Summary
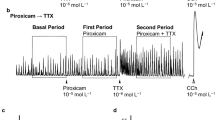
We have studied the motor response to ethyenediamine (EDA), a well known releaser of endogenous GABA, on the longitudinal muscle of the rat isolated proximal duodenum in presence of atropine (3 μM) and guanethidine (3 μM). EDA produced a concentration-(0.03 – 3 μM)-dependent relaxation which was potentiated when the preparations were exposed to GABA during the equilibration period. The GABA-induced potentiation of the response to EDA was prevented by nipecotic acid, an inhibitor of GABA uptake. The response to EDA was partially inhibited by 3-mercaptopropionic acid, a known inhibitor of GABA release. However, contrary to the relaxant response produced by exogenous GABA, the EDA-induced relaxation was picrotoxin-(0.1 μM)-resistant. In preparations pre-exposed to GABA, the response to EDA was partially tetrodotoxin-(1 μM)-sensitive. By contrast, in preparations not exposed to GABA, the EDA-induced relaxation was totally tetrodotoxin resistant. The response to EDA was abolished or largely inhibited in preparations excised from rats in which the proximal duodenum was chemically denervated by exposure (2 weeks before), to benzalkonium chloride (BZK). Likewise, the indirect relaxations produced by electrical field simulation, DMPP, capsaicin or GABA were abolished by BZK pretreatment while noradrenaline was still effective. These findings indicate that the relaxant response to EDA is neurogenic in origin, while being largely tetrodotoxin-resistant. A GABAergic mechanism could be involved but also other inhibitory transmitter(s) should be taken into account. EDA appears a useful tool to study the inhibitory non-adrenergic non-cholinergic innervation of the rat proximal duodenum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bowery NG, Doble DR, Hill DR, Hudson AL, Shaw S, Turnbull MG, Warrington R (1981) Bicuculline-insensitive GABA receptors on peripheral autonomic nerve terminals. Eur J Pharmacol 71:53–70.
Cherubini E, North RA (1984) Actions of GABA on neurones of guinea-pig myenteric plexus. Br J Pharmacol 82:93–100.
Fan SG, Wusteman M, Iversen LL (1981) 3-Mercaptopropionic acid inhibits GABA release from rat brain slices in vitro. Br J Pharmacol 229:371–377.
Fox DA, Epstein ML, Bass P (1983) Surfactants selectively ablate enteric neurons of the rat jejunum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 227:538–544.
Fox DA, Bass P (1986a) Ablation of the myenteric plexus impairs alpha but not beta adrenergic receptor-mediated mechanical response of rat jejunal longitudinal muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 239:9–14.
Fox DA, Bass P (1986b) Pharmacological characterization of rat jejunal contractility after chronic ablation of the myenteric plexus. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 238:372–377.
Fox DA, Herman JR, Bass P (1986) Differentiation between myenteric plexus and longitudinal muscle of the rat jejunum as the site of action of putative enteric transmitters. Eur J Pharmacol 131:39–47.
Gilon P, Reusens-Billen B, Remacle C, Janssens de Varebeke Ph, Pauwels G, Hoet JJ (1987) Localization of high affinity GABA uptake and GABA content in the rat duodenum during development. Cell Tissue Res 249:593–600.
Giotti A, Luzzi S, Spagnesi S, Zilletti L (1983) GABA-A and GABA-B receptor-mediated effects in guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol 78:469–478.
Giotti A, Luzzi S, Maggi CA, Spagnesi S, Zilletti L (1985) Modulatory activity of GABA-B receptors on cholinergic tone in guinea-pig distal colon. Br J Pharmacol 84:883–895.
Hills JM, Jessen KR, Mirsky R (1987) An immunohistochemical study of the distribution of enteric GABA-containing neurons in the rat and guinea-pig intestine. Neuroscience 22:301–312.
Jessen RK, Mirsky R, Dennison ME, Burnstock G (1979) GABA may be a neurotransmitter in the vertebrate peripheral nervous system. Nature (Lond) 281:71–74.
Jessen RK, Hills JM, Dennison ME, Mirsky R (1983) Gamma aminobutyrate as an autonomic neurotransmitter: release and uptake of [3H] gamma aminobutyrate in guinea-pig large intestine and cultured enteric neurons using physiological methods and electron microscopic autoradiography. Neuroscience 10: 1427–1442.
Jessen RK, Hills JM, Saffrey MJ (1986) Immunohistochemical demonstration of GABAergic neurons in the enteric nervous system. J Neurosci 6:1628–1634.
Johnston GAR, Krogsgaard-Larsen P, Stephanson AL, Twitchin B (1976) Inhibition of the uptake of GABA and related aminoacids in rat brain slices by the optical isomers of nipecotic acid. J Neurochem 26:1029–1032.
Kerr DIB, Krantis A (1983) Uptake and stimulus-evoked release of [3H]GABA by myenteric nerves of guinea-pig intestine. Br J Pharmacol 78:271–276.
Kerr DIB, Ong J (1984) Evidence that ethylenediamine acts in the isolated ileum of the guinea-pig by releasing of endogenous GABA. Br J Pharmacol 83:169–177.
Kerr DIB, Ong J (1986) GABAergic mechanisms in the gut: their role in the regulation of gut motility. In: Erdo SL, Bowery NG (eds) GABAergic mechanisms in the mammalian periphery. Raven Press, New York, pp 153–174.
Kleinrok A, Kilbinger H (1983) GABA and cholinergic transmission in the guinea-pig ileum. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 332:216–220.
Krantis A, Costa M, Furness JB, Orbach J (1980) γ-aminobutyric acid stimulates intrinsic inhibitory and excitatory nerves in the guinea-pig intestine. Eur J Pharmacol 67:461–468.
Krantis A, Harding RK (1987) GABA-related actions in isolated in vitro preparations of the rat small intestine. Eur J Pharmacol 141:291–295.
Krantis A, Kerr DIB (1981) GABA induced excitatory responses in the guinea-pig small intestine are antagonized by bicuculline, picrotoxin and chloride ions blockers. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 317:257–261.
Krantis A, Harding RK (1986) The distribution of GABA-transaminase-dehydrogenase activity in the myenteric plexus of rat small intestine: a histochemical analysis. Neurosci Lett 64:85–90.
Krogsgaard-Larsen P, Johnston GAR (1975) Inhibiton of GABA uptake in rat brain slices by nipecotic acid, various isoxazols and related compounds. J Neurochem 25:797–802.
Lloyd HGE, Perkins MN, Stone TW (1982) Ethylenediamine as a specific releasing agent of gamma-aminobutyric acid in rat striatal slices. J Neurochem. 38:1168–1169.
Maggi CA, Manzini S, Meli A (1984) Evidence that GABA-A receptors mediate relaxation of the rat duodenum by activating intramural nonadrenergic-noncholinergic neurons. J Anton Pharmacol 4:77–85.
Maggi CA, Santicioli P, Manzini S, Meli A (1986a) Capsaicin activates neurogenic non-adrenergic non-cholinergic relaxations of the isolated rat duodenum. Eur J Pharmacol 120: 367–370.
Maggi CA, Manzini S, Giuliani S, Santicioli P, Meli A (1986b) Extrinsic origin of the capsaicin-sensitive innervation of rat duodenum: possible involvement of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in the capsaicin-induced activation of intramural non-adrenergic non-cholinergic neurons. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 334:172–180.
Manzini S, Maggi CA, Meli A (1985) Further evidence for the involvement of ATP in nonadrenergic noncholinergic relaxation of the isolated rat duodenum. Eur J Pharmacol 113:399–405.
Manzini S, Maggi CA, Meli A (1986) Pharmacological evidence that at least two different nonadrenergic noncholinergic inhibitory systems are present in the rat small intestine. Eur J Pharmacol 123:229–236.
Micheletti R, Schiavone A, Giachetti A (1988) Muscarinic M1 receptors stimulate a nonadrenergic inhibitory pathway in the isolated rat duodenum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 244:680–688.
Ong J, Kerr DIB (1987) Comparison of GABA-induced responses in various segments of the guinea-pig intestine. Eur J Pharmacol 134:349–353.
Taniyama K, Kusunoki M, Saito N, Tanaka C (1982) Release of GABA from cat colon. Science 217:1030–1040.
Tanaka C, Taniyama K (1985) Substance P provoked γ-aminobutyric acid release from the myenteric plexus of the guinea-pig small intestine. J Physiol (Lond) 362:319–329.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to C.A. Maggi at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maggi, C.A., Giuliani, S., Santicioli, P. et al. The motor response to ethylenediamine of the rat isolated duodenum: Involvement of GABAergic transmission?. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 340, 419–423 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00167043
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00167043