Abstract
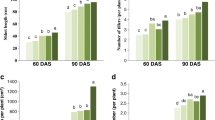
The effects of sewage sludge application on first year willows (Salix viminalis L.) and the accumulation of heavy metals in plants were investigated. Plants were exposed to 1–15 kg m−2 of sewage sludge under field conditions. Willows were grown in the field for 6 months. Sewage sludge application enhanced willows growth. Stem height of willows grown in soil treated with sludge were by 15–31 % higher than those grown in control plots. The biomass of stems and roots were by 26–61 % and 36–62 %, respectively, higher than that of control plants. Sludge application resulted in increased heavy metals concentrations in soil and willows. Metals concentrations were plants tissue and sludge application rate dependent. The highest bioconcentration factor was detected for Cd. Due to uptake of heavy metals by willows, the concentrations of Cu, Zn, Cd in soil (at 20 and 40 cm depth) were significantly reduced after the growing season.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hasselgren, K.: Use of municipal waste products in energy forestry: highlights form 15 years of experience. Biomass. Bioenerg. 15, 71–74 (1998)
Chary, N.S., Kamala, C.T., Suman Raj, D.S.: Assessing risk of heavy metals from consuming food grown on sewage irrigated soils and food chain transfer. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 69, 513–524 (2008)
Passuello, A., Mari, M., Nadal, M., Schuhmacher, M., Domingo, J.L.: POP accumulation in the food chain: integrated risk model for sewage sludge application in agricultural soils. Environ. Int. 36, 577–583 (2010)
Oleszczuk, P., Malara, A., Jośko, I., Lesiuk, A.: The phytotoxicity changes of sewage sludge-amended soils. Water Air Soil Poll. 223, 4937–4948 (2012)
Stefanakis, A.I., Tsihrintzis, V.A.: Heavy metal fate in pilot-scale sludge drying reed beds under various design and operational conditions. J. Hazard. Mater. 213–214, 393–405 (2012)
Roig, N., Sierra, J., Marti, E., Nadal, M., Schuhmacher, M., Domingo, J.L.: Long-term amendment of Spanish soils with sewage sludge: effects on soil functioning. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 158, 41–48 (2012)
Greger, M., Landberg, T.: Use of willow in phytoextraction. Int. J. Phytoremediation 1, 115–123 (1999)
Laidlaw, W.S., Arndt, S.K., Huynh, T.T., Gregory, D., Baker, A.J.M.: Phytoextraction of heavy metals by willows growing in biosolids under field conditions. J. Environ. Qual. 41, 134–143 (2012)
Council Directive 86/278/EEC on the protection of the environment, and in particular of the soil, when sewage sludge is used in agriculture (1986)
European Commission, DG Environment, Working Document—Sludge and Biowaste, Brussels (2010)
Olsen, S., Cole, C., Watanabe, F., Dean, L.: Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. USDA Circular Nr 939, US Gov. Print. Office, Washington, D.C. (1954)
Labrecque, M., Teodorescu, T.I.: Influence of plantation site and wastewater sludge fertilization on the performance and foliar nutrient status of two willow species grown under SRIC in southern Quebec (Canada). Forest Ecol. Manag. 150, 223–239 (2001)
Labrecque, M., Teodorescu, T.I., Daigle, S.M.: Effect of wastewater sludge on growth and heavy metal bioaccumulation of two Salix species. Plant Soil 171, 303–316 (1995)
Meers, E., Lamsal, S., Vervaeke, P., Hopgood, M., Lust, N., Tack, F.M.G.: Availability of heavy metals for uptake by Salix viminalis on a moderately contaminated dredged sediment disposal site. Environ. Pollut. 137, 354–364 (2005)
Maxted, A.P., Black, C.R., West, H.M., Crout, N.M.J., Mcgrath, S.P., Young, S.D.: Phytoextraction of cadmium and zinc by Salix from soil historically amended with sewage sludge. Plant Soil 290, 157–172 (2007)
Vervaeke, P., Luyssaert, S., Mertens, J., Meers, E., Tack, F.M.G., Lust, N.: Phytoremediation prospects of willow stands on contaminated sediment: a field trial. Environ. Pollut. 126, 275–282 (2003)
Žaltauskaitė, J., Šliumpaitė, I.: Evaluation of toxic effects and bioaccumulation of cadmium and copper in spring barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Environ. Res. Eng. Manag. 2(64), 51–58 (2013)
Sandalio, L.M., Dalurzo, H.C., Gómez, M., Romero-Puertas, M.C., del Río, L.A.: Cadmium-induced changes in the growth and oxidative metabolism of pea plants. J. Exp. Bot. 52, 2115–2126 (2001)
Dimitriou, I., Mola-Yudego, B., Aronsson, P.: Impact of willow short rotation coppice on water quality. Bioenerg. Res. 5, 537–545 (2012)
Dimitriou, I., Aronsson, P.: Wastewater and sewage sludge application to willows and poplars grown in lysimeters—plant response and treatment efficiency. Biomass Bioener. 35, 161–170 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Žaltauskaitė, J., Judeikytė, S., Sujetovienė, G. et al. Sewage Sludge Application Effects to First Year Willows (Salix Viminalis L.) Growth and Heavy Metal Bioaccumulation. Waste Biomass Valor 8, 1813–1818 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9691-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-016-9691-1