Abstract
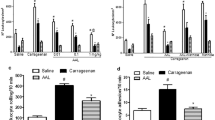
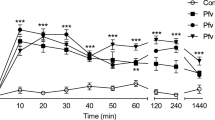
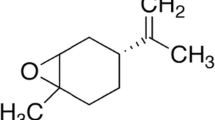
2-Chloro-3-methoxycarbonylpropionamido-1,4-naphthoquinone (PP1D1) produced a dose-dependent inhibition of the polymyxin B-induced hind-paw edema in normal as well as in adrenalectomized mice. A comparable inhibitory profile was observed in mice to which PP1D1 was injected i.p. or applied orally. Unlike dexamethasone, PP1D1 had no effect on the liver glycogen content in fasting adrenalectomized mice. Ear edema caused by passive cutaneous anaphylactic reaction, or by subcutaneous injection of compound 48/80, histamine, serotonin, bradykinin or substance P was reduced by PP1D1 in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, topical application of PP1D1 suppressed the capsaicin- and arachidonic acid-induced ear edema. In compound 48/80-pretreated mice, the tissue histamine content was greatly reduced. Under these conditions, PP1D1 reduced the bradykinin- and substance P-induced ear edema to a significantly greater extent than diphenhydramine plus methysergide. These results suggest that the inhibitory effect of PP1D1 on the edematous response is due to the protection of the microvasculature from mediator challenge.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrews PA, Helme RD, Thomas KL (1989) NK-1 receptor mediation of neurogenic plasma extravasation in rat skin. Br J Pharmacol 97:1232–1238
Appell KC, Fragale BJ, Loscig J, Singh S, Tomezuk BE (1992) Antagonists that demonstrate species differences in neurokinin-1 receptors. Mol Pharmacol 41:772–778
Austen KF (1979) Biologic implications of the structural and functional characteristics of the chemical mediators of immediate-type hypersensitivity. Harvey Lect 73:93–161
Bertelli A, Soldani G (1979) Polymyxin B-induced oedema in hind paw of the rat as an assay for anti-inflammatory drugs. Arzneimittelforschung 29:777–778
Brain SD, Williams TJ (1989) Interactions between the tachykinins and calcitonin gene-related peptide lead to the modulation of oedema formation and blood flow in rat skin. Br J Pharmacol 97:77–82
Chang J, Carlson RP, O'Neill-Davis L, Lamb B, Sharma RN, Lewis AJ (1986) Correlation between mouse skin inflammation induced by arachidonic acid and eicosanoid synthesis. Inflammation 10:205–214
Delay-Goyet P, Satoh H, Lundberg JM (1992) Relative involvement of substance P and CGRP mechanisms in antidromic vasodilation in the rat skin. Acta Physiol Scand 146:537–537
Fong J, Schaffer KL, Kirk PL (1953) The ultramicrodetermination of glycogen in liver: a comparison of the anthrone and reducing sugar methods. Arch Biochem Biophys 45:319–326
Foreman JC, Jordan CC (1984) Neurogenic inflammation. Trends Pharmacol Sci 5:116–119
Fujii E, Irie K, Muraki T (1994) Nitric oxide plays a role in increase in vascular permeability induced by bradykinin but not by platelet-activating factor (PAF) or histamine in mouse skin. Jpn J Pharmacol 64 [Suppl 1]:P488
Gabbiani G, Badonnel MC, Majno G (1970) Intra-arterial injections of histamine, scrotonin, or bradykinin: a topographic study of vascular leakage. Proc Soc Exp Biol New York 135:447–452
Heltianu C, Simionescu M, Simionescu N (1982) Histamine receptors of the microvascular endothelium revealed in situ with a histamine-ferritin conjugate: characteristic high affinity binding sites in venules. J Cell Biol 93:357–364
Holzer P (1991) Capsaicin: cellular targets, mechanisms of actions, and selectivity for thin sensory neurons. Pharmacol Rev 43:143–201
Inoue H, Mori T, Koshihara Y (1988) Sulfidopeptide-leukotrienes are major mediators of arachidonic acid-induced mouse ear edema. Prostaglandins 36:731–739
Inoue H, Nagata N, Koshihara Y (1993) Profile of capsaicin-induced mouse ear oedema as neurogenic inflammatory model: comparison with arachidonic acid-induced ear oedema. Br J Pharmacol 110:1614–1620
Ishizaka T, Ishizaka K, Komioka H (1972) Release of histamine and slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRS-A) by immunoglobulin E (IgE) anti-IgE reactions on monkey mast cells. J Immunol 108:513–520
Katayama S, Shionoya H, Ohtake S (1978) A new method for extraction of extravasated dye in the skin and the influence of fasting stress on passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in guinea pigs and rats. Microbiol Immunol 22:89–101
Kuo SC, Ibuka T, Huang LJ, Lien JC, Yean SR, Huang SC, Lednicer D, Morris-Natschke S, Lee KH (1996) Synthesis and cytotoxicity of 1,2-disubstituted naphth[2,3-d]imidazole-4,9-diones and related compounds. J Med Chem 39:1447–1451
Lembeck F, Donnerer J, Barthó L (1982) Inhibition of neurogenic vasodilatation and plasma extravasation by substance P antagonists, somatostatin and (D-Met2,Pro5)enkephalinamide. Eur J Pharmacol 85:171–176
Marceau F, Lussier A, Regoli D, Giroud JP (1983) Pharmacology of kinins: their relevance to tissue injury and inflammation. Gen Pharmacol 14:209–229
Mayhan WG, Joyner WL (1984) The effect of altering the external calcium concentration and a calcium channel blocker, verapamil, on microvascular leaky sites and dextran clearance in the hamster cheek pouch. Microvasc Res 28:159–179
Owen DAA (1987) Inflammation-histamine and 5-hydroxytryptamine. Br Med Bull 43:256–269
Regoli D, Barabé J (1980) Pharmacology of bradykinin and related kinins. Pharmacol Rev 32:1–46
Regoli D, Drapeau G, Rovero P, Dion S, D'Orleans-Juste P, Barabé J (1986) The actions of kinin antagonists on B1 and B2 receptor systems. Eur J Pharmacol 123:61–65
Rotrosen D, Gallin JI (1986) Histamine type I receptor occupancy increases endothelial cytosolic calcium, reduces F-actin, and promotes albumin diffusion across cultured endothelial monolayer. J Cell Biol 103:2379–2387
Saria A, Lundberg JM, Skofitsch G, Lembeck F (1983) Vascular protein leakage in various tissues induced by substance P, capsaicin, bradykinin, scrotonin, histamine and by antigen challenge. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 324:212–218
Saria A, Hua X, Skofitsch G, Lundberg JM (1984) Inhibition of compound 48/80-induced vascular protein leakage by pretreatment with capsaicin and a substance P antagonist. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 328:9–15
Schiatti P, Selva D, Galliani G, Baldoli E, Diena A, Glässer A, Leali M, Toja E (1986) High selective anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity of 3-(1-methylethyl)-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-3H-naphth[1,2-d]imidazole, a new non-acidic molecule. Arzneimittelforschung 36:102–109
Shore PA, Burkhalter A, Cohn VH Jr (1959) A method for the fluorometric assay of histamine in tissue. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 127:182–186
Taira M, Kohno SW, Yamamura H, Ohata K (1988) Lack of involvement of leukotriene and platelet activating factor in passive cutaneous anaphylaxis in rats. Agents Actions 24:189–195
Tallarida RJ, Murray RB (1989) Area under a curve: Trapezoidal and Simpson's rules. In: Tallarida RJ, Murray RB (eds) Manual of pharmacologic calculations with computer programs. Springer, New York, pp 77–81
Wang JP, Hsu MF, Ouyang C, Teng CM (1989) Edematous response caused by [This5,8,DPhe7]bradykinin, a B2 receptor antagonist, is due to mast cell degranulation. Eur J Pharmacol 161:143–149
Wang JP, Hsu MF, Raung SL, Chen CC, Kuo JS, Teng CM (1992) Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of magnolol. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 346:707–712
Wang JP, Hsu MF, Raung SL, Kuo SC (1994) Suppressive effect of 2-phenyl-4-quinolone (YT-1) on hind-paw edema and cutaneous vascular plasma extravasation in mice. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 349:324–330
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J.P., Chen, Y.H. & Kuo, S.C. Inhibition of hind-paw edema and cutaneous vascular plasma extravasation by 2-chloro-3-methoxycarbonylpropionamido-1,4-naphthoquinone (PP1D1) in mice. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 354, 779–784 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00166905
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00166905