Abstract
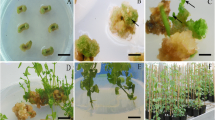
Calli from hypocotyl and root explants of Digitalis obscura L. showed regeneration of adventitious shoots, roots and embryos when transferred to Murashige & Skoog medium supplemented with cytokinins alone or in combination with auxins. Optimum shoot-bud formation was achieved in the presence of IAA and BA, while roots mainly appeared either in absence of growth regulators or with IAA and Kn. Embryo formation took place only in those combinations that included Kn. Embryo development was influenced by the type of auxin, and precocious germination occurred in media with NAA. Mechanically isolated cells from hypocotyl- and root-derived calli were plated in MS medium supplemented with several IAA and BA combinations. Single cells were able to proliferate forming callus within 20–30 days in culture. In order to induce organogenesis, calli were transferred to various regeneration media. Shoot-bud differentiation efficiency depended on both callus origin and medium initially used for cell culture, best results being obtained in calli grown from hypocotyl-derived cells cultured in the presence of casein hydrolysate. A further subculture to medium containing coconut milk and lower concentrations of NH4NO3 and sucrose promoted shoot development. Rooting was readily achieved upon transferring shoots onto half-strength MS medium. Plantlets were ultimately established in soil.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BA:
-
benzyladenine
- BM:
-
basal medium
- CH:
-
casein hydrolysate
- CM:
-
coconut milk
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- IAA:
-
indoleacetic acid
- Kn:
-
kinetin
- MS:
-
Murashige & Skoog
- NAA:
-
naphthaleneacetic acid
References
Ammirato PV (1985) Patterns of development in culture. In: Henke RR, Hughes KW, Constantin MJ, Hollaender A (Eds) Tissue Culture in Forestry and Agriculture (pp 9–29). Plenum Press, New York
Arrillaga I, Brisa MC, Segura J (1986) Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration from hypocotyl cultures of Digitalis obscura L. J. Plant Physiol 124: 425–430
Bergmann L (1960) Growth and division of single cells of higher plants in vitro. J Gen Physiol 43: 841–851
Brisa MC, Segura J (1987) Isolation, culture and plant regeneration from mesophyll protoplasts of Digitalis obscura. Physiol Plant 69: 680–686
Dougall DK (1987) Cell cloning and the selection of high yielding strains. In: Constabel F, Vasil IK (Eds) Cell Culture and Somatic Cell Genetics of Plants, Vol 4 (pp 117–124). Academic Press, New York
Haccius B (1978) Question of unicellular origin of nonzygotic embryos in callus cultures. Phytomorphol 28: 74–81
Halperin W (1986) Attainment and retention of morphogenetic capacity in vitro. In: Vasil IK (Ed) Cell Culture and Somatic Cell Genetics of Plants, Vol 3 (pp 3–47). Academic Press, Orlando
Lapeña L, Perez-Bermudez P, Segura J (1988) Morphogenesis in hypocotyl cultures of Digitalis obscura: influence of carbohydrate levels and sources. Plant Sci 57: 247–252
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassay with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15: 473–497
Perez-Bermudez P, Cornejo MJ, Segura J (1983) In vitro propagation of Digitalis obscura L. Plant Sci Lett 30: 77–82
Perez-Bermudez P, Brisa MC, Cornejo MJ, Segura J (1984) In vitro morphogenesis from excised leaf explants of Digitalis obscura L. Plant Cell Rep 3: 8–9
Perez-Bermudez P, Cornejo MJ, Segura J (1985) Pollen plant formation from anther cultures of Digitalis obscura L. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Culture 5: 63–68
Whitaker RJ, Hashimoto T (1986) Production of secondary metabolites. In: Evans DA, Sharp WR, Ammirato PV (Eds) Handbook of Plant Cell Culture, Vol 4 (pp 264–286). Macmillan Publ Co, New York
Yamada Y (1984) Selection of cell lines for high yields of secondary metabolites. In: Vasil IK (Ed) Cell Culture and Somatic Cell Genetics of Plants, Vol 1 (pp 629–636) Academic Press, Orlando
Zenk MH, El-Shagi H, Arens H, Stockigt J, Weiler EW, Deus B (1977) Formation of the indole alkaloids serpentine and ajmalicine in cell suspension cultures of Catharantus roseus. In: Barz W, Reinhard E, Zenk MH (Eds) Plant Tissue Culture and its Bio-technological Application (pp 27–43). Springer-Verlag, Berlin
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brisa, M.C., Segura, J. Morphogenic potential of mechanically isolated single cells from Digitalis obscura L. callus. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 19, 129–139 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00035812
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00035812