Summary
5-Hydroxytryptamine1B (5-HT1B) receptor mediated-inhibition of forskolin-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity in rat substantia nigra was characterized pharmacologically and compared to 5-HT1D receptor mediated-inhibition of forskolin-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity in calf substantia nigra. Special attention was paid to the effects of drugs known to bind with high affinity to 5-HT1B (pindolol, propranolol, cyanopindolol, SDZ 21-009, isamoltane) or 5-HT1D recognition sites (yohimbine, rauwolscine).
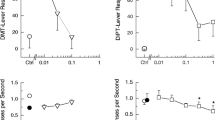
PEC50 or pK B values of a variety of 5-HT-receptor ligands (6 agonists including 5-HT, and 12 antagonists) for the inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity in rat substantia nigra, correlated significantly to the corresponding pK D values at 5-HT1B binding sites (r = 0.90, P = 0.0001). Amongst the α2- and β-adrenoceptor antagonists tested, none of the drugs expressed more than 35% of the intrinsic activity of 5-HT at 5-HT1B receptors. When tested as antagonists, their pK B values were in good agreement with their pK D values for 5-HT1B sites. By contrast, these drugs displayed marked intrinsic activity at 5-HT1D receptors: their pEC50 values were close to their pK D values for 5-HT1D sites and their effects could be potently antagonized by methiothepin. The rank orders of potency of the tested compounds at 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D were markedly different.
The results strengthen the identity between 5-HT receptors mediating inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity in rat and calf substantia nigra and 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D binding sites, respectively. They underline the differences between these receptors in terms of intrinsic activities and potencies of drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouhelal R, Smounya L, Bockaert J (1988) 5-HT1B receptors are negatively coupled with adenylate cyclase in rat substantia nigra. Eur J Pharmacol 151:189–196
De Lean A, Stadel JM, Lefkowitz RJ (1980) A ternary complex model explains the agonist-specific binding properties of the adenylate cyclase-coupled β-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem 255:7108–7117
De Vivo M, Maayani S (1986) Characterization of 5-hydroxytryptamine1A-receptor-mediated inhibition of forskolin-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity in guinea-pig and rat hippocampal membranes. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 238:248–253
Dumuis A, Sebben M, Bockaert J (1988) Pharmacology of 5-hydroxytryptamine-1A-receptors which inhibit cAMP production in hippocampal and cortical neurons in primary culture. Mol Pharmacol 33:178–186
Engel G, Göthert M, Hoyer D, Schlicker E, Hillebrand K (1986) Identity of inhibitory presynaptic 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) autoreceptors in the rat brain cortex with 5-HT1B binding sites. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 332:1–7
Fargin A, Raymond JR, Lohse MJ, Kobilka BK, Caron MG, Lefkowitz RJ (1988) The genomic clone G-21 which resembles a β-adrenergic receptor sequence encodes the 5-HT1A receptor. Nature 335:358–360
Feuerstein TJ, Hertting G, Jackisch R (1985) Endogenous noradrenaline as modulator of hippocampal serotonin (5-HT)-release. Dual effects of yohimbine, rauwolscine and corynanthine as a-adrenoceptor antagonists and 5-HT-receptor agonists. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 329:216–221
Feuerstein TJ, Lupp A, Hertting G (1987) The serotonin (5-HT) autoreceptor in the hippocampus of the rabbit: role of 5-HT biophase concentration. Neuropharmacology 26:1071–1080
Furchgott RF (1972) The classification of adrenoceptors (adrenergic receptors). An evaluation from the standpoint of receptor theory. In: Blaschko H, Muscholl E (eds) Catecholamines. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York Tokyo, pp 283–335
Hamon M, Cossery JM, Spampinato U, Gozlan H (1986) Are there selective ligands for 5-HT1A and 5-HT1B binding sites in brain? Trends Pharmacol Sci 7:336–338
Herrick-Davis K, Titeler M (1988) Detection and characterization of the serotonin 5-HT1D receptor in rat and human brain. J Neurochem 50:1624–1631
Heuring RE, Peroutka SJ (1987) Characterization of a novel 3H-5-hydroxytryptamine binding site subtype in bovine brain membranes. J Neurosci 7:894–903
Heuring RA, Schlegel JR, Peroutka SJ (1986) Species variations in RU 24969 interactions with non-5-HT1A binding sites. Eur J Pharmacol 122: 279–282
Hoyer D (1988a) Molecular pharmacology and biology of 5-HT1C receptors. TIPS 9:89–94
Hoyer D (1988b) Functional correlates to serotonin 5-HT1 recognition sites. J Rec Res 8:59–81
Hoyer D (1989) 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptors and effector coupling mechanisms in peripheral tissues. in: Fozard JR (ed) Peripheral actions of 5-HT. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 72–99
Hoyer D, Middlemiss DN (1989) The pharmacology of the terminal 5-HT autoreceptors in mammalian brain: evidence for species differences. TIPS 10:130–132
Hoyer D, Engel G, Kalkman HO (1985a) Characterization of the 5-HT1B recognition site in rat brain: binding studies with [125I]iodocyanopindolol. Eur J Pharmacol 118:1–12
Hoyer D, Engel G, Kalkman HO (1985b) Molecular pharmacology of 5-HT1 and 5-HT2 recognition sites in rat and pig brain membranes: radioligand binding studies with [3H]5-HT, [3H]8-OH-DPAT, (−) [125I]iodocyanopindolol, [3H]mesulergine and [3H]ketanserin. Eur J Pharmacol 118:13–23
Hoyer D, Pazos A, Probst A, Palacios JM (1986) Serotonin receptors in the human brain. I. Characterization and autoradiographic localization of 5-HT1A recognition sites. Apparent absence of 5-HT1B recognition sites. Brain Res 376:85–96
Hoyer D, Schoeffter P (1988) 5-HT1D receptors inhibit forskolin-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity in calf substantia nigra. Eur J Pharmacol 147:145–147
Hoyer D, Waeber C, Pazos A, Probst A, Palacios JM (1988) Identification of 5-HT1 recognition site in human brain membranes different from 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B and 5-HT1c sites. Neurosci Lett 85:357–362
Julius D, MacDermott AB, Axel R, Jessel TM (1988) Molecular characterization of a functional cDNA encoding the serotonin 1c receptor. Science 241:558–564
Markstein R, Hoyer D, Engel G (1986) 5-HT1A-receptors mediate stimulation of adenylate cyclase in rat hippocampus. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 333:335–341
Maura G, Ulivi M, Raiteri M (1987) (−)-Propranolol and (±)-cyanopindolol are mixed agonists-antagonists at serotonin autoreceptors in the hippocampus of the brain. Neuropharmacology 26:713–717
Middlemiss DN (1984) Stereoselective blockade at [3H]5-HT binding sites and the 5-HT autoreceptor by propranolol. Eur J Pharmacol 101: 289–293
Middlemiss DN, Fozard JR (1983) 8-Hydroxy-2-(di-n-propylamino)-tetralin discriminates between subtypes of the 5-HT1 recognition site. Eur J Pharmacol 90:151–153
Pazos A, Hoyer D, Palacios JM (1984) The binding of serotonergic ligand to the porcine choroid plexus: characterization of a new type of serotonin recognition site. Eur J Pharmacol 106:539–546
Pazos A, Palacios JM (1985) Quantitative auto-radiographic mapping of serotonin receptors in the rat brain. I. Serotonin-1 receptors. Brain Res 346:205–230
Pedigo NW, Yamamura HI, Nelson DL (1981) Discrimination of multiple [3H]5-hydroxytryptamine-binding sites by the neuroleptic spiperone in rat brain. J Neurochem 36:220–226
Peroutka SJ, Snyder SH (1979) Multiple serotonin receptors: differential binding of [3H]5-hydroxytryptamine, [3H]lysergic acid diethylamide and [3H]spiroperidol. Mol Pharmacol 16:687–699
Pritchett DB, Bach AWJ, Wozny M, Taleb O, Dal Toso R, Shih J, Seeburg PH (1988) Structure and functional expression of cloned rat serotonin 5-HT2 receptor. EMBO J 7:4135–4140
Salomon Y, Londos C, Rodbell M (1974) A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem 58:541–548
Schnellmann RG, Waters SJ, Nelson DL (1984) [3H]5-hydroxytryptamine binding sites: Species and tissue variation. J Neurocbem 42:65–70
Schoeffter P, Hoyer D (1988) Centrally acting hypotensive agents with affinity to 5-HT1A binding sites inhibit forskolin-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity in calf hippocampus. Br J Pharmacol 95:975–985
Schoeffter P, Hoyer D (1989) Interaction of arylpiperazines with 5-HT1A, 5-HTIB, 5-HT1C and 5-HT1D receptors: do discriminatory 5-HT1B receptor ligands exist? Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 339:675–682
Schoeffter P, Waeber C, Palacios JM, Hoyer D (1988) The serotonin 5-HT1D receptor subtype is negatively coupled to adenylate cyclase in calf substantia nigra. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 337:602–608
Waeber C, Dietl MM, Hoyer D, Probst A, Palacios JM (1988a) Visualization of a novel serotonin recognition site (5-HT1D) in the human brain by autoradiography. Neurosci Lett 88:11–16
Waeber C, Schoeffter P, Palacios JM, Hoyer D (1988b) Molecular pharmacology of 5-HT ID recognition sites: radioligand binding studies in human, pig and calf brain membranes. NaunynSchmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 337:595–601
Waldmeier PC, Williams M, Baumann PA, Bischoff S, Sills MA, Neale RF (1988) Interactions of isamoltane (CGP 361 A), an anxiolytic phenoxypropranolamine derivative, with 5-HT1 receptor subtypes in the rat brain. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 337:609–616
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to: D. Hoyer at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schoeffter, P., Hoyer, D. 5-Hydroxytryptamine 5-HT1B and 5-HT1D receptors mediating inhibition of adenylate cyclase activity. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 340, 285–292 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168512
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00168512