Abstract
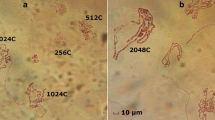
Polyethylene glycol was used to induce interspecific somatic cell fusion between human fibroblasts (stock F6) and Drosophila melanogaster cells from established cell lines (C1 82 and 11 P102), characterized by different ploidy levels. The present investigation defines some parameters for Drosophila cell fusion and interspecific fusion between Drosophila and human cells. The cytological analysis provided evidence of spontaneous as well as induced human-Drosophila heterokaryon formation. The presence in the same cell of two types of nuclei, distinguishable because of their different size and morphology, was confirmed autoradiographically by 3H-thymidine pre-labelling of Drosophila cells. Furthermore, the retained DNA synthetic activity and some examples of mitotic figures of both types of nuclei in the heterokaryons indicate the viability of the fused cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appels, R., Tallroth, D. M., Appels, D. M. & Ringertz, N. R., 1975. Differential uptake of protein into the chick nuclei of HeLa X chick erytrocyte heterokaryons. Expl Cell Res. 92: 70–79.
Becker, J. L., 1972. Fusions in vitro de cellules somatiques en culture de Drosophila melanogaster induites par la concanavaline. C. r. Acad. Sci. 275: 2969–2972.
Bernhard, H. P., 1976. Drosophila cells: fusion of somatic cells by Polythylene glycol. Experienta 32: 786 (abstract).
Crane, M. ST. J. & Dvorak, J. A., 1980. Vertebrate cells express protozoan antigen after hybridization. Science 208: 194–196.
Croce, C. M., Sawicki, W., Kritchevski, D. & Koprowski, H., 1971. Induction of homokaryocyte, heterokaryocyte and hybrid formation by lysolecithin. Expl. Cell Res. 67: 427–435.
Davidson, R. L., O'Malley, K. A. & Whealer, T. B., 1976. Polythylene glycol induced mammalian cell hybridization: effect of polythylene glycol molecular weight and concentration. Somatic Cell Genetics 2: 271–280.
Davidson, R. L. & Gerald, P. S., 1977. Induction of mammalian somatic cell hybridization by, polythylene glycol. In: M., Prescott (ed.) Methods in cell biology, vol. 15. New York, San Fransisco, London. Academic Press: 325–338.
Echalier, G., 1971. Established diploid cell lines of Drosophila melanogaster as potential material for the study of genetics of somatic cells. In: E., Weiss (ed.), Current Topics in Microbiology and immunology, vol. 55. Springer, Berlin-Heidelberg-New York: 226–227.
Echalier, G. & Ohanessian, A., 1970. In vitro culture of Drosophila melanogaster cells. In vitro 6: 162–172.
Engel, E., McGee, B.I. & Harris, H., 1969. Cytogenetic and nuclear studies on A9 and B82 cells fused together by Sendai virus: the early phase. J. Cell Sci. 5: 93–119.
Hadlacky, GY., Burg, K., Maroy, P. & Dudits, D., 1980. DNA synthesis and division in interkingdom heterokaryons. In vitro 16: 647–650.
Halfer, C. & Petrella, L., 1976. Cell fusion induced by lysolecithin and conacavalin A in Drosophila melanogaster somatic cells cultured in vitro. Expl Cell Res. 100: 399–404.
Halfer, C., Privitera, E. & Barigozzi, C., 1980. A study of spontaneous chromosome variations in seven cell lines derived from Drosophila melanogaster stocks marked by translocations. Chromosoma 76: 201–218.
Johnson, R. T. & Harris, H., 1969. DNA synthesis and mitosis in fused cells. II. HeLa-chick erythrocytes heterokaryons. J. Cell Sci. 5: 625–643.
Kao, F. T. (1973). Identification of chick chromosomes in cell hybrids formed between chick erytrocytes and adenine-requiring mutants of chinese hamster cells. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 70: 2893–2898.
Lima de Faria, A., Eriksson, T. & Kjellen, L., 1977. Fusion of human cells with Haplopappus protoplast by means of Sendai virus. Hereditas 87: 57–66.
Makajima, S. & Miyake, T., 1978. Cell fusion between temperature sensitive mutants of Drosophila melanogaster cell line. Somatic Cell Genetics 4: 131–141.
Mastrangelo, I. A. & Mitra, J., 1981. Chinese hamster ovary chromosomes and antigens in tobacco/hamster heterokaryons. J. Heredity 72: 81–86.
Mukherjee, A. B. & Cohen, M. M., 1969. The development of DNA containing nuclear bridges in human cells. Can. J. Genet. Cytol. 11: 317–324.
Nii, S. & Kamahora, J., 1963. High frequency appearance of amitotic nuclear division in PS cells induced by herpes simplex virus. Biken Journal 6: 33–35.
Norwood, TH. H. & Zeigler, C. J., 1977. Complementation between senescent human diploid cells and thymidine kinase-deficient murine cell line. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 19: 355–367.
Norwood, TH.H. & Zeigler, C.J., 1982. The use of dimethyl sulfoxide in mammalian cell fusion. In: J. W. Shaw (ed.) Techniques in somatic cell genetics. Plenum Press: 35–45.
Raskó, I., Péter, S. L., Burg, K., Dallmann, L. & Bajszár, G., 1979. Pattern of segregation of chicken HPRT phenotype in chinese hamster-chick red blood cell hybrids. Cytogenet. Cell. Genet. 24: 129–137.
Rassoulzadegan, M., Binetruy, B. & Cuzin, F., 1982. High frequency of gene transfer after fusion between bacteria and eurokaryotic cells. Nature 295: 275–259.
Ringertz, M. R. & Savage, E., 1976. Cell hybrids. Acad. Press New York.
Rizki, R. M., Rizki, T. M. & Andrews, C. A., 1975. Drosophila cell fusion induced by wheat germ agglutinin. J. Cell Sci. 18: 113–121.
Schwartz, A. G., Cook, P. R. & Harris, H., 1971. Correction of a genetic defect in a mammalian cell. Nature New Biology 230: 5–7.
Steplewski, Z., Koprowski, H. & Leibovitz, A., 1976. Polyethylene glycol mediated fusion of human tumor cells with mouse cells. Somatic Cell Genetics 2: 559–564.
Szpirer, C., 1974. Reactivation of chick erytrocyte nuclei in heterokaryons with rat hepatoma cells. Expl Cell Res. 83: 47–54.
Wyss, C., 1979. TAM selection of Drosophila somatic cell hybrids Somatic Cell Genetics 5: 29–37.
Zepp, H. D., Conover, J. H., Hirschhorn, K. & Hodes, H. L., 1971. Human-mosquito somatic hybrids induced by ultraviolet inactivated Sendai virus. Nature New Biology 229: 119–121.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Halfer, C., Del Pin, D. & Dell'Oro, A. Fusion between human and Drosophila melanogaster cells induced by polyethylene glycol. Genetica 75, 173–187 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00123572
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00123572