Summary
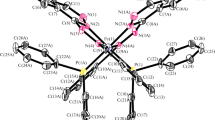
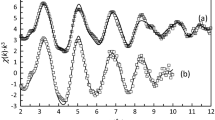
Cyclopropanecarbohydroxamic acid (CPAH) and cyclohexylacetohydroxamic acid (CHAH) were synthesized, characterized and their pK a's determined spectro-photometrically as 9.80 and 9.85, respectively, at 25 °C and in buffers of 0.1 mol dm−3 ionic strength (I). A spectroscopic investigation of their reactions with FeIII in aqueous solutions revealed the sole formation of the 1:3 complexes at equilibrium. Stability constants (log β 3 at 25 °C and I = 0.1 mol dm−3 are 34.80 and 34.22 for [Fe(CPA)3] and [Fe(CHA)3], respectively. Spectral and magnetic studies of the isolated complexes indicate octahedral coordination via the O atoms of the hydroxamate group.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. B. Nielands, Structure and Bonding, 1, 59 (1968).
D. A. Brown and M. V. Chidambaram in H. Sigel (Ed.), Metal Ions in Biological Systems, Vol. 14, Dekkar, New York, 1982, p. 125.
H. Kehl, Chemistry and Biology of Hydroxamic Acids, Karger, New York, 1982.
B. Kurzak, H. Kozlowski and F. Farkas, Coord. Chem. Rev., 114, 169 (1992).
J. B. Nielands, Microbial Iron Metabolism, Academic Press, New York, 1974.
J. H. Weisburger and E. K. Weisburger, Pharm. Rev., 25, 1 (1973).
M. Maehr, Pure Appl. Chem., 28, 603 (1971).
T. Emery in H. Sigel (Ed.), Metal Ions in Biological Systems, Vol. 7, Dekkar, New York, 1978, p. 77.
G. W. Bates and P. Saltman in D. R. Williams (Ed.), An Introduction to Bioinorganic Chemistry, Thomas, Illinois, 1972, p. 145.
P. S. Dobbin and R. C. Hider, Chem. Britain, 26, 565 (1990).
W. B. Martin and L. R. Swett, US 2, 928, 875, Chem. Abstr. 54, 15272f (1960).
E. L. Jones and A. W. Scott, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 44, 407 (1922).
A. Albert and E. P. Serjeant, The Determination of Ionization Constants, 2nd Edit., Chapman & Hall, London, 1971, p. 44.
D. D. Perrin, Aust. J. Chem., 16, 572 (1963).
F. R. Hartley, C. Burgess and R. M. Alcock, Solution Equilibria, Ellis Horwood, Sussex, 1980, p. 33.
D. J. Legget and W. A. E. McBryde, Anal. Chem., 41, 1065 (1975).
A. Braibanti and C. Bruschi, Ann. Chim., 67, 471 (1977).
D. J. Legget in D. Legget (Ed.), Computational Methods for the Determination of Stability Constants, Plenum, London, 1985, p. 159.
D. A. Brown, D. McKeith and W. K. Glass, Inorg. Chim. Acta, 35, 5 (1979).
R. L. Dutta and S. Lahiri, J. Indian Chem. Soc., 39, 860 (1962).
B. Chatterjee, J. Indian Chem. Soc., 48, 929 (1971).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nwabueze, J.N. Complexes of iron(III) with cyclopropanecarbo- and cyclohexyl-acetohydroxamic acids. Transition Met Chem 21, 258–261 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00165979
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00165979