Summary
The cytotoxic effect of aluminium was studied on cultured goat brain microvascular endothelial cells used as an in vitro model of the blood—brain barrier. Confluent monolayers of these cells were exposed for 4 days to aluminium maltol and, for control purposes, to maltol alone, and also to cadmium chloride as a known cytotoxic substance. The localization of plasmalemma-bound enzymatic activities of 5′-nucleotidase and Ca2+-ATPase and the distribution of sialic acid residues were studied at the ultrastructural level.
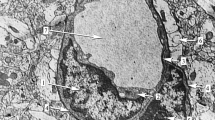
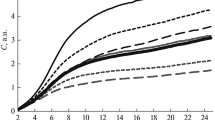
It was observed that the reaction for 5′-nucleotidase activity was only insignificantly affected, indicating its resistance to the cytotoxic action of both substances used. On the contrary, the activity of Ca2+-ATPase was evidently suppressed, especially in the interendothelial clefts where junctional complexes are presumably to be formed. Aluminium also affects the density of sialic acid residues, as shown by their redistribution, leading to the appearance of relatively long segments of unlabelled apical cell surface.
The data obtained suggest that observed changes in the localization of Ca2+-ATPase and sialic acid residues can lead ultimately to impairment of the formation and maintenance of intercellular junctions and to disturbances in the negatively charged domains of the endothelial cell surface. Whether these alterations, induced in vitro, contribute to in vivo disturbances of blood—brain barrier function requires further experimental study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Audus, K. L. & Borchardt, R. T. (1987) Bovine brain microvessel endothelial cell monolayers as a model system for the blood-brain barrier. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 507, 9–18.
Audus, K. L., Shinogle, J. A., Guillot, F. L. & Holthaus, S. R. (1988) Aluminum effects on brain microvessel endothelial cell monolayer permeability. Int. J. Pharm. 45, 249–57.
Banks, W. A. & Kastin, A. J. (1983) Aluminum increases permeability of the blood—brain barrier to labelled DSIP and beta-endorphin: possible implications for senile and dialysis dementia. Lancet ii, 1227–9.
Banks, W. A. & Kastin, A. J. (1989) Aluminum-induced neurotoxicity: alterations in membrane function at the blood-brain barrier. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 13, 47–53.
Banks, W. A., Kastin, A. J. & Fasold, M B. (1988) Differential effect of aluminum on the blood—brain barrier transport of peptides, technetium and albumin. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 244, 579–85.
Cardy, J. D. & Firth, J. A. (1993) Adenosine triphosphate—lead histochemical reactions in ependymal epithelia of the murine brains do not represent calcium transport adenosine triphosphatase. Histochem. J. 25, 319–24.
Cutler, L., Rodan, G. & Feinstein, M. B. (1978) Cytochemical localization of adenylate cyclase and of calcium ion, magnesium ion-activated ATPases in the dense tubular system of human blood platelets. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 542, 357–66.
Favarato, M., Zatta, P., Perazzolo, M., Fontana, L. & Nicolini, M. (1992) Aluminum (III) influences the permeability of the blood-brain barrier to (14C) sucrose in rats. Brain Res. 569, 330–35.
Firth, J. A. (1978) Cytochemical approaches to the localization of specific adenosine triphosphatase. Histochem. J. 10, 253–69.
Firth, J. A. (1980) Reliability and specificity of membrane adenosine triphosphatase localizations. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 28, 69–71.
Galli, P., Brenna, A., De Camilli, P. & Meldolesi, J. (1976) Extracellular calcium and the organization of tight junctions in pancreatic acinar cells. Exp. Cell. Res. 99, 178–86.
Kang, Y. H. & Watson, L. P. (1988) Ultracytochemical study of the effect of bacterial endotoxin and calmodulin on Ca2+-ATPase activity in human NK cells. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 36, 908.
Kim, Y. S., Lee, M. H. & Wisniewski, H. M. (1986) Aluminum induced reversible change in permeability of the blood—brain barrier to (14C) sucrose. Brain Res. 377, 286–91.
Reese, T. S. & Karnovsky, M. J. (1967) Fine structural localization of a blood-brain barrier to exogenous peroxidase. J. Cell Biol. 34, 207–17.
Robinson, J. M. & Karnovsky, M. J. (1983) Ultrastructural localization of 5′-nucleotidase in guinea pig neutrophils based upon the use of cerium as capturing agent. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 31, 1190–6.
Roth, J., Lucocq, J. M. & Charest, P. M. (1984) Light and electron microscopic demonstration of sialic acid residues with the lectin from Limax flavus: a Cytochemical affinity technique with the use of fetuin—gold complexes. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 32, 1167–76.
Sedar, A. W. & Forte, J. G. (1964) Effects of calcium depletion on the junctional complex between oxyntic cells of gastric glands. J. Cell Biol. 22, 173–82.
Vorbrodt, A. W. (1987) Demonstration of anionic sites on the luminal and abluminal fronts of endothelial cells with poly-l-lysine—gold complex. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 35, 1261–6.
Vorbrodt, A. W. (1988) Ultrastructural cytochemistry of blood-brain barrier endothelia. Prog. Histochem. Cytochem. 18, 1–99.
Vorbrodt, A. W. (1989) Ultracytochemical characterization of anionic sites in the wall of brain capillaries. J. Neurocytol. 18, 359–68.
Vorbrodt, A. W. & Trowbridge, R. S. (1991) Ultracytochemical characteristics of cultured sheep brain microvascular endothelial cells. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 39, 1555–63.
Vorbrodt, A. W. & Trowbridge, R. S. (1993) Aluminum-induced alteration of surface anionic sites in cultured brain micro-vascular endothelial cells. Acta Neuropathol. 86, 371–77.
Vorbrodt, A. W., Dobrogowska, D. H., Lossinsky, A. S. & Wisniewski, H. M. (1986) Ultrastructural localization of lectin receptors on the luminal and abluminal aspects of brain micro-blood vessels. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 34, 251–61.
Zatta, P. F., Nicolini, M. & Corain, B. (1991) Aluminum (III) toxicity and blood—brain barrier permeability. In Aluminum in Chemistry, Biology and Medicine (edited by Nicolini, M., Zatta, P. F. & Corain, B.), pp. 97–112. New York: Raven Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vorbrodt, A.W., Trowbridge, R.S. & Dobrogowska, D.H. Cytochemical study of the effect of aluminium on cultured brain microvascular endothelial cells. Histochem J 26, 119–126 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00157960
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00157960