Abstract
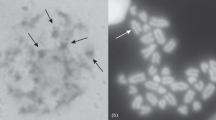
The whole-mount SC preparations from males of three species of the genus Ellobius (Ellobius fuscocapillus, Ellobius lutescens), and Ellobius tancrei Footnote 1 were studied by electron microscopy. In the males of Ellobius fuscocapillus, behavioral peculiarities of the sex bivalent (viz. the normal male heterozygosity) are characterized by early complete desynapsis of sex chromosomes (X, Y), occurring at late pachytene-early diplotene. The karyotype of species Ellobius lutescens is unique for mammals. In both sexes it is characterized by an odd number of chromosomes (2n=17). At prophase I the unpaired chromosome 9 is not involved in synapsis with other chromosomes and forms a sex body at the end of pachytene.
The complete Robertsonian fan has been described for superspecies Ellobius tancrei. As shown on the basis of G-band patterns the male and female sex chromosomes are cytologically indistinguishable.
Analysis of whole-mount SC preparations revealed the formation of a closed sex SC bivalent and showed some morphological differences in the axes of sex chromosomes at meiotic prophase I. A number of assumptions are made about the relationship between the behavior of sex chromosomes, their evolution and the sex determination system in the studied species of genus Ellobius.
Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Ellobius tancrei has been distinguished as a separate superspecies recently (Vorontsov & Yakimenko, 1984); earlier it was systematically attributed to species Ellobius talpinus.
References
Ashley, T., 1984. A re-examination of the case for homology between the X and Y chromosomes of mouse and man. Hum. Genet. 66: 372–377.
Ashley, T. & Moses, M. J., 1980. End association and segregation of the achiasmatic X and Y chromosomes of the sand rat Psammomys obesus. Chromosoma (Berl.) 78: 203–210.
Bogdanov, Y. F., Kolomiets, O. L., Lyapunova, E. A., Yanina, I. Yu. & Mazurova, T. F., 1986. Synaptonemal complexes and chromosome chains in the Ellobius talpinus heterozigous for ten Robertsonian translocations. Chromosoma (Berl.) 94: 94–102.
Baklushinskaya, I. Ya. & Lyapunova, E. A., 1990. The nomenclature of chromosomes of Ellobius tancrei. Cytology (USSR) 32: 378–383. (in Russian.)
Castro-Sierra, E. & Wolf, U., 1967. Replication patterns of the unpaired chromosome 9 of the rodent Ellobius lutescens TH. Cytogenetics 6: 268–275.
Castro-Sierra, F. & Wolf, U., 1968. Studies on the male meiosis of Ellobius lutescens. Cytogenetics 7: 241–248.
Chandley, A. C., Goets, P., Hargreave, T. B., Joseph, A. M. & Speed, R. M., 1984. On the nature and extent of XY pairing at meiotic prophase in man. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 38: 241–247.
De la Mazia, L. M. & Sawyer, I. R., 1976. The G and Q banding of Ellobius lutescens. A unique case of sex determination in mammals. Canad. J. Genet. Cytol. 18: 497–502.
Dietrich, A. J. J. & Mulder, R. J. P., 1981. A light microscopic study of the development and behaviour of the synaptonemal complex in spermatocytes of the mouse. Chromosoma (Berl.) 83: 409–418.
Djalali, M., Hameister, H. & Vogel, W., 1986. Further chromosomal studies in Ellobius lutescens: Heteromorphism of chromosome is not associated with sex determination. Experientia 42: 1281–1282.
Dresser, M. E. & Moses, M. J., 1980. Synaptonemal complex karyotyping in spermatocytes of the Chinese hamster (Cricetulus griseus). 1Y. Light and electron microscopy of synapsis and nucleolar development by silver staining. Chromosoma (Berl.) 76: 1–22.
Hale, D. & Greenbaum, I. F., 1986. The behaviour and morphology of X and Y chromosomes during prophase 1 in the Stika deer mouse (Peromyscus sitkensis) Chromosoma (Berl.) 94: 235–242.
Joseph, A. M. & Chandley, A. C., 1984. The morphological sequence of XY pairing in the Norway rat Rattus norvegicus. Chromosoma (Berl.) 89: 381.
Kolomiets, O. L., Lyapunova, E. A., Mazurova, T. F., Yanina, I. Yu. & Bogdanov, Yu. F., 1986. Role of the heterochromatin in synaptonemal complex chain formation in mammals heterozygous for numerous Robertsonian translocations. Genetica 22: 273–280 (In Russian).
Lyapunova, E. A., Ivnitsky, S. V., Korablev, V. P. & Yanina, I. Ya., 1984. Complete Robertsonian fan of chromosomal forms of slepoushoncas of infragenus Ellobius talpinus. Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR 273: 5–8 (in Russian).
Lyapunova, E. A. & Vorontsov, N. N., 1978. Genetics of Ellobius (Rodentia). 1. Karyological characteristic of four species of genus Ellobius. Genetica 14: 2012–2022.
Lyapunova, E. A., Vorontsov, N. N., Korobitsina, K. V., Ivanitskaya, E. Yu., Borisov, Yu. M., Yakimenko, L. V. & Dovgal, V. Ye., 1980. A Robertsonian fan of Ellobius talpinus. Genetica 52/53: 239–247.
Lyapunova, E. A., Vorontsov, N. N. & Zakarian, G. G. 1975. Zygotic mortality in Ellobius lutescens. Experientia 31: 417–418.
Matthey, R., 1953. La formule chromosomique et le probleme de la determination sexuelle chez Ellobius lutescens (Rodentia-Muridae-Microtinae). Arch. Julius Klaus-Stift. Vererbungsforch. 28: 271–280.
Matthey, R., 1958. Un nouveau type de determination chromosomique du sex chez les mamiferes Ellobius lutescens. Th et Microtus (Chilotus) Bachm (Murides-Microtines). Experientia 14: 240–241.
Matthey, R., 1964. Etudes sur les d'Ellobius lutescens (Mammalian-Muridae Microtinae). II. Informations complementaires sur les divisions meiotiques. Rev. Suiss Zool. 71: 401–410.
Moses, M. J., 1980. New cytogenetic studies on mammalian meiosis. In Animal Models in Human Reproduction (ed. M. Serio & L. Martini) pp. 169–190. New-York, Raven Press.
Pathak, S. & Stock, A. D., 1974. The X-chromosomes of mammals: Karyological homology as revealed by banding techniques. Genetics 78: 53–60.
Seabright, M., 1971. A rapid banding teachnique for human chromosomes. Lancet. 1: 971–972.
Sharp, P., 1982. Sex chromosome pairing during male meiosis in Marsupials. Chromosoma (Berl.) 86: 27–47.
Solari, A. J., 1974. The behaviour of chromosoma axes in Searle's X-autosome translocation. Chromosoma (Berl.) 34: 99–112.
Solari, A. J., 1980. Synaptonemal complexes and associated structures in microspread human spermatocytes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 81: 315–337.
Solari, A. J. & Ashley, T., 1977. Ultrastructure and bechaviour of the achiasmatic telosynaptic XY pair of the sand rat (Psammomys obesus) Chromosoma (Berl.) 62: 319–336.
Solari, A. J. & Bianchi, N. O., 1975. The synaptic bechaviour of X and Y chromosomes in the Marsupial Monodelphis dimidiata Chromosoma (Berl.) 52: 11–25.
Solari, A. J. & Rahn, M. I., 1985. Assymetry and resolution of synaptonemal complex in XY pair of Chinchilla laniger. Genetica 67: 63–71.
Speed, R. M., 1986. Oocyte development in XO foetuses of man and mouse: The possible role of heterologous X-chromosome pairing in germ cell survival. 94: 115–124.
Sumner, A. T. & Speed, R. M., 1987. Immunocytochemical labelling of the kinetochore of human synaptonemal complexes, and extent of pairing of the X and Y chromosomes. Chromosoma (Berl.) 95: 359–365.
Tress, L. L., 1977. Extensive pairing of the XY bivalent in mouse spermatocytes as visualized by whole-mount electron microscopy. J. Cell Sci. 25: 1–15.
Vogel, W., Steinbach, P., Djalali, M., Mechnert, K., Ali, S. & Epplen, J. T., 1988. Chromosome 9 of Ellobius lutescens is the X-chromosome Chromosoma (Berl.) 96: 112–118.
Vorontsov, N. N. & Lyapunova, E. A., 1984. Explosive chromosomal speciation in seismic active regions. Cromosomes Today 8: 279–284.
Vorontsov, N. N., Lyapunova, E. A., Borisov, Yu. M. & Dovgal, V. E., 1980. Variability of sex chromosomes in Mammals. Genetica 52/53: 361–372.
Vorontsov, N. N. & Yakimenko, L. Y., 1984. The morfometric analysis of the skull in mole-voles (Ellobius, Rodentia). Zoologichesky Zhyrnal. 63: 1865–1877. (in Russian).
White, M. J. D., 1957. Interpretation of the unique sex-chromosome mechanism of the rodent, Ellobius lutescens Thomas. Proc. Zool. Soc., Calcutta Mookerjee memor. 113: 113–114.
Wolf, M., Schempp, W. & Vogel, W., 1979. Ellobius lutescens Th (Rodentia, Microtinae): Z-, R-, and replication banding patterns. Chromosome 1 polymorphism in the male and presumptive heterogamety in the female Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 23: 117–123.
Wolf, U., 1974. Cell culture from tissue explants. In: Schwarzachter, HG, Wolf, U (eds.). Methods in human cytogenetics. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kolomiets, O.L., Vorontsov, N.N., Lyapunova, E.A. et al. Ultrastructure, meiotic behavior, and evolution of sex chromosomes of the genus Ellobius . Genetica 84, 179–189 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00127245
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00127245