Abstract
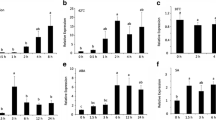
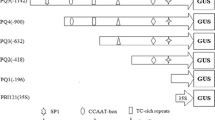
The gln-δ gene, which encodes the plastid-located glutamine synthetase of Phaseolus vulgaris, was cloned and its promoter region was sequenced. Primer extension analysis was used to map the two major transcription initiation sites which are about 90 nucleotides apart. A fusion of 2.3 kb of the upstream region of the gln-δ gene to the reporter gene uidA encoding β-glucuronidase was shown to be expressed in the chlorophyllous cell types of leaves and stems and in the root meristem region of transgenic tobacco. Analysis of a series of three 5′ promoter deletion fusions revealed the presence of a region essential for promoter activity between −786 and −327 and regions involved in tissue-specific regulation and light regulation between −786 and +43.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoyagi, K, Kuhlemeier, C, Chua, N-H: The pea rbcS-3A enhancer-like element directs cell-specific expression in transgenic tobacco. Mol Gen Genet 213: 179–185 (1988).
Benfey, PN, Ren, L, Chua, N-H: The CaMV 35S enhancer contains at least two domains which can confer different developmental and tissue-specific expression patterns. EMBO J 8: 2195–2202 (1989).
Bennett, MJ, Lightfoot, DA, Cullimore, JV: cDNA sequence and differential expression of the gene encoding the glutamine synthetase δ polypeptide of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Plant Mol Biol 12: 553–565 (1989).
Blackwell, RD, Murray, AJS, Lea, PJ: Inhibition of photosynthesis in barley with decreased levels of chloroplastic glutamine synthetase activity. J Exp Bot 38: 1799–1809 (1987).
Cock, JM, Brock, IW, Watson, AT, Swarup, R, Morby, AP, Cullimore, JV: Regulation of glutamine synthetase genes in leaves of Phaseolus vulgaris. Plant Mol Biol 17: 671–771 (1991).
Cullimore JV, Cock JM, Daniell TJ, Swarup R, Bennett MJ: Inducibility of the glutamine synthetase gene family of Phaseolus vulgaris L. In: Wray JL (ed) Biochemistry and Molecular Biology of Inducible Enzymes and Proteins in Higher Plants. Cambridge University Press (1991), in press.
Dupree, P, Pwee, K-H, Gray, JC: Expression of photosynthesis gene-promoter fusions in leaf epidermal cells of transgenic plants. Plant J 1: 115–120 (1991).
Edwards, JW, Walker, EL, Coruzzi, GM: Cell-specific expression in transgenic plants reveals non-overlapping roles for chloroplast and cytosolic glutamine synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 3459–3463 (1990).
Forde, BG, Cullimore, JV: Molecular biology of glutamine synthetase. Oxford Surv Plant Mol Cell Biol 6: 247–296 (1989).
Goodall, GJ, Filipowicz, W: The AU-rich sequences present in the introns of plant nuclear pre-mRNAs are required for splicing. Cell 58: 473–483 (1989).
Hemon, P, Robbins, MP, Cullimore, JV: Targeting of glutamine synthetase to the mitochondria of transgenic tobacco. Plant Mol Biol 15: 895–904 (1990).
Horsch, RB, Fry, JE, Hoffman, NL, Eichholtz, D, Rogers, SG, Fraley, RT: A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants. Science 227: 1229–1231 (1985).
Jefferson, RA, Kavanagh, TA, Bevan, MW: GUS fusions: β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6: 3901–3907 (1987).
Lightfoot, DA, Green, NK, Cullimore, JV: The chloroplast-located glutamine synthetase of Phaseolus vulgaris L.: nucleotide sequence, expression in different organs and uptake into isolated chloroplasts. Plant Mol Biol 11: 191–202 (1988).
Miflin, BJ: The location of nitrate reductase and other enzymes related to amino acid biosynthesis in the plastids of roots and leaves. Plant Physiol 54: 550–555 (1974).
Murashige, T, Skoog, F: A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue culture. Plant Physiol 15: 473–497 (1962).
Sambrook, J, Fritsch, E, Maniatis, T: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1989).
Sanger, F, Miklen, S, Coulson, AR: DNA sequencing with chain terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 5463–5467 (1977).
Shen, W-J, Forde, BG: Efficient transformation of Agrobacterium spp. by high voltage electroporation. Nucl Acids Res 17: 8385 (1989).
Wallsgrove, RM, Turner, JC, Hall, NP, Kendall, AC, Bright, SWJ: Barley mutants lacking chloroplastic glutamine synthetase-biochemical and genetic analysis. Plant Physiol 83: 155–158 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cock, J.M., Hémon, P. & Cullimore, J.V. Characterization of the gene encoding the plastid-located glutamine synthetase of Phaseolus vulgaris: regulation of β-glucuronidase gene fusions in transgenic tobacco. Plant Mol Biol 18, 1141–1149 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00047717
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00047717