Summary
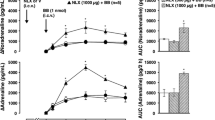
This study was initiated to characterize the receptors which mediate the cardiovascular responses elicited by the intrathecal (i. th.) administration of neurokinins (NK) in the conscious freely moving rat. The dose response profile for substance P (SP), neurokinin A (NKA) and neurokinin B (NKB) was determined over 0.065—65 nmol doses of the peptides. After i.th. administration at the T8–T10 thoracic level, only SP elicited a dose dependent pressor response. However, all NK elicited a dose dependent increase in heart rate (HR), and the following rank order of potency was observed: SP > NKA > NKB. SP (6.5 nmol) produced cardiovascular responses markedly greater than an equimolar dose of any of the seven SP fragments which were studied. The C-terminal sequences SP (4-11), [pGlu5]SP (5-11), [pGlu6]SP (6–11), and SP (7–11), as a group were slightly more potent than the N-terminal fragments, SP (1–4), SP (1–7) and SP (1–9) which were almost inactive. The NK-1 receptor selective agonists [Pro9, Met(O2)11]SP and [β-Ala4, Sar9, Met(O2)11]SP (4–11), produced pressor and positive chronotropic responses equal to or greater in intensity than SP. With up to 6.5 nmol of the NK-2 receptor selective agonist [Nle10]NKA (4–10), no dose dependent cardiovascular response was produced and the NK-3 receptor selective agonist senktide (succinyl-[Asp6, McPhe8]SP (6–11)), produced neither a cardiac nor pressor response when 6.5 nmol was administered. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that, receptors of the NK-1 subtype mediate the cardiovascular responses evoked by the spinal action of NK.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barber A, Wild A, Wedel R (1987) Do local vasomotor effects elicit the motor deficits induced by intrathecally applied substance P antagonists in the rat? Neurosci Lett 80:219–223
Buck SH, Burcher E, Shults CW, Lovenberg W, O'Donohue TL (1984) Novel pharmacology of substance K-binding sites: a third type of tachykinin receptor. Science 226:987–989
Buck SH, Helke CJ, Burcher E, Shultz CW, O'Donohue TL (1986) Pharmacologic characterization and autoradiographic distribution of binding sites for iodinated tachykinins in the rat central nervous system. Peptides 7(6):1109–1120
Buck SH, Burcher E (1986) The tachykinins: a family of peptides with a brood of receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci February 65–68
Ciriello J, Caverson MM, Polosa C (1986) Function of the ventrolateral medulla in the control of the circulation. Brain Res Rev 11:359–391
Couture R, Gupta A, Kerouac R, Escher E, Regoli D (1987a) Spinal actions of substance P analogues on cardiovascular responses in the rat: a structure-activity analysis. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 65:412–418
Couture R, Gupta A, Kerouac R, Regoli D (1987b) Studies on the cardiovascular effects produced by the spinal action of two substance P analogues in the rat: evidence for a central catecholaminergic mechanism. Eur J Pharmacol 135:345–354
Couture R, Hassessian H, Gupta A (1988) Studies on the cardiovascular effects produced by the spinal action of substance P in the rat. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 11:270–283
Dion S, D'Orléans-Juste P, Drapeau G, Rhaleb N-E, Rouissi N, Tousignant C, Regoli D (1987) Characterization of neurokinin receptors in various isolated organs by the use of selective agonists. Life Sci 41:2269–2278
Drapeau G, D'Orléans-Juste P, Dion S, Rhaleb N-E, Rouissi N-E, Regoli D (1987a) Selective agonists for substance P and neurokinin receptors. Neuropeptides 10:43–54
Drapeau G, D'Orléans-Juste P, Dion S, Rhaleb N-E, Regoli D (1987b) Specific agonists for neurokinin B receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 136:401–403
Drapeau G, Dion S, D'Orléans-Juste P, Rhaleb N-E, Regoli D (1988) Development of selective agonists for substance P and neurokinin receptors. In: Peptides, Chemistry and Biology, G.R. Marshall (ed.) pp 497–499, ESCOM, Leiden
Hall ME, Miley FB, Stewart JM (1987) Modulation of blood pressure by substance P: Opposite effects of N and C terminal fragments on anesthetized rats. Life Sci 40:1909–1914
Hássessian H, Couture R, Jacques L (1987) Spinal action of neurokinins in the rat: effects on mean arterial pressure, heart rate, and vascular permeability. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 65:2182–2187
Hasséssian H, Couture R (1988 a) Cardiovascular responses induced by the intrathecal administration of substance P in the conscious freely moving rat. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol (in press)
Hasséssian H, Couture R (1988b) Cardiovascular responses induced by the intrathecal administration of substance P fragments and of selective agonists for neurokinin receptor subtypes. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 66:Axix
Helke CJ, Charlton CG, Keeler JR (1985) Bulbospinal substance P and sympathetic regulation of the cardiovascular system: A review. Peptides 6:(Supp. 2) 69–74
Kangawa K, Minamino N, Fukuda A, Matsuo H (1983) Neuromedin K: A novel mammalian tachykinin identified in porcine spinal cord. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 114:533–540
Nawa H, Hirose T, Takashima H, Inayama S, Nakanishi S (1983) Nucleotide sequences of cloned cDNA for two types of bovine brain substance P precursor. Nature 306:32–36
Post C, Butterworth JF, Strichartz GR, Karlsson J-A, Persson CGA (1985) Tachykinin antagonists have potent local anaesthetic actions. Eur J Pharmacol 117:347
Post C, Paulsson I (1985) Antinociceptive and neurotoxic actions of substance P analogues in the rats spinal cord after intrathecal administration. Neurosci Lett 57:159–164
Quirion R, Pilapil C (1984) Comparative potencies of substance P, substance K and neuromedin K on brain substance P receptors. Neuropeptides 4:325–329
Quirion R (1985) Multiple tachykinin receptors. Trends Neurosci 8:183–185
Regoli D, Mizrahi J, D'Orléans-Juste P, Escher E (1984) Receptors for substance P. II. Classification by agonist fragments and homologues. Eur J Pharmacol 97:171–177
Regoli D, Drapeau G, Dion S, D'Orléans-Juste P (1987) Mini Review. Pharmacological receptors for substance P and neurokinins. Life Sci 40:109–117
Regoli D, Drapeau G, Dion S, Couture R (1988) New selective agonists for neurokinin receptors: pharmacological tools for receptor characterization. Trends Pharmacol Sci 9:290–295
Takano Y, Loewy AD (1985) Reduction of [3H]-Substance P binding in the intermediolateral cell column after sympathectomy. Brain Res 333:193–196
Takano Y, Nagashima A, Masui H, Kuromizu K, Kamiya H-O (1986) Distribution of substance K (neurokinin A) in the brain and peripheral tissues of rats. Brain Res 369:400–404
Wormser V, Laufer R, Hart Y, Choner M, Grilon C, Selinger Z (1986) Highly selective agonists for substance P receptor subtypes. The EMBO J 5:2805–2808
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to R. Couture at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hasséssian, H., Drapeau, G. & Couture, R. Spinal action of neurokinins producing cardiovascular responses in the conscious freely moving rat: evidence for a NK-1 receptor mechanism. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 338, 649–654 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00165629
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00165629