Abstract
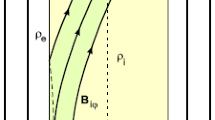
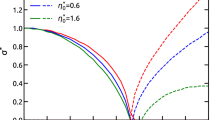
Satellite observations of the heliospheric current sheet indicate that the plasma flow velocity is low at the center of the current sheet and high on the two sides of current sheet. In this paper, we investigate the growth rates and eigenmodes of the sausage, kind, and tearing instabilities in the heliospheric current sheet with the observed sheared flow. These instabilities may lead to the formation of the plasmoids and kink waves in the solar wind. The results show that both the sausage and kink modes can be excited in the heliospheric current sheet with a growth time ∼ 0.05–5 day. Therefore, these modes can grow during the transit of the solar wind from the Sun to the Earth. The sausage mode grows faster than the kink mode for β ∞ < 1.5, while the streaming kink instability has a higher growth rate for β ∞ > 1.5. Here β ∞ is the ratio between the plasma and magnetic pressures away from the current layer. If a finite resistivity is considered, the streaming sausage mode evolves into the streaming tearing mode with the formation of magnetic islands. We suggest that some of the magnetic clouds and plasmoids observed in the solar wind may be associated with the streaming sausage instability. Furthermore, it is found that a large-scale kink wave may develop in the region with a radial distance greater than 0.5–1.5 AU.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alfvén, H. and Fälthammar, C.-G.: 1963, Cosmical Electrodynamics, Clarendon Press, Oxford.
Birn, J.: 1980, J. Geophys. Res. 85, 1214.
Borroni, G., Gosling, J. T., Bame, S. J., Feldman, W. C, and Wilcox, J. M: 1981, J. Geophys. Res. 86, 4565.
Forbes, T. G. and Priest, E. R.: 1983, J. Geophys. Res. 88, 863.
Fry, C. D. and Akasofu, S.-I.: 1987, Planetary Space Sci. 7, 913.
Furth, H. P., Killeen, I, and Rosenbluth, M. N.: 1963, Phys. Fluids 6, 459.
Gosling, J. T. and McComas, D. J.: 1987, Geophys. Res. Letters 14, 355.
Gosling, J. T., Borroni, G., Asbridge, J. R., Bame, S. J., Feldman, W. C., and Houson, R. T.: 1981, J. Geophys. Res. 86, 5438.
Hakamada, K. and Munakata, Y.: 1984, J. Geophys. Res. 89, 357.
Hasegawa, A.: 1975, Plasma Instabilities and Nonlinear Effects, Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Hones, E. W. Jr.: 1979, in S.-I. Akasofu (ed.), Dynamics of the Magnetosphere, D. Reidel, Publ. Co., Dordrecht, Holland, p. 545.
Kruskal, M. and Schwarzchild, M.: 1954, Proc. Roy. Soc. London, Ser. A223, 348.
Lee, L. C. and Fu, Z. F.: 1986, J. Geophys. Res. 91, 3311.
Lee, L. C, Fu, Z. F., and Akasofu, S.-I.: 1985, J. Geophys. Res. 90, 10896.
Lee, L. C., Wang, S., Wei, C. Q., and Tsurutani, B. T.: 1988, J. Geophys. Res. (in press).
Lyon, J. G., Brecht, S. H., Kuba, J. D., Fedder, J. A., and Palmadesso, P. J.: 1981, Phys. Rev. Letters 46, 1038.
Newkirk, G. R. Jr. and Fisk, L. A.: 1985, J. Geophys. Res. 90, 3391.
Parker, E. N.: 1963, Interplanetary Dynamical Processes, Interscience Publishers, New York.
Priest, E. R.: 1984, Solar Magnetohydrodynamics, D. Reidel Publ. Co., Dordrecht, Holland.
Rickett, B. J. and Coles, W. A.: 1983, in M. Neugebauer (ed.), Solar Wind V, NASA Conf. Publ.
Sime, D. G.: 1983, in M. Neugebauer (ed.), Solar Wind V, NASA Conf. Publ.
Steinolfson, R. S.: 1984, Phys. Fluids 27, 781.
Wang, S., Lee, L. C., and Wei, C. Q.: 1988, Phys Fluids (in press).
Zhao, X.-P. and Hundhausen, A. J.: 1983, J. Geophys. Res. 88, 451.
Zhao, X.-P., Wilcox, J. M., and Scherrer, P. H.: 1983, Chinese J. Space Sci. 3, 1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Also at Department of Earth and Space Science, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei Anhui 230029, China.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, S., Lee, L.C., Wei, C.Q. et al. A mechanism for the formation of plasmoids and kink waves in the heliospheric current sheet. Sol Phys 117, 157–169 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00148579
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00148579