Summary
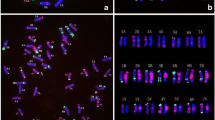
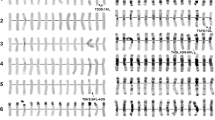
A Giemsa-C-banded karyotype of a partial amphiploid, Triticum turgidum L. var. durum cv. ‘Nodak’ × Agropyron intermedium (Host) P.B., called MT-2, was analyzed. MT-2 is a winterhardy grasslike octoploid germplasm which survived 5 winters in Montana, and its seed weight is 3 times that of A. intermedium seed. The MT-2 C-banding karyotype shows 6 chromosome pairs each of the A and B wheat genomes with 3A and 4B missing. Chromosomes 1B and 2B are involved in a reciprocal homozygous translocation (T1BS·2BS, T1BL·2BL) which was also confirmed by a nucleolus-associated quadrivalent in an MT-2 × durum wheat backcross. In addition to the wheat chromosomes, MT-2 consistently shows 16 A. intermedium chromosome pairs which are designated from A to P. These chromosomes show C-banding patterns similar to those reported earlier in the literature. A large amount of C-banding polymorphism and structural rearrangements in A. intermedium itself presently make a definite chromosome assignment to the homeologous groups of the Triticeae difficult. The data presented are crucial for further directed manipulation of this germplasm aimed at producing valuable chromosome additions and substitutions in wheat.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aizatulina, K.H.S., G.L. Yachevskaya & T.P. Pereladova, 1989. Study of the genome structure of Agropyron intermedium (Host) Beauv. Tsitolog. Genet. 23: 15–22.
Brettell, R.I.S., P.M. Banks, Y. Cauderon, X. Chen, Z.M. Chen, P.J. Larkin & P.M. Waterhouse, 1988. A single wheatgrass chromosome reduces the concentration of barley yellow dwarf virus in wheat. Ann. Appl. Biol. 113: 599–603.
Cauderon, Y., 1966. Etude cytogénétique de l'évolution du matérial issu de croisement entre Triticum aestivum et Agropyron intermedium. Ann. Amélior. Plantes 16: 43–70.
Cauderon, Y., B. Saigne & M. Dauge, 1973. The resistance to wheat rusts of Agropyron intermedium and its use in wheat improvement. Proc. 4th Intern. Wheat Genet. Symp., Columbia, Missouri, USA, pp. 401–407
Dewey, D.R., 1960. Salt tolerance of 25 strains of Agropyron. Agron. J. 52: 631–635.
Dewey, D.R., 1984. The genomic system of classification as a guide to intergeneric hybridization with the perennial Triticeae. pp. 209–280. In: J.P. Gustafson (Ed.) Gene manipulation in plant improvement, Plenum, New York.
Forster, B.P., S.M. Reader, S.A. Forsyth, R.M.D. Koebner, T.E. Miller, M.D. Gale & Y. Cauderon, 1987. An assessment of the homology of six Agropyron chromosomes added to wheat. Genet. Res. 50: 91–97.
Friebe, B., Y. Mukai, H.S. Dhaliwal, T.J. Martin & B.S. Gill, 1991. Identification of alien chromatin specifying resistance to wheat streak mosaic virus and greenbug in wheat germplasm by C-banding and in situ hybridization. Theor. Appl. Genet. 81: 381–389.
Friebe, B., Y. Mukai, B.S. Gill & Y. Cauderon, 1992a. Chromosome and genome analysis by C-banding and in situ hybridization of Agropyron intermedium, a partial wheat × A. intermedium amphiploid, and six chromosome addition lines. Theor. Appl. Genet. 83: 775–782.
Friebe, B., F.J. Zeller, Y. Mukai, B.P. Forster, P. Bartos & R.A. McIntosh, 1992b. Characterization of rust-resistant wheat Agropyron intermedium derivatives by C-banding, in situ hybridization and isozyme analysis. Theor. Appl. Genet. 83: 775–782.
Gill, B.S., B. Friebe & T.R. Endo, 1991. Standard karyotype and nomenclature system for description of chromosome bands and structural aberrations in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Genome 34: 830–839.
Knott, D.R., 1968. Agropyron as a source of rust resistance in wheat breeding. Proc. 3rd Intern. Wheat Genet. Symp., Canberra, pp. 204–212
Littlejohn, G.M., 1988. Salt tolerance of amphiploids and derivatives of crosses between wheat and wild Thinopyrum speciess. 7th Intern. Wheat Genet. Symp., Cambridge, England, pp. 845–849.
McGuire, P.E. & J. Dvořák, 1981. High salt tolerance potential in wheatgrasses. Crop Sci. 21: 701–705.
Schlegel, G. & R. Schlegel, 1989. A compendium of reciprocal intervarietal translocations in hexaploid wheat. Kulturpflanze 37: 163–176.
Schulz-Schaeffer, J., 1970. The Triticum × Agropyron hybridization project at Montana State University. Wheat Inf. Serv. 30: 26–29.
Schulz-Schaeffer, J., 1989. Registration of Montana-4 annual hexaploid Agrotriticum germplasm. Crop Sci. 29: 1098.
Schulz-Schaeffer, J. & S.E. Haller, 1987. Registration of Montana-2 perennial XAgrotriticum intermedium Khizhnyak. Crop Sci. 27: 822–823.
Schulz-Schaeffer, J. & S.E. Haller, 1988. Alien chromosome addition in durum wheat. II. Advanced progeny. Genome 30: 303–306.
Schulz-Schaeffer, J. & F.H. McNeal, 1977. Alien chromosome addition in wheat. Crop Sci. 17: 891–896.
Sears, E.R., 1952. Misdivision of univalents in common wheat. Chromosoma 4: 535–550.
Sharma, H.C., B.S. Gill & J.K. Uyemoto, 1984. High level of resistance in Agropyron species to barley yellow dwarf and wheat streak mosaic virus. Phytopath. Z. 119: 143–147.
Smith, D.C., 1942. Intergeneric hybridization of cereals and other grasses. J. Agric. Res. 64: 33.
Smith, L., 1947. The acetocarmine smear technique. Stain Tech. 22: 17–31.
Suneson, C.A. & W.K. Pope, 1946. Progress with Triticum × Agropyron crosses in California. J. Amer. Soc. Agron. 38: 956–963.
Vinall, H.N. & M.A. Hein, 1937. Breeding miscel aneous grasses. pp. 1032–1102. Yearb. Agric. USDA. U.S. Government Print. Off., Washington, DC.
Wagoner, P., 1989. Study of intermediate wheatgrass as a perennial grain crop. 1988 Research Summary, Rodale Press, Emmaus, PA.
Wagoner, P., 1990. Perennial grain development: past efforts and potential for the future. Critical Rev. Plant Sci. 9: 381–409.
Wienhues, A., 1966. Transfer of rust resistance of Agropyron to wheat by addition, substitution, and translocation. Proc. 2nd Int. Wheat Genet. Symp., Lund, Sweden. Hereditas (suppl. 2): 328–341.
Xin, Z.Y., R.I.S. Brettell, Z.M. Cheng, P.M. Waterhouse, R. Appels, P.M. Banks, G.H. Zhou, X. Chen & P.J. Larkin, 1988. Characterization of a potential source of barley yellow dwarf virus resistance for wheat. Genome 30: 250–257.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
contribution No. J-2767 from Montana Agric. Exp. Stn.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schulz-Schaeffer, J., Friebe, B. Karyological characterization of a partial amphiploid, Triticum turgidum L. var. durum × Agropyron intermedium (Host) P.B.. Euphytica 62, 83–88 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00037932
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00037932