Abstract
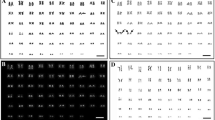
The karyotypes of 25 species from the scincid genera Egernia, Corucia and Tiliqua have been investigated using C-banding, silver staining of nucleolar organiser regions (NORs) and Hoechst 33258 induced condensation inhibition. At least one member from each of the species groups of Egernia recognised by Storr et al. (1981) was studied. The three genera have very similar conventionally stained karyotypes of 32 chromosomes. Some species show departures from this basic karyotype but these are due to additions of C-band positive material. Silver stained. NOR patterns are variable but most species have a silver staining site on a pair of larger microchromosomes. All specimens studied except one have a proximal C-band on the acrocentric ninth pair, which shows failure to condense following treatment with the fluorochrome Hoechst 33258. Heterogamety was not observed in any species. Mabuya multifasciata, proposed as a relative of the Egernia group, while having 32 chromosomes does not share the C-band marker on pair nine, unique to the Egernia group. Tribolonotus gracilis, sometimes allied with the Egernia group, has 32 chromosomes and a similiar karyotype, but prominent procentric C-bands on all chromosome pairs obscure the detection of the proximal C-band marker on pair nine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrighi F. E. & Hsu T. C., 1971. Localization of heterochromatin in human chromosomes. Cytogenetics 10: 81–86.
Becak M. L., Becak W. & Denaro L., 1972. Chromosome polymorphism, geographical variation and karyotypes in Sauria. Caryologia 25: 313–326.
Bhatnagar A. N. & Yoniss Y. T., 1977. Chromosome cytology of two lizards, Agama ruderata and Mabuya aurata septemtaeniata. Caryologia 30: 399–409.
Blake, J. A., 1983. Chromosomal C-banding in Anolis grahami. In: A. G. J. Rhodin and K. Miyata (eds), Advances in Herpetology and Evolutionary Biology: 621–625.
Bloom S. E. & Goodpasture C., 1976. An improved technique for the selective silver staining of nucleolar organiser regions in human chromosomes. Hum. Genet. 34: 199–206.
Boulenger G. A., 1987. Catalogue of the lizards in the British Museum (Natural History) (2nd ed.) Vol. 3. Taylor and Francis, London.
Bull, 1978. Sex chromosome differentiation: an intermediate stage in a lizard. Can. J. Genet. Cytol. 20: 205–209.
Cano J., Pretel A. & Lopez-Jurando L. F., 1985. Studies of the herpetofauna of the Canary Islands. II. The karyotype of the lizard Chalcides sexlineatus. J. Herp. 19: 416–417.
Cogger H. G., 1975. Reptiles and Amphibians of Australia. A. H. and A. W. Reed, Sydney.
Colus I. M. & Ferrari I., 1988. Mitotic chromosomes of Mabuya (Scincidae: Reptilia). Genetica 77: 105–111.
De Smet W. H. O., 1981. Description of the orcein stained karyotypes of 36 lizard species (Lacertilia, Reptilia) belonging to the families Teiidae, Scincidae, Lacertidae, Cordylidae and Varanidae (Autarchoglossa). Acta Zool. et Pathol. Antverp. 76: 73–118.
Drets M. E. & Shaw M. W., 1971. Specific banding patterns of human chromosomes. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA. 68: 2073–2077.
Ferraro M., Lavia P., Pelliccia F. & de Capoa A., 1981. Clonal inheritance of rRNA gene activity: cytological evidence in human cells. Chromosoma: 84: 345–351.
Gatti M., Pimpinella S. & Santini G., 1976. Characterisation of Drosophila heterochromatin. Chromosoma 57: 351–375.
Gorman G. C., 1973. The chromosomes of the Reptilia, a cytotaxonomic interpretation. In: A. B. Chiarelli and E. Capanna, (eds), Cytotaxonomy and vertebrate evolution. Academic Press, London-New York: 349–424.
Greer A. E., 1970. A subfamilial classification of scincid lizards. Bull. Mus. Comp. Zool. 139: 151–183.
Greer A. E., 1979. A phylogenetic subdivision of Australian skinks. Rec. Aust. Mus. 32: 339–371.
Greer A. E., 1986. Lygosomine (Scincidae) monophyly: a third, corroborating character and a reply to crities. J. Herp. 20: 123–126.
Haiduk M. W., Baker R. J., Robbins C. W. & Schlitter D. A., 1981. Chromosomal evolution in African megachiroptera: G- and C-band assessment of the magnitude of change in similar standard karyotypes. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 29: 221–232.
Hardy G. S., 1979. The karyotypes of two scincid lizards, and their bearing on relationships in genus Leiolopisma and its relatives (Scincidae: Lygosominae). N.Z. J. Zool. 6: 609–612.
Hayman D. & Sharp P., 1981. Hoechst 33258 induced uncondensed sites in marsupial chromosomes. Chromosoma 83: 249–262.
Hilwig I. & Gropp A., 1973. Decondensation of constitutive heterochromatin in L cell chromosomes by a benzimidazole compound (‘33258’ Hoechst). Exp. Cell. Res. 81: 474–477.
Horton D. R., 1972. Evolution in the genus Egernia (Lacertilia: Scincidae). J. Herp. 6: 101–109.
Horton, D. R., 1974. Evolution in the genus Mabuya (Lacertilia, Scincidae) Unpubl. Ph.D. Thesis, University of New England, Armidale.
Hutchinson M. N., 1980. The systematic relationships of the genera Egernia and Tiliqua (Lacertilia: Scincidae). A review and immunological reassessment. In: C. B. Banks and A. A. Martin, (eds.), Proceedings of the Melbourne Herpetological Symposium. Zoological Board of Victoria, Melbourne: 176–193.
King M., 1973a. Chromosomes of two Australian lizards of the families Scincidae and Gekkonidae. Cytologia 38: 205–210.
King M., 1973b. Karyotypic studies of some Australian Scincidae (Reptilia). Aust. J. Zool. 21: 21–32.
King M., 1980. C-Band studies on Australian hylid frogs: secondary constriction structure and the concept of euchromatin transformation. Chromosoma 80: 191–217.
King M., Mengden G. A. & King D., 1983. A pericentric inversion polymorphism and a ZZ/ZW sex-chromosome system in Varanus acanthurus Boulenger analysed by G- and C-banding and Ag staining. Genetica 58: 39–45.
Kuprianova L., 1973. The karyotype characteristics of two species of the Scincidae family. Tsitologiya 15: 1135–1142.
Leviton A. E., Gibbs R. H., Heal E. & Dawson C. E., 1985. Standards in herpetology and ichthyology: Part I. Standard symbolic codes for institutional resource collections in herpetology and ichthyology. Copeia 1985: 802–832.
Marcus M., Goitein R. & Gropp A., 1979. Condensation of all human chromosomes in phase G2 and early mitosis can be drastically inhibited by 33258 Hoechst treatment. Hum. Genet. 51: 99–105.
Miller D. A., Tantravahi R., Dev V. G. & Miller O. J., 1977. Frequency of satellite association of human chromosomes is correlated with amount of Ag-staining of the nucleolus organiser region. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 24: 490–502.
Nardi I., Barsacci-Pilone G., Bastistoni R. & Andronico F., 1977. Chromosome location of the ribosmal RNA genees in Triturus vulgaris meridonalis (Amphibia: Urodela). II Intraspecific variability in number and position of the chrosome loci for 18S and 28S ribosomal RNA. Chromosoma 64: 67–84.
Ota H., Hikida T., Matsui M. & Hasegawa M., 1985. Karyotype of a scincid lizard, Carlia fusca, from Guam, the Mariana Islands. Zoological Science 5: 901–903.
Rocchi A., Pranterra G., Pimpinelli S. & Gastro M. Di., 1976. Effects of Hoechst 33258 on Chinese hamster chromosomes. Chromosoma 56: 41–46.
Schmid M., 1978a. Chromosome banding in Amphibia. I Constitutive heterochromatin and nucleolus organiser regions in Bufo and Hyla. Chromosoma 66: 361–388.
Schmid M., 1978b. Chromosome banding in Amphibia. II Constitutive heterochromatin and nucleolus organiser regions in Ranidae, Microhylidae and Rhacophoridae. Chromosoma 68: 131–148.
Schmid M., 1982. Chromosome Banding in Amphibia. VII. Analysis of the structure and variability of NORs in Anura. Chromosoma 87: 327–344.
Schmid M. & Guttenbach M., 1988. Evolutionary diversity of reverse (R) fluorescent chromosome bands in vertebrates. Chromosoma 97: 101–114.
Seabright M., 1972. The use of proteolytic enzymes for the mapping of structural rearrangements in the chromosomes of man. Chromosoma 36: 204–210.
Seuanez H. N., 1979. The phylogeny of human chromosomes. Springer-Verlag, New York.
Storr G. M., 1976. The genus Omolepida (Lacertilia, Scincidae) in Western Australia. Rec. West. Aust. Mus. 4: 163–170.
Storr G. M., 1978: The genus Egernia (Lacertilia, Scincidae) in Western Australia. Rec. West. Aust. Mus. 6: 147–187.
Storr G. M., Smith L. A. & Johnstone R. E., 1981. Lizards of Western Australia. I. Skinks. Univ. W. A. Press, Nedlands.
Sumner A. T., 1972. A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp. Cell Res. 75: 304–306.
Tantravahi R., Miller D. A., Dev V. G. & Miller O. J., 1976. Detection of nucleolar organiser regions in chromosomes of human, chimpanzee, gorilla, orangutan and gibbon. Chromosoma 56: 16–27.
Varley J. M. & Morgan G. T., 1978. Silver staining of the lampbrush chromosomes of Triturus cristatus carnifex. Chromosoma 67: 233–244.
White M. J. D., Dennis E. S., Honeycutt R. L., Contreras N. & Peacock W. J., 1982. Cytogenetics of the parthenogenetic grasshopper Warramaba virgo and its bisexual relatives. IX. The ribosomal DNA cistrons. Chromosoma 85: 181–199.
Wright J. W., 1973. Evolution of the X2X2Y sex chromosome mechanism in the scincid lizard Scincella laterale (Say). Chromosoma 43: 101–108.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Donnellan, S.C. Chromosomes of Australian lygosomine skinks (Lacertilia: Scincidae). Genetica 83, 207–222 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00126227
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00126227