Abstract
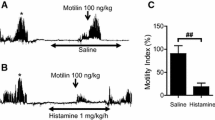
The migrating motor complex (MMC) is responsible for emptying the stomach during the interdigestive period, in preparation for the next meal. It is known that gastric phase III of MMC starts from the proximal stomach and propagates the contraction downwards. We hypothesized that a certain region of the stomach must be more responsive to motilin than others, and that motilin-induced strong gastric contractions propagate from that site. Stomachs of the Suncus or Asian house shrew, a small insectivorous mammal, were dissected and the fundus, proximal corpus, distal corpus, and antrum were examined to study the effect of motilin using an organ bath experiment. Motilin-induced contractions differed in different parts of the stomach. Only the proximal corpus induced gastric contraction even at motilin 10−10 M, and strong contraction was induced by motilin 10−9 M in all parts of the stomach. The GPR38 mRNA expression was also higher in the proximal corpus than in the other sections, and the lowest expression was observed in the antrum. GPR38 mRNA expression varied with low expression in the mucosal layer and high expression in the muscle layer. Additionally, motilin-induced contractions in each dissected part of the stomach were inhibited by tetrodotoxin and atropine pretreatment. These results suggest that motilin reactivity is not consistent throughout the stomach, and an area of the proximal corpus including the cardia is the most sensitive to motilin.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adachi H et al (1981) Mechanism of the excitatory action of motilin on isolated rabbit intestine. Gastroenterology 80:783–788
Broad J, Mukherjee S, Samadi M, Martin JE, Dukes GE, Sanger GJ (2012) Regional- and agonist-dependent facilitation of human neurogastrointestinal functions by motilin receptor agonists. Br J Pharmacol 167:763–774. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2012.02009.x
Brown JC, Cook MA, Dryburgh JR (1973) Motilin, a gastric motor activity stimulating polypeptide: the complete amino acid sequence. Can J Biochem 51:533–537
Code CF (1979) The gastrointestinal interdigestive housekeeper of the gastrointestinal tract. Perspect Biol Med 22:894–913
Coulie B, Tack J, Peeters T, Janssens J (1998) Involvement of two different pathways in the motor effects of erythromycin on the gastric antrum in humans. Gut 43:395–400
De Smet B, Mitselos A, Depoortere I (2009) Motilin and ghrelin as prokinetic drug targets. Pharmacol Therapeut 123:207–223. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2009.04.004
Depoortere I, Macielag MJ, Galdes A, Peeters TL (1995) Antagonistic properties of [Phe3, Leu13]porcine motilin. Eur J Pharmacol 286:241–247
Douady CJ, Douzery EJ (2003) Molecular estimation of eulipotyphlan divergence times and the evolution of “Insectivora”. Mol Phylogenet Evol 28:285–296
Hall KE, Greenberg GR, El-Sharkawy TY, Diamant NE (1983) Vagal control of migrating motor complex-related peaks in canine plasma motilin, pancreatic polypeptide, and gastrin. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 61:1289–1298
He J, Irwin DM, Chen R, Zhang YP (2010) Stepwise loss of motilin and its specific receptor genes in rodents. J Mol Endocrinol 44:37–44. doi:10.1677/JME-09-0095
Husebye E (1999) The patterns of small bowel motility: physiology and implications in organic disease and functional disorders. Neurogastroenterol Motil Off J Euro Gastrointest Motil Soc 11:141–161
Ishida Y, Sakahara S, Tsutsui C, Kaiya H, Sakata I, Oda S, Sakai T (2009) Identification of ghrelin in the house musk shrew (Suncus murinus): cDNA cloning, peptide purification and tissue distribution. Peptides 30:982–990. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2009.01.006
Ito H, Nishibayashi M, Kawabata K, Maeda S, Seki M, Ebukuro S (2002) Immunohistochemical demonstration of c-fos protein in neurons of the medulla oblongata of the musk shrew (Suncus murinus) after veratrine administration. Exp Animals/Japan Assoc Lab Anim Sci 51:19–25
Itoh Z (1997) Motilin and clinical application. Peptides 18:593–608
Itoh Z, Sekiguchi T (1983) Interdigestive motor activity in health and disease. Scandinavian J Gastroenterol Suppl 82:121–134
Itoh Z, Honda R, Hiwatashi K, Takeuchi S, Aizawa I, Takayanagi R, Couch EF (1976) Motilin-induced mechanical activity in the canine alimentary tract. Scandinavian J Gastroenterol Suppl 39:93–110
Itoh Z et al (1978) Changes in plasma motilin concentration and gastrointestinal contractile activity in conscious dogs. Am J Digest Dis 23:929–935
Janssens J, Vantrappen G, Peeters TL (1983) The activity front of the migrating motor complex of the human stomach but not of the small intestine is motilin-dependent. Regul Pept 6:363–369
Kellow JE, Borody TJ, Phillips SF, Tucker RL, Haddad AC (1986) Human interdigestive motility: variations in patterns from esophagus to colon. Gastroenterology 91:386–395
Kitazawa T, Ichikawa S, Yokoyama T, Ishii A, Shuto K (1994) Stimulating action of KW-5139 (Leu13-motilin) on gastrointestinal motility in the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol 111:288–294
Kitazawa T, Taneike T, Ohga A (1995) Excitatory action of [Leu13]motilin on the gastrointestinal smooth muscle isolated from the chicken. Peptides 16:1243–1252
Kitazawa T, Taneike T, Ohga A (1997) Functional characterization of neural and smooth muscle motilin receptors in the chicken proventriculus and ileum. Regul Pept 71:87–95
Kuromaru MNT, Mochizuki K (1980) Morphological study on the intestine of the musk shrew, Suncus murinus. Jpn J VeT Sci 42:61–71
Lee KY, Chey WY, Tai HH, Yajima H (1978) Radioimmunoassay of motilin. Validation and studies on the relationship between plasma motilin and interdigestive myoelectric activity of the duodenum of dog. Am J Digest Dis 23:789–795
Lee KY, Chang TM, Chey WY (1983) Effect of rabbit antimotilin serum on myoelectric activity and plasma motilin concentration in fasting dog. Am J Physiol 245:G547–G553
Mizumoto A, Sano I, Matsunaga Y, Yamamoto O, Itoh Z, Ohshima K (1993) Mechanism of motilin-induced contractions in isolated perfused canine stomach. Gastroenterology 105:425–432
Mondal A et al (2011) Myenteric neural network activated by motilin in the stomach of Suncus murinus (house musk shrew). Neurogastroent Motil Off J Euro Gastroint Motil Soc 23:1123–1131. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2982.2011.01801.x
Mondal A et al (2012) Coordination of motilin and ghrelin regulates the migrating motor complex of gastrointestinal motility in Suncus murinus. Am J Physiol Gastroint Liver Physiol 302:G1207–G1215. doi:10.1152/ajpgi.00379.2011
Murphy WJ, Pringle TH, Crider TA, Springer MS, Miller W (2007) Using genomic data to unravel the root of the placental mammal phylogeny. Genome Res 17:413–421. doi:10.1101/gr.5918807
Nieuwenhuijs VB, Verheem A, van Duijvenbode-Beumer H, Visser MR, Verhoef J, Gooszen HG, Akkermans LM (1998) The role of interdigestive small bowel motility in the regulation of gut microflora, bacterial overgrowth, and bacterial translocation in rats. Ann Surg 228:188–193
Ohshiro H, Nonaka M, Ichikawa K (2008) Molecular identification and characterization of the dog motilin receptor. Regul Pept 146:80–87. doi:10.1016/j.regpep.2007.08.012
Ozaki K et al (2009) An orally active motilin receptor antagonist, MA-2029, inhibits motilin-induced gastrointestinal motility, increase in fundic tone, and diarrhea in conscious dogs without affecting gastric emptying. Eur J Pharmacol 615:185–192. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.04.059
Pearse AG, Polak JM, Bloom SR, Adams C, Dryburgh JR, Brown JC (1974) Enterochromaffin cells of the mammalian small intestine as the source of motilin Virchows Archiv B. Cell Pathol 16:111–120
Peeters TL, Aerssens J, De smet ?b, Mitselos A, Thielemans L, Coulie B, Depoortere I (2004) The mouse is a natural knock-out for motilin and for the motilin receptor. Functionally they have been replaced by ghrelin. Neurogastroenterol Motil Off J Euro Gastroint Motil Soc 16:687
Phillis JW, Kirkpatrick JR (1979) Motilin excites neurons in the cerebral cortex and spinal cord. Eur J Pharmacol 58:469–472
Poitras P (1984) Motilin is a digestive hormone in the dog. Gastroenterology 87:909–913
Sakahara S et al (2010) Physiological characteristics of gastric contractions and circadian gastric motility in the free-moving conscious house musk shrew (Suncus murinus). Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 299:R1106–R1113. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00278.2010
Sanger GJ, Hellstrom PM, Naslund E (2010) The hungry stomach: physiology, disease, and drug development opportunities. Front Pharmacol 1:145. doi:10.3389/fphar.2010.00145
Sarna SK (1985) Cyclic motor activity; migrating motor complex: 1985. Gastroenterology 89:894–913
Sarna S, Chey WY, Condon RE, Dodds WJ, Myers T, Chang TM (1983) Cause-and-effect relationship between motilin and migrating myoelectric complexes. Am J Physiol 245:G277–G284
Shim SGRJ, Rhee PL, Choi KW, Jeon SK, Kang TM, Uhm DY, Lee JS, Sung IK, Kim HS (2002) Mechanisms of motilin action on smooth muscle of the human stomach. Korean J Gastroenterol 39:4–12
Sudo H et al (2008) Oral administration of MA-2029, a novel selective and competitive motilin receptor antagonist, inhibits motilin-induced intestinal contractions and visceral pain in rabbits. Eur J Pharmacol 581:296–305. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.11.049
Suzuki A et al (2012) Molecular identification of GHS-R and GPR38 in Suncus murinus. Peptides 36:29–38. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2012.04.019
Szurszewski JH (1969) A migrating electric complex of canine small intestine. Am J Physiol 217:1757–1763
Tack JFJW, Janssens J, Vantrappen G, Wood JD (1991) Motilin and erythromycin excite myentric neurons in the gastric antrum of the guinea pig. Gastroenterol 100:A50
Tsutsui C, Kajihara K, Yanaka T, Sakata I, Itoh Z, Oda S, Sakai T (2009) House musk shrew (Suncus murinus, order: Insectivora) as a new model animal for motilin study. Peptides 30:318–329. doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2008.10.006
Van Assche G, Depoortere I, Thijs T, Janssens JJ, Peeters TL (1997) Concentration-dependent stimulation of cholinergic motor nerves or smooth muscle by [Nle13]motilin in the isolated rabbit gastric antrum. Eur J Pharmacol 337:267–274
Vantrappen G, Janssens J, Hellemans J, Ghoos Y (1977) The interdigestive motor complex of normal subjects and patients with bacterial overgrowth of the small intestine. J Clin Investig 59:1158–1166. doi:10.1172/JCI108740
Vantrappen G, Janssens J, Peeters TL, Bloom SR, Christofides ND, Hellemans J (1979) Motilin and the interdigestive migrating motor complex in man. Dig Dis Sci 24:497–500
Venkova K, Thomas H, Fraser GL, Greenwood-Van Meerveld B (2009) Effect of TZP-201, a novel motilin receptor antagonist, in the colon of the musk shrew (Suncus murinus). J Pharm Pharmacol 61:367–373. doi:10.1211/jpp/61.03.0012
Wingate DL (1981) Backwards and forwards with the migrating complex. Dig Dis Sci 26:641–666
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Funding
No funding declared.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institution at which the studies were conducted.
Additional information
Communicated by I.D. Hume.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dudani, A., Aizawa, S., Zhi, G. et al. The proximal gastric corpus is the most responsive site of motilin-induced contractions in the stomach of the Asian house shrew. J Comp Physiol B 186, 665–675 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-016-0985-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00360-016-0985-1