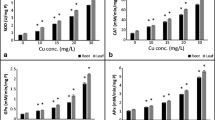
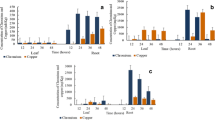
Copper uptake and toxicity were evaluated in Hydrilla verticillata. Its effect on lipid peroxidation, chlorophyll, protein, ascorbate, cysteine and sugars was studied at pH 6.8. Dose- and durationdependent uptake of Cu followed by a significant decrease in malondialdehyde and sugar content was found in plant tissue. Chlorophyll, ascorbic acid and protein contents were increased non-significantly up to 8, 16 and 32 þM Cu, respectively. Cysteine content was slightly increased at lower concentrations followed by a significant decline. At 80 þM Cu, plants of H. verticillata showed significant toxic effects after 168 h of exposure indicating the sensitivity of the plant to this level of Cu stress. The effect of low and high pH in combination with different concentrations of Cu was determined at 168 h of exposure. Low pH (4.5) enhanced Cu toxicity while at high pH (9.5) toxicity was considerably reduced.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnon D.I. (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplast. Polyphenol oxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol. 24, 1–15.
De Filippis L.F. (1979) The effect of heavy metal compounds on the permeability of Chlorella cells. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. Bd. 92, 39–49.
De Vos C.H.R., Vooijs R., Schat H. and Ernst W.H.O. (1989) Copper induced damage to permeability barrier in roots of Silene cucubalus. J. Plant Physiol. 135, 165–9.
De Vos C.H.R., Schat H., De Waal M.A.M., Vooijs R. and Ernst W.H.O. (1991) Increased resistance to copper-induced damage of the root cell plasmalemmna in copper tolerant Silene cucubalus. Physiol. Plant. 82, 523–8.
De Vos C.H.R., Vonk M.J., Vooijs R. and Schat H. (1992) Glutathione depletion due to copper-induced phytochelatin synthesis causes oxidative stress in Silene cucubalus. Plant Physiol. 98, 853–8.
Dubios N., Gilles K., Hamilton J.K., Rebers P.A. and Smith F. (1956) A calorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Ann. Chem. 28, 350–6.
Elstner E.F. (1982) Oxygen activation and oxygen toxicity. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 33, 73–96.
Flemming C.A. and Trevors J.T. (1989) Copper toxicity and chemistry in the environment. A review. Water Air Soil Pollut. 44, 143–58.
Gaitonde M.K. (1967) A spectrophotometric method for the direct determination of cysteine naturally occurring amino acids. Biochem. J. 104, 627–33.
Girotti A.G., Thomas J.P. and Jordan J.E. (1985) Inhibitory effect of zinc (II) on free radical lipid peroxidation in erythrocyte membranes. J. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 1, 395–401.
Gomez K.A. and Gomez A.A. (1984) Statistical Procedure for Agricultural Research. New York: John Wiley and Sons.
Guilizzoni P. (1991) The role of heavy metals and toxic materials in the physiological ecology of submerged macrophytes. Aquat. Bot. 41, 87–109.
Halliwell B. and Gutteridge J.M.C. (1984) Oxygen toxicity, oxygen radicals, transition metals and disease. Biochem. J. 219, 1–14.
Halliwell B. and Gutteridge J.M.C. (1990) Role of free radicals and catalytic metal ions in human disease. An overview. Method Enzymol. 186, 1–85.
Heath R.L. and Packer L. (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. I. Kinetics and stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 196, 385–95.
Jones G.J., Nichols P.D., Johns B. and Smith J.D. (1987) The effect of mercury and cadmium on the fatty acid and sterol composition of the marine diatom Asterionella glacialis Phytochemistry 26, 1343–8.
Kappus H. (1985) Lipid peroxidation: mechanisms, analysis, enzymology and biological relevance. In Sies H. ed. Oxidative stress, pp. 273–310. London: Academic Press.
Keller Th. and Schwger H. (1977) Air pollution and ascorbic acid. Eur. J. For. Pathol. 7, 338–50.
Kremer B. and Markham W. (1982) Primary metabolic effects of cadmium in the brown alga Laminaria saccharina. Zeitschrift. fur Plafenzenphysiol. 108, 125–30.
Kunert K.J. and Ederer M. (1985) Leaf aging and lipid peroxidation: the role of the antitoxidants vitamin C and E. Physiol. Plant. 65, 85–8.
Lee E.H.L., Jersey J.A., Gilford C. and Benett J. (1984) Differential ozone tolerance in soybean and snapbeans: analysis of ascorbic acid in O -3 susceptible and O -3 resistant cultivars by high-performance liquid chromatography. Environ. Exp. Bot. 24, 331–41.
Lowry O.H., Rosebrough N.J., Farr A.L. and Randall R.J. (1951) Protein measurement with folinphenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 193, 265–75.
Nishikimi M. and Yagi K. (1976) Oxidation of ascorbic acid and tocopherol by superoxide. In Hayashi O. and Asada K. eds. Biochemical and medical aspects of active oxygen, pp. 79–87. Tokyo: University Park Press.
Nussbaum S., Schmutz D. and Brunold C. (1988) Regulation of assimilatory sulfate reduction by cadmium in Zea mays. L. Plant Physiol. 88, 1407–10.
Overnell J. (1975) The effect of heavy metals on photosynthesis and loss of cell potassium in two species of marine algae, Dunaliella tertiolecta and Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Mar. Biol. 29, 99–103.
Pandolfini T., Gabbierlli R. and Comparini C. (1992) Nickel toxicity and peroxidase activity in seedings of Triticum aestivum L. Plant Cell Environ. 15, 719–25.
Prasad D.D. and Prasad A.R., (1987) Altered Đ-aminolevulenic acid metabolism by lead and mercury in germinating seedlings of Bajra (Pennisetum typhoideum). Plant Physiol. 127, 241–4.
Rai U.N. and Chandra P. (1992) Accumulation of copper, cadmium, manganese and iron by field population of Hydrodictyon reticulatum (Linn.) Lagerheim. Sci. Total Environ. 116, 203–11.
Rooney M.L. (1983) Ascorbic acid as a photoxidative inhibitor. Photochem. Photobiol. 38, 619–21.
Sandmann G. and Bo\:ger P. (1980) Copper-mediated lipid peroxidation processes in photosynthestic membranes. Plant Physiol. 66, 797–800.
Smith S., Peterson P.J. and Kwan K.H.M. (1989) Chromium accumulation, transport and toxicity in plants. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 24, 241–51.
Somashekariah B.V., Padmaja K. and Prasad A.R.K. (1992) Phytotoxicity of cadmium ions on germinating seedlings of mung bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Involvement of lipid peroxides in chlorophyll degradation. Physiol. Plant. 85, 85–9.
Sutton D.L. and Blackburn R.D. (1971) Uptake of copper in Hydrilla. Weed Res. 11, 47–53.
Thompson J.E., Legge R.L. and Barber R.F. (1987) The role of free radicals in senescence and wounding. New Phytol. 105, 317–44.
Wise R.R. and Naylor A.W. (1987) Chilling-enhanced photoxidation: evidence for the role of singlet oxygen and superoxide in the breakdown of pigments and endogenous antioxidants. Plant Physiol. 83, 278–82.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, M., Sinha, S. & Chandra, P. Copper-induced toxicity in aquatic macrophyte, Hydrilla verticillata: effect of pH. Ecotoxicology 5, 23–33 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00116321
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00116321