Abstract
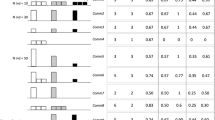
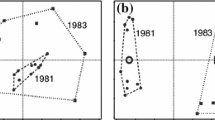
Gradients in beta diversity and species richness cause different forms of distortion in reciprocal averaging ordinations. Detrended correspondence analysis largely removes the beta diversity effect and reduces, but does not eliminate, the influence of species richness.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austin, M. P. & Noy-Meir, I., 1972. The problem of non-linearity in ordination: experiments with two-gradient models. J. Ecol. 59: 763–774.
Dargie, T. C. D., 1979. A numerical analysis of semi-arid vegetation in S.E. Spain. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Sheffield.
Dargie, T. C. D., 1984. On the integrated interpretation of indirect site ordinations: a case study using semi-arid vegetation in southeastern Spain. Vegetatio 55: 37–55.
Gauch, H. G.Jr., Whittaker, R. H. & Wentworth, T. R., 1977. A comparative study of reciprocal averaging and other ordination techniques. J. Ecol. 65: 157–174.
Hill, M. O., 1973. Reciprocal averaging: an eigenvector method of ordination. J. Ecol. 61: 237–251.
Hill, M. O., 1974. Correspondence analysis: a neglected multivariate technique. Appl. Statist. 23: 340–354.
Hill, M. O., 1979. DECORANA — a FORTRAN program for detrended correspondence analysis and reciprocal averaging. Ecology and Systematics, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York 14850. 52 pp.
Hill, M. O. & Gauch, H. G.Jr., 1980. Detrended correspondence analysis: an improved ordination technique. Vegetatio 42: 47–58.
Peet, R. K., Glenn-Lewin, D. G. & Wolf, J. W., 1983. Prediction of man's impact on plant species diversity: a challenge for vegetation science. In: W., Holzner, M. J. A., Werger & I., Ikusima (eds), Man's Impact on Vegetation, pp. 41–54. Junk, The Hague.
Swan, J. M. A., 1970. An examination of some ordination problems by use of simulated vegetational data. Ecology 51: 89–102.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dargie, T.C.D. Species richness and distortion in reciprocal averaging and detrended correspondence analysis. Vegetatio 65, 95–98 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00044879
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00044879