Abstract
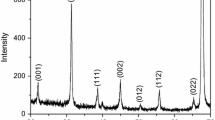
Ferroelectric Pb(Zr0.4Ti0.6) O3 (PZT 40/60) thin films with uniform composition have been fabricated using the metallo-organic precursor compounds lead di-ethylhexanoate Pb(C7H15COO)2, titanium di-methoxy-di-neodecanoate Ti(OCH3)2(C9H19COO)2 and zirconium octoate Zr(C7H15COO)4. These metallo-organic precursors were stored for more than four years and are very stable in ambient conditions, compared to sol-gel solutions. The structural development of these films under different annealing temperatures was systematically studied using X-ray diffraction, FT-IR spectroscopy and Raman scattering. The results show that the overlapping of (h 0 0) and (0 0 I) peaks of the PZT 40/60 films in X-ray diffraction patterns, mainly due to the small grain sizes in films, makes it very difficult to distinguish individual diffraction peaks and to identify the phases. In FT-IR measurements, the intensity of Zr/TiO6 metal-oxygen octahedral vibrational modes becomes stronger with increasing annealing temperatures, while the FT-IR spectral peaks of vibrations of the residual carbon ligands (COO−) finally disappear at high temperatures, showing that FT-IR spectroscopy is a good way to monitor the growth of the perovskite phase in PZT 40/60 films. Raman measurements undoubtedly reveal the Raman spectra of these PZT 40/60 films in the tetragonal phase field, demonstrating that Raman spectroscopy is an effective tool to identify structures, especially in the case of thin films having small grains. The values of high dielectric constant and the total remanent polarization obtained by ferroelectric pulse measurements show that the PZT film is a suitable material for non-volatile random access memory and dynamic random access memory applications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
J. F. SCOTT and C. A. PAZ de ARAIYO, Science, 246 (1989) 1400.
J. T. EVANS and R. WOMACK, IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits, 23 (1988) 1171.
R. MOAZZAMI and C. HU, IEEE Trans. Electronic Devices, 39 (1992) 2044.
R. W. VEST and W. ZHU, Ferroelectrics, 119 (1991) 61.
S. D. BERNSTEIN, T. Y. WONG, Y. KISLER and R. W. TUSTISON, J. Mater. Res., 8(1993) 12.
J. F. CHANG and S. B. DESU, ibid. J. Mater. Res. 9 (1994) 955.
B. A. TUTTLE, T. J. HEADLEY, B. C. BUNKER, R. W. SCHWARTZ, T. J. ZENDER, C. L. H, D. C. GOODNOW, R. J. TISSOT and J. MICHAEL, ibid. J. Mater. Res. 7 (1992) 1876.
G. H. HEARTLING, Chapter 3 Piezoelectric and Electrooptic Ceramics, in “Ceramic Materials for Electronics”, edited by R. C. Buchanan, Marcel Dekker, New York, 1986, p 184.
R. CUPPENS, P. K. LARSEN and G. A. C. M. SPIERINGS, Microelectronic Engineering, 19 (1992) 245.
M. OIKAWA and K. TODA, Appl. Phys. Lett., 29 (1976) 491.
R. CASTELLANO, Ferroelectrics, 28 (1980) 387.
X. CHEN, A. I. KINGON, L. MANTESE, O. AUCIELLO, and K. Y. HSIEH, Int Ferroelectrics, 3 (1993) 355.
C. H. PENG and S. B. DESU, Appl. Phys. Lett., 61 (1992) 1.
K. D. BUDD, S. K. DEY and D. A. PAYNE, Proc. Brit. Ceram. Soc., 36 (1985) 107.
W. ZHU, R. W. VEST, M. S. TSE, M. K. RAO and Z. Q. LIU, J. Mater. Sc Materials in Electronics, 5 (1994) 173.
C. Y. KUO, Solid State Technology, February (1974) pp49.
R. W. VEST, Ferroelectrics, 102 (1990) 53.
G. M. VEST and S. SINGARAM, Mat. Res. Soc. Symp. Proc., 60 (1986) 35.
JAFFE, R. S. ROTH and S. MARZULLO, J. Res. NBS, 55 (1955) 239.
G. SHIRANE and K. SUZUKI, J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 7 (1952) 333.
G. SHIRANE, K. SUZUKI, and A. TAKEDA, ibid. J. Phys. Soc. Jpn. 7 (1952) 12.
S. Fushimi and T. Ikeda, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 50 (1967) 129.
G. H. HEARTLING and C. E. LAND, ibid. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 54 (1971) 1.
C. K. KWOK and B. DESU, Appl. Phys. Lett. 60 (1992) 1430.
L. A. BURSILL and K. G. BROOKS, J. Appl. Phys. 75 (1994) 4501.
B. D. CULLITY, “Elements of X-Ray Diffraction”, 2nd Edn. (Addison-Wesley, Menlo Park, USA, 1978).
L. H. SCHWARTZ and J. B. COHEN, “Diffraction From Materials” (Academic Press, New York, 1977).
R. E. RIMAN, D. M. HAALAND, C. J. M. NORTHRUP Jr, H. K. BOWEN and A. BLEIER, Mater. Res. Soc. Symp. 23 (1984) 233.
N. T. MCDEVITT and W. L. BAUN, Spectrochim. Acta 70 (1964) 799.
V. ZELEZNY, P. SIMON, F. GERVAIS and T. KALA, Mater. Res. Bull. 22 (1987) 1695.
C. T. LIN, L. LI, J. S. WEBB, R. A. Lipeles and M. S. LEUNG, Integrated Ferroelectrics 3 (1993) 333.
S. LI, R. A. CONDRATE and R. M. SPRIGGS, J. Can. Ceram. Soc. 57 (1988) 61.
I. TAGUCHI, A. PIGNOLET, L. WANG, M. PROCTOR, F. LEVY and P. E. SCHMID, J. Appl. Phys. 73 (1993) 394.
G. BURNS and B. A. SCOTT, Phys. Rev. Lett. 25 (1970) 1191.
W. J. BRYA, ibid. Phys. Rev. Lett. 26 (1971) 1114.
Z. C. FENG, B. S. KWAK, A. ERBIL and L. A. BOATNER, Appl. Phys. Lett. 64 (1994) 2350.
J. A. SANIURJO, E. L. CRUZ and G. BURNS, Phys. Rev. B 28 (1983) 7260.
A. LURIO and G. BURNS, J. Appl. Phys. 45 (1974) 1986.
M. H. LEE and B. C. CHOI, J.Am. Ceram. Soc. 74 (1991) 2309.
D. R. TALLANT, R. W. SCHAWRTZ, B. A. TUTTLE, S. C. EVERIST and B. C. TAFOYA, Ferroelectrics, in press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, W., Liu, Z.Q., Tse, M.S. et al. Raman, FT-IR and dielectric studies of PZT 40/60 films deposited by MOD technology. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 6, 369–374 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00144636
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00144636