24:509–581
Burnstock G, Satchell DG, Smythe A (1972) A comparison of the excitatory and inhibitory effects of non-adrenergic, non-cholinergic nerve stimulation and exogenously applied ATP on a variety of smooth muscle preparations from different vertebrate species. Br J Pharmacol 46:234–242
Campbell G, Gannon BJ (1976) The splanchnic nerve supply to the stomach of the trout, Salmo trutta and S. gairdneri. Comp Biochem Physiol 55C:51–53
Ekblad E, Winther C, Ekman R, Hakanson R, Sundler F (1987) Projections of peptide-containing neurons in rat small intestine. Neuroscience 20:169–188
Franco R, Costa M, Furness JB (1979) Evidence for the release of endogenous substance P from intestinal nerves. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 306:195–201
Gintzler AR, Hyde D (1983) A specific substance P antagonist attenuates non-cholinergic electrically induced contractures of the guinea-pig isolated ileum. Neurosci Lett 40:75–79
Holmgren S, Vaillant C, Dimaline R (1982) VIP-, substance P-, gastrin/CCK-, bombesin-, somatostatin- and glucagon-like immunoreactivities in the gut of the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. Cell Tissue Res 223:141–153
Holmgren S (1985) Substance P in the gastrointestinal tract of Squalus acanthias. Molecular Physiol 8:119–130
Holmgren S, Grove DJ, Nilsson S (1985) Substance P acts by releasing 5-hydroxytryptamine from enteric neurons in the stomach of the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri. Neuroscience 14:683–693
Holzer P (1984) Characterization of the stimulus-induced release of immunoreactive substance P from the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig small intestine. Brain Res 297:127–136
Huidobro-Toro JP, Chelala CA, Bahouth S, Nordar R, Musacchio JM (1982) Fading and tachyphylaxis to the contractile effects of substance P in the guinea-pig ileum. Eur J Pharmacol 81:21–34
Jensen J, Holmgren S (1985) Neurotransmitters in the intestine of the Atlantic cod; Gadus morhua. Comp Biochem Physiol 82C:81–89
Kitazawa T, Hoshi T, Temma K, Kondo H (1986) Effects of morphine and methionine-enkephalin on the smooth muscle tonus and the contraction induced by transmural stimulation in the carp (Cyprinus carpio) intestinal bulb. Comp Biochem Physiol 84C:299–305
Kitazawa T, Furuhashi H, Umezawa K, Ohkoshi N, Temma K, Kondo H (1987) Pharmacological properties of the atropine-resistant contraction of the carp (Cyprinus carpio) intestinal bulb induced by transmural stimulation. Comp Biochem Physiol 88C:225–232
Kitazawa T, Kimura A, Furuhashi H, Temma K, Kondo H (1988) Contractile response to substance P in isolated smooth muscle strips from the intestinal bulb of the carp (Cyprinus carpio). Comp Biochem Physiol 890:277–285
Leander S, Hakanson R, Rosell S, Folkers K, Sundler F, Tornqvist K (1981) A specific substance P antagonist blocks smooth muscle contractions induced by non-cholinergic, non-adrenergic nerve stimulation. Nature (Lond) 294:467–469
Matusak O, Bauer V (1986) Effect of desensitization induced by adenosine 5′-triphosphate, substance P, bradykinin, serotonin, r-aminobutyric acid and endogenous noncholinergic-nonadrenergic transmitter in the guinea-pig ileum. Eur J Pharmacol 126:199–209
Nilsson S, Holmgren S (1983) Splanchnic nervous control of the stomach of the spiny dogfish, Squalus acanthias. Comp Biochem Physiol 76C:271–276
Pearse AGE, Polak JM (1975) Immunocytochemical localization of substance P in mammalian intestine. Histochemistry 41:373–375
Rombout JHWM, Reinecke M (1984) Immunohistochemical localization of (neuro)peptide hormones in endocrine cells and nerves of the gut of a stomachless teleost fish, Barbus conchonius (Cyprinidae). Cell Tissue Res 237:57–65
Schultzberg M, Hokfelt T, Nilsson G, Terenius L, Rehfeld JF, Brown M, Elde R, Goldstein M, Said S (1980) Distribution of peptide and catecholamine containing neurons in the gastrointestinal tract of rat and guinea-pig; Immunohistochemical studies with antisera to substance P, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, enkephalins, somatostatin, gastrin/cholecystokinin, neurotensin and dopamine β-hydroxylase. Neuroscience 5:689–744
Von Euler US, Gaddum JH (1931) An unidentified depressor substance in certain tissue extracts. J Physiol (Lond) 72:74–87
Wali FA (1985) Possible involvement of substance P in the contraction produced by periarterial nerve stimulation in the rat ileum. J Auton Pharmacol 5:143–148
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to T. Kitazawa at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kitazawa, T., Kudo, K., Ishigami, M. et al. Evidence that a substance P-like peptide mediates the non-cholinergic excitatory response of the carp intestinal bulb (Cyprinus carpio). Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 338, 68–73 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168814
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168814