Abstract
The temperature and density are obtained for coronal plasma in thermal and hydrostatic equilibrium and located in a force-free magnetic arcade. The isotherms are found to be inclined to the magnetic field lines and so care should be taken in inferring the magnetic structure from observed emission.
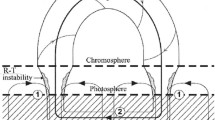
When the coronal pressure becomes too great, the equilibrium ceases to exist and the material cools to form a quiescent prominence. The same process can be initiated at low heating rates when the width or shear of the arcade exceeds a critical value.
We suggest that the prominence should be modelled as a dynamic structure with plasma always draining downwards. Material is continually sucked up along field lines of the ambient arcade and into the region lacking a hot equilibrium, where it cools to form new prominence material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cargill, P. J. and Priest, E. R.: 1979, Solar Phys., in press.
Craig, I. J. D., McClymont, A. N., and Underwood, J. H.: 1979, Astron. Astrophys. 70, 1.
Dunn, R.: 1960, Ph.D. thesis, Harvard University.
Engvold, O.: 1976, Solar Phys. 49, 283.
Heasley, J. N. and Mihalas, D.: 1976, Astrophys. J. 205, 273.
Hildner, E.: 1971, Ph.D. thesis, Univ. of Colorado.
Hildner, E.: 1974, Solar Phys. 35, 123.
Hood, A. W. and Priest, E. R.: 1979, Astron. Astrophys. 77, 233.
Kuperus, M. and Tandberg-Hanssen, E.: 1967, Solar Phys. 2, 39.
Lites, B. W., Bruner, E. C., Chipman, E. G., Shine, R. A., Rottman, G. J., White, O. R., and Athay, R. G.: 1976, Astrophys. J. 210, L111.
Low, B. C.: 1975, Astrophys. J. 197, 251.
Meyer, F. and Schmidt, H. U.: 1968, Z. Angew. Math. Mech. 48, 218.
Milne, A. M., Priest, E. R., and Roberts, B.: 1979, Astrophys. J. 232, 304.
Nakagawa, Y. and Tanaka, K.: 1974, Astrophys. J. 190, 711.
Pikel'ner, S. B.: 1971, Solar Phys. 17, 44.
Priest, E. R.: 1978, Solar Phys. 58, 57.
Rosner, R., Tucker, W. H., and Vaiana, G. S.: 1978, Astrophys. J. 220, 643.
Serio, S. Vaiana, G., Godoli, G., Mata, S., Pirronello, V., and Zappala, R.: 1978, Solar Phys. 59, 65.
Smith, E. A. and Priest, E. R.: 1977, Solar Phys. 53, 25.
Tandberg-Hanssen, E.: 1974, Solar Prominences, D. Reidel Publ. Co., Dordrecht, Holland.
Tandberg-Hanssen, E.: 1979, ‘The Physics of Solar Prominences’, IAU Coll. 44, 138.
Tur, T. J. and Priest, E. R.: 1978, Solar Phys. 58, 181.
Uchida, Y. and Sakurai, T.: 1977, Solar Phys. 51, 413.
Vaiana, G., Krieger, A., and Timothy, A.: 1973, Solar Phys. 32, 81.
Wragg, M. and Priest, E. R.: 1979, submitted for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Priest, E.R., Smith, E.A. The structure of coronal arcades and the formation of solar prominences. Sol Phys 64, 267–286 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00151439
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00151439