Summary
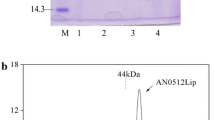
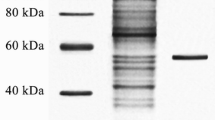
The pink snow mold, Microdochium nivale (syn. Fusarium nivale) SUF 1377 strain produced an extracellular low temperature active lipase during growth at 4°C. The lipase had the highest activity at 20°C, and retained 19% of its maximum activity at 0°C.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Årsvoll, K. (1975). Meld. Norg. LandbrHøgsk. 54, (9) 49 pp.
Fiore, J.V. and Nord, F.F. (1949). Arch. Biochem. 23, 473–479.
Hoshino, T., Sasaki, T., Watanabe, Y., Nagasawa, T. and Yamane, T. (1992). Biosci. Biotech. Biochem. 56, 660–664.
Joshi, S. and Dhar, D.N. (1987). Acta Microbiol. Hung. 31, 111–114
Mulanax, M. and Huber, D. (1972). Phytopathology 62, 1105.
Rubylone, N. (1985). European Patent 0-130-064-B1.
Shimada, Y., Koga, C., Sugihara, A., Nagao, T., Takada, N., Tsujisawa, S. and Tominaga, Y. (1993). J. Ferment. Bioeng. 75, 349–352.
Stuer, W., Jaeger, K. and Winkler, U. (1986). J. Bacteriol. 168, 1070–1074.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hoshino, T., Ohgiya, S., Shimanuki, T. et al. Production of low temperature active lipase from the pink snow mold, Microdochium nivale (syn. Fusarium nivale). Biotechnol Lett 18, 509–510 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00140193
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00140193