Abstract
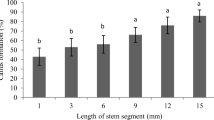
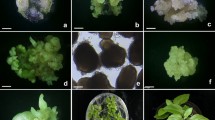
For 18 sugarcane cultivars, four distinct callus types developed on leaf explant tissue cultured on modified MS medium, but only Type 3 (embryogenic) and Type 4 (organogenic) were capable of plant regeneration. Cell suspension cultures were initiated from embryogenic callus incubated in a liquid medium. In stage one the callus adapted to the liquid medium. In stage two a heterogeneous cell suspension culture formed in 14 cultivars after five to eight weeks of culture. In stage three a homogeneous cell suspension culture was developed in six cultivars after 10 to 14 weeks by selective subculturing to increase the proportion of actively dividing cells from the heterogeneous cell suspension culture. Plants were regenerated from cell aggregates in heterogeneous cell suspension cultures for up to 148 days of culture but plants could not be regenerated from homogeneous cell suspension cultures. High yields of protoplasts were obtained from homogeneous cell suspension cultures (3.4 to 5.2 × 106 protoplasts per gram fresh weight of cells [gfwt-1]) compared to heterogeneous cell suspension cultures (0.1 × 106 protoplasts gfwt-1). Higher yields of protoplasts were obtained from homogeneous cell suspension cultures for cultivars Q63 and Q96 after regenerating callus from the cell suspension cultures, then recycling this callus to liquid medium (S-cell suspension cultures). This process increased protoplast yield to 9.4 × 106 protoplasts gfwt-1. Protoplasts isolated from S-cell suspension cultures were regenerated to callus and recycled to produce SP-cell suspension cultures yielding 6.4 to 13.2 × 106 protoplasts gfwt-1. This recycling of callus to produce S-cell suspension cultures allowed protoplasts to be isolated for the first time from cell lines of cultivars Q110 and Q138.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdullah R, Cocking EC & Thompson JA (1986) Efficient plant regeneration from rice protoplasts through somatic embryogenesis. Bio/Technology 4: 1087–1090
Chen WH, Davey MR, Power JB & Cocking EC (1988a) Control and maintenance of plant regeneration in sugarcane callus cultures. J Exp Bot 39: 251–261
Chen WH, Davey MR, Power JB & Cocking EC (1988b) Sugarcane protoplasts: factors affecting division and plant regeneration. Plant Cell Rep 7: 344–347
Fitch M (1986) N6 medium for long-term regeneration of friable, embryogenic callus cultures. Hawaii Sugar Plant Assoc Exp Stn Ann Rep 1985: 7–8
Fromm N, Taylor LP & Walbot V (1985) Expression of genes transferred into monocot and dicot plant cells by electroporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci, USA 82: 5824–5828
Guiderdoni E (1986) Culture in vitro de cellules et de protoplastes de canne à sucre (Saccharum sp.) L'Agron Trop 40: 309–314
Ho WJ & Vasil IK (1983a) Somatic embryogenesis in sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) I. The morphology and physiology of callus formation and the ontogeny of somatic embryos. Protoplasma 118: 169–180
Ho WJ & Vasil IK (1983b) Somatic embryogenesis in sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) Growth and plant regeneration from embryogenic cell suspension cultures. Ann Bot 51: 719–726
Kao KN & Michayluk MR (1975) Nutritional requirements for growth of Vicia hajastana cells and protoplasts at a very low population density in liquid media. Planta 126: 105–100
Lee L, Schroll RE, Grimes HD & Hodges TK (1989) Plant regeneration from indica rice (Oryza sativa L.) protoplasts. Planta 178: 325–333
Lührs R & Lörz H (1988) Initiation of morphogenic cell suspension and protoplast cultures of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Planta 175: 71–81
Ogura H, Kyozuka J, Hayashi Y, Koba T & Shimamoto K (1987) Field performance and cytology of protoplast derived rice (Oryza sativa L.). High yield and low degree of variation of four japonica cultivars. Theor Appl Genet 74: 670–676
Rhodes CA, Lowe KS & Ruby KL (1988) Plant regeneration from protoplasts isolated from embryogenic maize cell cultures. Bio/Technology 6: 56–60
Srinivasan C & Vasil IK (1986) Plant regeneration from protoplasts of sugarcane (Saccharum officinarum L.) J Plant Physiol 126: 41–48
Thompson JA, Abdullah R & Cocking EC (1986) Protoplast culture of rice (Oryza sativa L.) using media solidified with agarose. Plant Sci 47: 123–133
Vasil V & Vasil IK (1980) Isolation and culture of cereal protoplasts. Part 2: Embryogenesis and plantlet formation from protoplasts of Pennisetum americanum. Theor Appl Gen 56: 97–99
Vasil V & Vasil IK (1984) Isolation and culture of embryogenic protoplasts of cereals and grasses. In: Vasil IK (Ed) Cell Culture and Somatic Cell Genetics of Plants, Vol 1 (pp 398–403). Academic Press, New York, London
Vasil V, Redway F & Vasil IK (1990) Regeneration of plants from embryogenic suspension culture protoplasts of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Bio/Technology 8: 429–434
Wang HB, Li XH, Sun YR, Chen J Zhu Z, Fang R, Wang P & Wei JK (1990) Culture of wheat protoplast — high frequency microcolony formation and plant regeneration. Sci China (Series B) 33: 294–302
Wildholm JM (1972) The use of fluorescein diacetate and phenosafranine for determining viability of cultured plant cells. Stain Technol 47: 189–194
Yamada Y, Yang ZQ & Tang DT (1986) Plant regeneration from protoplasts — derived callus of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Plant Cell Rep 5: 85–88
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taylor, P.W.J., Ko, HL., Adkins, S.W. et al. Establishment of embryogenic callus and high protoplast yielding suspension cultures of sugarcane (Saccharum spp. hybrids). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 28, 69–78 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00039917
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00039917