Abstract
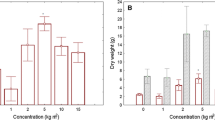
Municipal sewage sludge containing heavy metals had a toxic effect on the development of the cabbage looper, Trichoplusia ni (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae), one of two herbivorous insects commonly found in an Ohio old-field which had been subjected to long-term sewage sludge application. Soils were removed in 1992 from an old-field following 11 years of heavy nutrient enrichment (1978 to 1988) with applications of either sewage sludge (Milorganite®) containing heavy metal contaminants or urea-phosphate fertilizer. Egg to adult development rate and survival of the blackfaced leafhopper, Graminella nigrifrons (Homoptera: Cicadellidae), and the cabbage looper was determined on maize (leafhopper) and broccoli (looper) seedlings grown in soils from sludge-treated, fertilizer-treated, or untreated control plots of the old-field. Fertilizer and sludgetreated soils had higher levels of N. P and organic matter, and a lower pH than the untreated control soils, while sludge-treated soils contained significantly higher concentrations of Cd, Cu, Pb, and Zn. Maize appeared to be unaffected by the three soil treatments, and survival and rate of egg to adult development of the leafhopper was not affected. Broccoli seedlings grown in both the high nutrient fertilizer and sludge soils were greener and larger than broccoli grown in control soils. However, the cabbage looper had significant larval and pupal mortality (25 to 40%) and prolonged egg to adult development on sludge-grown broccoli compared to control and fertilizer treatments. As assimilation into the food chain of heavy metals and other organic pollutants, such as PCBs, is in part a function of the interaction of soil chemistry and type of plant, the application of municipal sludges to old-fields needs to be carefully monitored, as contaminants may have significant developmental and behavioural effects on some secondary links in the old-field food chain.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, T.J. and Barrett, G.W. (1982) Effects of dried sewage on meadow vole (Microtus pennsylvanicus) populations in two grassland communities. Journal of Applied Ecology 19 759–72.
Benninger-Truax, M. and Taylor, D.H. (1993) Municipal sludge metal contamination of old-field ecosystems: does liming and tilling affect remediation? Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry 12, 1931–43.
Carson, W.P. and Barrett, G.W. (1988) Succession in old-field plant communities: effects of contrasting types of nutrient enrichment. Ecology 69, 984–94.
CAST (1980) Effects of Sewage Sludge on the Cadmium and Zinc Content of Crops. Report No. 83. Ames, Iowa: Council for Agricultural Science and Technology.
Chapman, R.F. (1982) The Insects, Structure and Function (third edition)., Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press.
Culliney, T.W. and Pimentel, D. (1986) Effects of chemically contaminated sewage sludge on an aphid population. Ecology 67, 1665–9.
Culliney, T.W., Pimentel, D. and Lisk, D.J. (1986) Impact of chemically contaminated sewage sludge on the collard arthropod community. Environmental Entomology 15, 826–33.
D'Arcy, C.J. and Nault, L.R. (1982) Insect transmission of plant viruses and mycoplasmalike and ricketsialike organisms. Plant Disease 66, 99–104.
Fulkerson, W. and Goeller, H.E. (1973) Cadmium—the Dissipated Element. Oak Ridge, Tennessee: Oak Ridge National Laboratory.
Furr, A.K., Lawrence, A.W., Tong, S.C.C., Grandolfo, M.C., Hofstader, R.A., Bache, C.A., Gutenmann, W.H. and Lisk, D.J. (1976) Multielement and chlorinated hydrocarbon analysis of municipal sewage sludges of American cities. Environmental Science and Technology 10 683–7.
Golley, F.B. and Gentry, J.B. (1964) Bioenergetics of the southern harvester ant, Pogonomyrmex badius. Ecology 45, 217–225.
Grant, R.O. and Oleson, S.E. (1984) Sludge utilization in spruce plantations on sandy soils. In S.Berglund, R.D.Davis and P.L'Hermite (eds) Utilization of Sewage Sludge on Land: Rates of Application and Long-term Effects of Metals, pp. 79–90. Dordrecht, Holland: D. Reidel Publishing Co.
Hughes, P.R., Weinstein, L.H., Wettlaufer, S.H., Chiment, J.J., Doss, G.J., Culliney, T.W., Gutenmann, W.H., Bache, C.A. and Lisk, D.J. (1987) Effect of fertilization with municipal sludge on the glutathione, polyamine, and cadmium content of cole crops and associated loopers (Trichoplusia ni). Journal of Agricultural Food Chemistry 35, 50–54.
Hurd, L.C. and Wolf, L.L. (1974) Stability in relation to nutrient enrichment in arthropod consumers of old-field successional ecosystems. Ecological Monographs 44, 465–482.
Hyder, B.M. and Barrett, G.W. (1986) Effects of nutrient enrichment on the producer trophic level of a six-year old-field community. Ohio Journal of Science 86, 10–14.
Janssen, M.P.M. and Hogervorst, R.F. (1993) Metal accumulation in soil arthropods in relation to micro-nutrients. Environmental Pollution 79, 181–9.
Kelling, K.A., Keeney, D.R., Walsh, L.M. and Ryan, J.A. (1977) A field study of the agricultural use of sewage sludge. III. Effects on uptake and extractability of sludge-borne metals. Journal of Environmental Quality 6, 352–8.
Kiemnec, G.L., Hemphill, D.D., Hickey, M., Jackson, T.L. and Volk, V.V. (1990) Sweet corn yield and tissue metal concentration after seven years of sewage sludge applications. Journal of Productive Agriculture 3, 232–7.
Kirchner, T.B. (1977) The effects of resource enrichment on the diversity of plants and arthropods in a shortgrass prairie. Ecology 58, 1334–44.
Larsen, K.J., Madden, L.V. and Nault, L.R. (1990) Effect of temperature and host plant on the development of the blackfaced leafhopper. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata 55, 285–94.
Levine, M.B., Hall, A.T., Barrett, G.W. and Taylor, D.H. (1989) Heavy metal concentrations during ten years of sludge treatment to an old-field community. Journal of Environmental Quality 18, 411–18.
Lindqvist, L. (1988) Transport of cadmium from herbs to insects in a terrestrial environment. Entomologisk Tidskrift 109, 119–22.
Lindqvist, L. (1992) Accumulation of cadmium, copper, and zinc in five species of phytophagous insects. Environmental Entomology 21, 160–3.
MacLean, A.J. (1975) Cadmium in different plant species. Canadian Journal of Soil Science 56, 129–38.
Maly, M.S. and Barrett, G.W. (1984) Effects of two types of nutrient enrichment on the structure and function of contrasting old-field communities. American Midland Naturalist 111, 342–57.
Martoja, R., Bouquegneau, J.M. and Verthe, C. (1983) Toxicological effects and storage of cadmium and mercury in an insect Locusta migratoria (Orthoptera). Journal of Invertebrate Pathology 42, 17–32.
Medici, J.C. and Taylor, M.W. (1967) Interrelationships among copper, zinc, and cadmium in the diet of the confused flour beetle. Journal of Nutrition 93, 307–309.
Mumma, R.O., Raupach, D.C., Waldman, J.P., Tong, S.S.C., Jacobs, M.L., Babish, J.G., Hotchkiss, J.H., Wszolek, P.C., Gutenman, W.H., Bache, C.A. and Lisk, D.J. (1984) National survey of elements and other constituents in municipal sewage sludges. Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 13, 75–83.
Odum, E.P., Connell, C.E. and Davenport, L.B. (1962) Population energy flow of three primary consumer components of old-field ecosystems. Ecology 43, 88–96.
Page, A.L., Logan, T.J. and Ryan, J.A. (1987) Land Application of Sludge: Food Chain Implications. Chelsea, Michigan: Lewis Publishers.
Pahren, H.R., Lucas, J.B., Ryan, J.A. and Ditson, G.K. (1979) Health risks associated with land application of municipal sludge. Journal of the Water Pollution Control Federation 51, 2588–2601.
Perämäki, P., Itämies, J., Karttunen, V., Lajunen, L.H.J. and Pulliainen, E. (1992) Influence of pH on the accumulation of cadmium and lead in earthworms (Aporrectodea caliginosa) under controlled conditions. Annales Zoologici Fennici 29, 105–111.
Petrusewicz, K. and Macfadyen, A. (1970) Productivity of Terrestrial Animals: Principles and Methods. International Biological Programme Handbook No. 13. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: F.A. Davis, Co.
Pimentel, D. and Warneke, A. (1989) Ecological effects of manure, sewage sludge and toher organic wastes on arthropod populations. Agricultural Zoology Reviews 3, 1–30.
Poinar, G.O. and Thomas, G.M. (1978) Laboratory Guide to Insect Pathogens and Parasites. New York: Plenum Press.
Prestidge, R.A. and McNeill, S. (1982) The role of nitrogen in the ecology of grassland Auchenorrhyncha. In J.A.Lee, S.McNeill and I.H.Rorison (eds) Nitrogen as an Ecological Factor, pp. 257–81. Symposium of the British Ecological Society, 22. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications.
Roberts, R.D. and Johnsson, M.S. (1978) Dispersal of heavy metals from abandoned mine workings and their transference through terrestrial food chains. Environmental Pollution 16, 294–310.
Schmidt, G.H., Ibrahim, N.M.M. and Abdallah, M.D. (1992) Long-term effects of heavy metals in food on developmental stages of Aiolopus thalassinus (Saltatoria: Acrididae). Archives of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology 23, 375–82.
Sedlacek, J.D., Barrett, G.W. and Shaw, D.R. (1988) Effects of nutrient enrichment on the Auchenorrhyncha (Homoptera) in contrasting grassland communities. Journal of Applied Ecology 25, 537–50.
Sivapalan, P. and Gnanapragasam, N.C. (1980) Influence of copper on the development and adult emergence of Homona coffearia (Lepidoptera: Tortricidae) reared in vitro. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata 28, 59–63.
Sopper, W.E. and Kerr, S.N. (1979) Utilization of Municipal Sewage Effluent and Sludge on Forest and Disturbed Land. University Park, Pennsylvania: Pennsylvania State University Press.
Strauch, D. (1977) Health hazards of agricultural, industrial and municipal wastes applied to land. In R.C.Loehr (ed.) Land as a Waste Management Alternative, pp. 317–42. Ann Arbor, Michigan: Ann Arbor Science Publishers.
Sutton, S.D., Barrett, G.W. and Taylor, D.H. (1991) Microbial metabolic activities in soils of old-field communities following eleven years of nutrient enrichment. Environmental Pollution 73, 1–10.
White, T.C.R. (1984) The abundance of invertebrate herbivores in relation to the availability of nitrogen in stressed food plants. Oecologia 63, 90–105.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Larsen, K.J., Litsch, A.L., Brewer, S.R. et al. Contrasting effects of sewage sludge and commercial fertilizer on egg to adult development of two herbivorous insect species. Ecotoxicology 3, 94–109 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00143408
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00143408