Summary
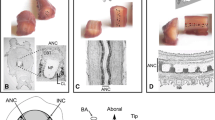
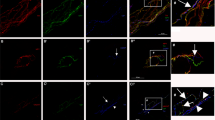
In the present study we describe the application of the non-specific cholinesterase (nChE) histochemical method for the detection of encapsulated sensory nerve endings prior to immunofluorescence staining of the sensory nerve fibres. The nChE staining of Schwann-derived structures surrounding sensory terminals allowed us to identify unequivocally the sensory corpuscles in the skin and the muscle proprioceptors (muscle spindles and Golgi tendon organs) in longitudinal sections of muscle tissue. The nChE staining of sensory nerve endings and immunofluorescence-labelled nerve fibres and their terminals could be viewed and photographed in the same section using appropriate filters. Since nChE activity persists in terminal Schwann cells for a long time after loss of the sensory axons, this combined enzyme- and immunohistochemical approach is also useful for experimental studies involving denervation and re-innervation of sensory nerve endings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andres, K. H. & VonDuring, M. (1973) Morphology of cutaneous receptors. In Handbook of Sensory Physiology, Vol II, (edited by Iggo, A.) pp 3–28. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer-Verlag.
Barker, D. (1974) The morphology of muscle receptors. In Handbook of Sensory Physiology, Vol III/2, Muscle Receptors (edited byHunt, C. C.) pp 1–190. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer-Verlag.
Boyd, I. A. & Gladden, M. H. (1985) Morphology of mammalian muscle spindles. Review. In The Muscle Spindle (edited by Boyd, I. A. & Gladden, M. H.) pp 3–22. Basingstoke: Macmillan.
Björklund, H., Dalsgaard, C. J., Jonsson, C. E. & Hermansson, A. (1986) Sensory and autonomic innervation of non-hairy and hairy human skin. An immunohistochemical study. Cell Tissue Res. 243, 51–7.
Castrignano, F., DeStefano, M. E., Leone, F., Mulatero, B., Tata, A. M., Fasolo, A. & Augusti-Tocco, G. (1990) Ontogeny of acetylcholinesterase, substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity in chick dorsal root ganglia. Neuroscience 34, 499–510.
Chouchkov, C. (1978) Cutaneous receptors. Adv. Anat. Embryol. Cell Biol. 54, 1–98.
Dalsgaard, C. J. (1988) The sensory system. In Handbook of Chemical Neuroanatomy, Vol 6, The Peripheral Nervous System (edited by Björklund, A., Hökfelt, T. & Owman, C.) pp 599–635. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publisher.
Dalsgaard, C. J., Björklund, H., Jonsson, C. E., Hermansson, A. & Dahl, D. (1984) Distribution of neurofilament-immunoreactive nerve fibres in human digital skin. Histochemistry 81, 111–4.
Dubový, P. (1983) To the problem of localization of cholinesterase activity in Pacinian corpuscles by electron microscopy. Histochem. J. 15, 287–8.
Dubový, P. (1989) Electron microscopical study of non-specific cholinesterase activity in simple lamellar corpuscles of glabrous skin from cat rhinarium: a histochemical evidence for the presence of collagenase-sensitive molecular forms and their secretion. Acta Histochem. 86, 63–77.
Dubový, P. (1990) A fine structural localization of the non-specific cholinesterase activity in glomerular nerve formations [endings]. Z. mikrosk.-anat. Forsch. 104, 87–96.
Dubový, P. & Soukup, T. (1987) Ultrastructural localization of non-specific cholinesterase activity in rat muscle spindles. Acta Histochem. 82, 159–70.
Dubový, P. & Soukup, T. (1989) Fine structural localization of non-specific cholinesterase activity in rat tendon organs. Acta Histochem. 85, 195–202.
Dubový, P. & Svíženská, I. (1990) Recovery of non-specific cholinesterase activity in sensory corpuscle of mouse toe skin after irreversible inhibition of this enzyme and cold injury. Acta Histochem. 88, 77–91.
Gibbins, I. L., Wattchow, D. & Coventry, B. (1987) Two immunohistochemically identified populations of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)-immunoreactive axons in human skin. Brain Res. 414, 143–8.
Gulbenkian, S., Valenca, A., Wharton, J., Polak, J. M. & David-Ferreira, J. F. (1991) Simultaneous visualization of neuropeptide and acetylcholinesterase nerve populations in the perivascular plexus. Histochem. J. 23, 553–8.
Halata, Z. (1975) The mechanoreceptors of the mammalian skin. Ultrastructure and morphological classification. Adv. Anat. Embryol. Cell Biol. 50, 5–77.
Idé, C. (1982) Degeneration of mouse digital corpuscles. Am. J. Anat. 163, 59–72.
Idé, C. & Saito, T. (1980) Electron microscopic cytochemistry of cholinesterase activity in mouse digital corpuscle. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 13, 218–25.
Ishida-Yamamoto, A., Senba, E. & Tohyama, M. (1988) Calcitonin gene-related peptide- and substance P-immunoreactive nerve fibres in Meissner's corpuscles of rat: an immunohistochemical analysis. Brain Res. 453, 362–6.
Karnovsky, M. J. (1964) The localization of cholinesterase activity in rat cardiac muscle by electron microscopy, J. Cell Biol. 23, 217–32.
Kinnman, E., Aldskogius, H., Wiesenfeld-Hallin, Z. & Johansson, O. (1991) Expansion of sensory innervation after peripheral nerve injury. Proceedings of the VIth World Congress on Pain (edited by Bond, M. R., Charlton, J. E. & Woolf, C. J.) pp 277–81. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Lawson, S. N. & Waddell, P. J. (1991) Soma neurofilament immunoreactivity is related to cell size and fibre conduction velocity in rat primary sensory neurons. J. Physiol. 435, 41–63.
Malinovský, L. & Páč, L. (1982) Morphology of sensory corpuscles mammals. Acta Fac. Med. Univ. Brunensis 79, 5–219.
Massoulié, J. & Bon, S. (1982) The molecular forms of cholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase in vertebrates. Ann. Rev. Neurosci. 5, 57–106.
Molander, C., Ygge, J. & Dalsgaard, C. J. (1987) Substance P-, somatostatin- and calcitonin gene-related peptide-like immunoreactivity and fluoride resistant acid phosphatase-activity in relation to retrogradely labeled cutaneous, muscular and visceral primary sensory neurons in the rat. Neurosci. Lett. 74, 37–42.
Munger, B. L. & Idé, C. (1988) The structure and function of cutaneous sensory receptors. Arch. Histol. Cytol. 51, 1–34.
Perry, M. J., Lawson, S. N. & Robertson, J. (1991) Neurofilament immunoreactivity in populations of rat primary afferent neurons: a quantitative study of phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated subunits. J. Neurocytol. 20, 746–58.
Proske, U. (1979) The Golgi tendon organ. Trends Neurosci. 2, 7–8.
Rice, F. L., Mance, A. & Munger, B. L. (1986) A comparative light microscopic analysis of the sensory innervation of the mystacial pad. I. Innervation of vibrissal follicle-sinus complex. J. Comp. Neurol. 252, 154–74.
Rosario, C. M., Aldskogius, H., Carlstedt, T. & Sidman, R. L. (1992) Centrifugal growth in orthotopic grafts of allogeneic dorsal root ganglia in adult rats: evidence for possible central ingrowth? Exp. Neurol. 115, 158–62.
Strasmann, T., Weihe, E. & Halata, Z. (1990) CGRP-like immunoreactivity in sensory nerve endings of the Golgi tendon organ. Acta Anat. 137, 278–81.
Winkelmann, R. K. (1960) The end-organ of feline skin. A morphologic and histochemical study. Am. J. Anat. 107, 281–90.
Wood, J. W. & Anderton, B. H. (1981) Monoclonal antibodies to mammalian neurofilaments. Biosci. Rep. 1, 263–8.
Zamboni, L. & De Martino, C. (1967) Buffered picric acidformaldehyde: a new rapid fixative for electron microscopy. J. Cell Biol 35, 148A.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dubový, P., Rosario, C.M. & Aldskogius, H. Combination of non-specific cholinesterase histochemistry and immunofluorescence staining for the study of the sensory innervation of skin and muscle. Histochem J 25, 112–118 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00157982
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00157982