Summary
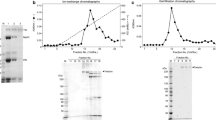
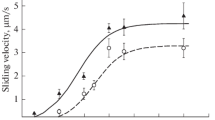
Light chain binding domains of rabbit skeletal, turkey gizzard and scallop myosin comprised of equimolar amounts of a short heavy chain fragment, essential light chain, and regulatory light chain have been obtained following extensive tryptic digestion. These complexes that are analogous to the regulatory domain prepared previously from scallop myosin by digestion with clostripain resist proteolysis due to the mutual protection of the heavy chain and the light chains, and are common structural features of the myosins studied. Specific Ca2+-binding by the regulatory domains reflects the behaviour of intact myosin; only scallop regulatory domain has a specific Ca2+-binding site. The heavy chain fragments of the different regulatory domains have been isolated under denaturing conditions and reconstituted with scallop essential light chain and scallop regulatory light chain or turkey gizzard regulatory light chain to yield regulatory domain hybrids. Hybrids containing the turkey gizzard regulatory light chain were used in Ca2+-binding studies since they were far more stable than their counterparts with the scallop regulatory light chain. The gizzard hybrid binds Ca2+ with a comparable specificity but somewhat lower affinity than native scallop regulatory domain. The rabbit regulatory domain hybrid also binds Ca2+, although with a reduced affinity and specificity. The results indicate that Ca2+-binding ability is determined by the light chains and modified by the heavy chains.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
ADELSTEIN, R. S. & EISENBERG, E. (1980) Regulation and kinetics of the actin-myosin-ATP interaction. Ann. Rev. Biochem. 49, 921–56.
CHALOVICH, J. M., CHANTLER, P. D., SZENT-GYÖRGYI, A. G. & EISENBERG, E. (1984) Regulation of molluscan actomyosin ATPase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 259, 2617–21.
CHANTLER, P. D. & SZENT-GYÖRGYI, A. G. (1980) Regulatory light-chains of scallop myosin: full dissociation reversibility and co-operative effects. J. Mol. Biol. 138, 473–92.
CHENEY, R. J. & MOOSEKER, M. J. (1992) Unconventional myosins. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 4, 27–35.
CROSS, R. A., CROSS, K. E. & SOBIESZEK, A. (1986) ATP-linked monomer-polymer equilibrium of smooth muscle myosin: the free folded monomer traps ADP.Pi. EMBO J. 5, 2637–41.
EDELHOCH, H. (1967) Spectroscopic determination of tryptophan and tyrosine in proteins. Biochem. 6, 1948–54.
FLICKER, P. F., WALLIMANN, T. & VIBERT, P. (1983) Electron microscopy of scallop myosin: location of regulatory light chains. J. Mol. Biol. 216, 723–41.
FOCANT, B. & HURIEUX, F. (1976) Light chains of carp and pike skeletal muscle myosins. Isolation and characterization of the most anodic light chain on alkaline pH electrophoresis. FEBS Lett. 65, 16–19.
FUNK, M. O., NAKAGAWA, Y., SKOCHDOPOLE, J. & KAISER, E. T. (1979) Affinity chromatographic purification of papain. Int. J. Peptide Protein Res. 13, 296–313.
JAKES, R., NORTHORP, F. & KENDRICK-JONES, J. (1976) Calcium binding regions of myosin ‘regulatory’ light chains. FEBS Lett. 70, 229–34.
JANSCO, A. & SZENT-GYÖRGYI, A. G. (1994) Regulation of scallop myosin by the regulatory light chain depends on a single glycine residue. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., in press.
KATOH, T. & LOWEY, S. (1989) Mapping myosin light chains by immunoelectron microscopy. Use of anti-fluorescyl antibodies as structural probes. J. Cell Biol. 109, 1549–60.
KENDRICK-JONES, J. (1974) Role of myosin light chains in calcium regulation. Nature 249, 631–4.
KENDRICK-JONES, J., SZENTKIRALYI, E. M. & SZENT-GYÖRGYI, A. G. (1976) Regulatory light chains in myosin. J. Mol. Biol. 104, 747–75.
KENDRICK-JONES, J., SMITH, R. C., CRAIG, R. & CITI, S. (1987) Polymerization of vertebrate non-muscle and smooth muscle myosins. J. Mol. Biol. 198, 244–52.
KWON, H., HELANDRI, F. D. & SZENT-GYÖRGYI, A. G. (1992) Role of gizzard myosin light chains in calcium binding. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 13, 315–20.
KWON, H., GOODWIN, E. B., NYITRAY, L., BERLINER, E., O'NEALLHENNESSEY, E., MELANDRI, F. D. & SZENT-GYÖRGYI, A. G. (1990) Isolation of the regulatory domain of scallop myosin: role of the essential light chain in calcium binding. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 4771–5.
LAEMMLI, U. K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the bacteriophage T4. Nature 227, 446–8.
LEAVIS, P. C. & GERGELY, J. (1984) Thin filament proteins and thin filament-linked regulation of vertebrate muscle contraction. CRC Crit. Rev. Biochem. 16, 235–305.
LOWEY, S., WALLER, G. S. & TRYBUS, K. M. (1993) Skeletal muscle myosin light chains are essential for physiological speeds of shortening. Nature 365, 454–6.
MATSUDAIRA, P. (1987) Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylene difluoride membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 262, 10035–8.
MOORE, R. L., HOUSTON, M. E., IWAMOTO, G. A. & STULL, J. T. (1985) Phosphorylation of rabbit skeletal muscle myosin in situ. J. Cell Physiol. 125, 301–5.
NYITRAY, L., GOODWIN, E. B. & SZENT-GYÖRGYI, A. G. (1991) Complete primary structure of a scallop striated muscle myosin heavy chain. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 18469–76.
ONISHI, H. & WAKABAYASHI, T. (1982) Electron microscopic studies of myosin molecules from chicken gizzard muscle: the formation of the intramolecular loop in the myosin tail. J. Biochem. 92, 871–9.
RAYMENT, I., RYPNIEWSKI, W. R., SCHMIDT-BASE, K., SMITH, R., TOMCHICK, D. R., BENNING, M. M., WINKELMANN, D.A., WESENBERG, G. & HOLDEN, H. M. (1993) Three dimensional structure of myosin subfragment-1: a molecular motor. Science 261, 50–8.
SCHOLEY, J. M., TAYLOR, K. A. & KENDRICK-JONES, J. (1981) The role of myosin light chains in regulating acti-myosin interactions. Biochimie 63, 255–71.
SEIDEL, J. C. (1980) Fragmentation of gizzard myosin by a-chymotrypsin and papain, the effects of ATPase activity, and the interaction with actin. J. Biol. Chem. 255, 4355–61.
SELLERS, J. R. (1985) Mechanisms of the phosphorylation dependent regulation of smooth muscle heavy meromyosin. J. Biol. Chem. 260, 15185–9.
SELLERS, J. R., EISENBERG, E. & ADELSTEIN, R.S. (1982) The binding of smooth muscle heavy meromyosin in the presence of ATP. J. Biol. Chem. 257, 13880–3.
SELLERS, J. R., PATO, M. D. & ADELSTEIN, R. S. (1981) Reversible phosphorylation of smooth muscle myosin, heavy meromyosin, and platelet myosin. J. Biol. Chem. 256, 13137–42.
SIMMONS, R. M. & SZENT-GYÖRGYI, A. G. (1980) Control of tension development in scallop muscle fibers with foreign regulatory light chains. Nature 286, 626–8.
SOBIESZEK, A. & BREMEL, R. D. (1975) Preparation of vertebrate smooth muscle myofibrils and actomyosin. Eur. J. Biochem. 55, 49–60.
STAFFORD, W. F., SZENTKIRALYI, E. M. & SZENT-GYÖGRYI, A. G. (1979) Regulatory properties of single-headed fragments of scallop myosin. Biochem. 18, 5273–80.
STREHLER, E. E., STREHLER-PAGE, M. A., PERRIAD, J. C., PERIASAMY, M. & NADAL-GINARD, B. (1986) Complete nucleotide and encoded amino acid sequence of a mammalian myosin heavy chain gene. Evidence against introndependent evolution of the rod. J. Mol. Biol. 190, 291–317.
SZENT-GYÖRGYI, A. G., SZENTKIRALYI, E. M. & KENDRICK-JONES, J. (1973) The light chains of scallop myosin as regulatory subunits. J. Mol. Biol. 74, 179–203.
SZENTKIRALYI, E. M. (1984) Tryptic digestion of scallop S1: evidence for a complex between the two light-chains and a heavy-chain peptide. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 5, 147–64.
TAKAHASHI, M., SOHMA, H. & MORITA, F. (1988) The steady state intermediate of scallop smooth muscle myosin ATPase and effect of light chain phosphorylation. A molecular mechanism for catch contraction. J. Biochem. 104, 102–7.
TRYBUS, K. M. & CHATMAN, T. A. (1993) Chimeric regulatory light chains as probes of smooth muscle myosin. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 4412–19.
TRYBUS, K. & LOWEY, S. (1988) The regulatory light chain is required for folding of smooth muscle myosin. J. Biol. Chem. 263, 16485–92.
TRYBUS, K. M., HUIATT, T. W. & LOWEY, S. (1982) A bent monomeric conformation of myosin from smooth muscle. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79, 6151–5.
XIE, X., HARRISON, D., SCHLICHTING, I., SWEET, R., KALABOKIS, V. N., SZENT-GYÖRGYI, A. G. & COHEN, C. (1994) Structure of the regulatory domain of scallop myosin at 2.8 Å resolution. Nature 368, 306–12.
WARRICK, H. M. & SPUDICH, J. A. (1987) Myosin structure and function in cell motility. Ann. Rev. Cell Biol. 3, 379–421.
WELLS, C., WARRINER, K. E. & BAGSHAW, C. R. (1985) Fluorescence studies on the nucleotide and Ca2+-binding domains of molluscan myosin. Biochem. J. 231, 31–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kalabokis, V.N., O'Neall-Hennessey, E. Regulatory domains of myosins: influence of heavy chain on Ca2+-binding. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 15, 547–553 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00121160
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00121160