Summary
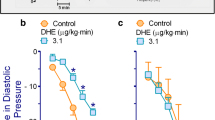
Frequency-dependent pupillary dilations were evoked by electrical stimulation of the pre- or post-ganglionic cervical sympathetic nerve (sympatho-excitation) or the hypothalamus (parasympatho-inhibition) in sympathectomized anesthetized cats. Systemic administration of the selective histamine H3 receptor agonist (R)-α-methylhistamine (RαMeHA) produced a dose-dependent depression of mydriasis due to direct neural sympathetic activation but had no effect on responses elicited by parasympathetic withdrawal. The histamine H2 receptor agonist, dimaprit, was inactive. RαMeHA was much more effective in depressing sympathetic responses obtained at lower frequencies when compared to higher frequencies of stimulation.
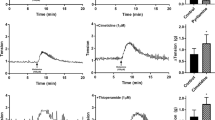
Responses evoked both pre- and postganglionically were inhibited by RαMeHA. This peripheral sympathoinhibitory action of RαMeHA was antagonized by the histamine H3 receptor blocker thioperamide but not by intravenous pretreatment with the histamine H1 receptor antagonist chlorpheniramine. Histamine H2 receptor blockers cimetidine and ranitidine were also without effect. RαMeHA did not depress pupillary responses elicited by i.v. (-)-adrenaline.
The results demonstrate that histamine H3 receptors modulate sympathetic activation of the iris at a site proximal to the iris dilator muscle. The predominant mechanism of action appears to the prejunctional inhibition of noradrenaline release from postganglionic sympathetic nerve endings. However, a concomitant ganglionic inhibitory action cannot be excluded.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrang J-M, Garbarg M, Schwartz J-C (1983) Auto-inhibition of brain histamine release mediated by a novel class (H3) of histamine receptor. Nature 302:832–837
Arrang J-M, Garbarg M, Lancelot J-C, Lecomte J-M, Pollard H, Robba M, Schunack W, Schwartz J-C (1987) Highly potent and selective ligands for histamine H3-receptors. Nature 327:117–123
Campos HA, Briceño E (1992) Two models of peripheral sympathetic autoregulation: role of neuronal histamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 261:943–950
Christian EP, Weinreich D (1992) Presynaptic histamine H1 and H3 receptors modulate sympathetic ganglionic synaptic transmission in the guinea-pig. J Physiol 457:407–430
Hey JA, del Prado M, Egan RW, Kreutner W, Champan RW (1992) Inhibition of sympathetic hypertensive responses in the guinea-pig by prejunctional histamine H3-receptors. Br J Pharmacol 107: 347–351
Hill SJ (1990) Distribution, properties, and functional characteristics of three classes of histamine receptor. Pharmacol Rev 42:45–83
Koss MC, Hey JA (1992) Activation of histamine H3 receptors produces presynaptic inhibition of neurally evoked cat nictitating membrane responses in vivo. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 346:208–212
Koss MC, Rieger JA (1976) Differential transmission in the superior cervical ganglion of the cat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 199:538–543
Koss MC, Gherezghiher T, Nomura A (1984) CNS adrenergic inhibition of parasympathetic oculomotor tone. J Anton Nerv Syst 10:55–68
Koss MC, Gherezghiher T (1988) Pharmacological characterization of alpha-adrenoceptors involved in nictitating membrane and pupillary responses to sympathetic nerve stimulation in cats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 337:18–23
Lin J-S, Sakai K, Vanni-Mercier G, Arrang J-M, Garbarg M, Schwartz J-C, Jouvet M (1990) Involvement of histaminergic neurons in arousal mechanisms demonstrated with H3-recptor ligands in the cat. Brain Res 523:325–330
Lokhandwala M (1978) Inhibition of sympathetic nervous system by histamine: studies with H1- and H2-receptor antagonists. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 206:115–122
Malinowska B, Schlicker E (1991) H3 receptor-mediated inhibition of the neurogenic vasopressor response in pithed rats. Eur J Pharmacol 205:307–310
Marshall I (1981) Histamine modulation of neurotransmission in the sympathetic nervous system. J Auton Pharmacol 1:235–250
McGrath MA, Shepherd JT (1976) Inhibition of adrenergic neurotransmission in canine vascular smooth muscle by histamine. Circ Res 39:566–573
Powell JR (1979) Effects of histamine on vascular sympathetic neuroeffector transmission. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 208:360–365
Schwartz JC, Arrang JM, Garbarg M, Pollard H, Ruat M (1991) Histaminergic transmission in the mammalian brain. Physiol Rev 71:1–51
Starke K, Göthert M, Kilbinger H (1989) Modulation of neurotransmitter release by presynaptic autoreceptors. Physiol Rev 69:864–989
Tamura K, Palmer JM, Wood JD (1988) Presynaptic inhibition produced by histamine at nicotinic synapses in enteric ganglia. Neuroscience 25:171–179
Timmerman H (1990) Histamine H3 ligands: Just pharmacological tools or potential therapeutic agents? J Med Chem 33:4–11
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to M. C. Koss at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koss, M.C., Hey, J.A. Prejunctional inhibition of sympathetically evoked pupillary dilation in cats by activation of histamine H3 receptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 348, 141–145 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00164790
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00164790