Abstract
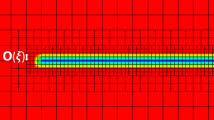
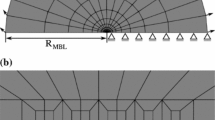
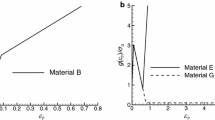
A finite element analysis is presented for quasi-statically steady crack growth in an elastic-viscoplastic material under Mode I, plane strain and small scale yielding conditions. The effects of material rate-sensitivity on the fields in the vicinity of the moving crack tip are examined. Our analysis employs a modified boundary layer formulation whereby the remote tractions are given by the first two-terms of elastic asymptotic stress field, characterized by K Iand T. When the physical coordinates are scaled by % MathType!MTEF!2!1!+-% feaafiart1ev1aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn% hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr% 4rNCHbGeaGak0dh9WrFfpC0xh9vqqj-hEeeu0xXdbba9frFj0-OqFf% ea0dXdd9vqaq-JfrVkFHe9pgea0dXdar-Jb9hs0dXdbPYxe9vr0-vr% 0-vqpWqaaeaabaGaciaacaqabeaadaqaaqaaaOqaaGqaciaa-Hcaca% WFlbWaaSbaaSqaaGqaaiaa+fdaaeqaaOGaai4laiabeo8aZnaaBaaa% leaacaaIWaaabeaakiaacMcadaahaaWcbeqaaiaaikdaaaaaaa!3ECA!\[(K_1 /\sigma _0 )^2 \], where % MathType!MTEF!2!1!+-% feaafiart1ev1aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn% hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr% 4rNCHbGeaGak0dh9WrFfpC0xh9vqqj-hEeeu0xXdbba9frFj0-OqFf% ea0dXdd9vqaq-JfrVkFHe9pgea0dXdar-Jb9hs0dXdbPYxe9vr0-vr% 0-vqpWqaaeaabaGaciaacaqabeaadaqaaqaaaOqaaiabeo8aZnaaBa% aaleaacaaIWaaabeaaaaa!3A07!\[\sigma _0 \] is the tensile yield stress, the near-tip fields over a wide range of stress triaxialities are members of a family of self-similar solutions parameterized by % MathType!MTEF!2!1!+-% feaafiart1ev1aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn% hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr% 4rNCHbGeaGak0dh9WrFfpC0xh9vqqj-hEeeu0xXdbba9frFj0-OqFf% ea0dXdd9vqaq-JfrVkFHe9pgea0dXdar-Jb9hs0dXdbPYxe9vr0-vr% 0-vqpWqaaeaabaGaciaacaqabeaadaqaaqaaaOqaaGqaciaa-rfaca% WFVaGaeq4Wdm3aaSbaaSqaaiaa-bdaaeqaaaaa!3B8E!\[T/\sigma _0 \]. Members of this family are found to collapse into a single near-tip distribution when the physical coordinates are normalized by a characteristic length L g, which is a significant fraction of the plastic zone length directly ahead of the crack tip. This distribution depends only on the relative crack speed given by the dimensionless number % MathType!MTEF!2!1!+-% feaafiart1ev1aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn% hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr% 4rNCHbGeaGak0dh9WrFfpC0xh9vqqj-hEeeu0xXdbba9frFj0-OqFf% ea0dXdd9vqaq-JfrVkFHe9pgea0dXdar-Jb9hs0dXdbPYxe9vr0-vr% 0-vqpWqaaeaabaGaciaacaqabeaadaqaaqaaaOqaaGqaciaa-zfaca% WFVaGaa8hkaiaa-XeadaWgaaWcbaGaa83zaaqabaacciGccuGFiiIZ% gaGaamaaBaaaleaacaaIWaaabeaakiaacMcaaaa!3EB2!\[V/(L_g \dot \in _0 )\] where V is the crack speed and % MathType!MTEF!2!1!+-% feaafiart1ev1aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn% hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr% 4rNCHbGeaGak0dh9WrFfpC0xh9vqqj-hEeeu0xXdbba9frFj0-OqFf% ea0dXdd9vqaq-JfrVkFHe9pgea0dXdar-Jb9hs0dXdbPYxe9vr0-vr% 0-vqpWqaaeaabaGaciaacaqabeaadaqaaqaaaOqaaGGaciqb-HGioB% aacaWaaSbaaSqaaiaaicdaaeqaaaaa!39D6!\[\dot \in _0 \] is the material's viscoplastic strain rate at a reference stress. Near-tip field distributions are obtained for several values of % MathType!MTEF!2!1!+-% feaafiart1ev1aaatCvAUfeBSjuyZL2yd9gzLbvyNv2CaerbuLwBLn% hiov2DGi1BTfMBaeXatLxBI9gBaerbd9wDYLwzYbItLDharqqtubsr% 4rNCHbGeaGak0dh9WrFfpC0xh9vqqj-hEeeu0xXdbba9frFj0-OqFf% ea0dXdd9vqaq-JfrVkFHe9pgea0dXdar-Jb9hs0dXdbPYxe9vr0-vr% 0-vqpWqaaeaabaGaciaacaqabeaadaqaaqaaaOqaaGqaciaa-zfaca% WFVaGaa8hkaiaa-XeadaWgaaWcbaGaa83zaaqabaacciGccuGFiiIZ% gaGaamaaBaaaleaacaaIWaaabeaakiaacMcaaaa!3EB2!\[V/(L_g \dot \in _0 )\] and material strain rate sensitivity, m. Our results show that strong material rate sensitivity and high crack speed elevate the stress level ahead of the moving crack tip.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N.P. O'Dowd and C.F. Shih, Family of Crack-Tip Fields Characterized by a Triaxiality Parameter — I. Structure of Fields, Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 39 (1991) 989–1015.
N.P. O'Dowd and C.F. Shih, Family of Crack-Tip Fields Characterized by a Triaxiality Parameter — II. Fracture Applications. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 40 (1992) 939–963.
C. Betegón, and J.W. Hancock, Two Parameter Characterization of Elastic-Plastic Crack Tip Fields. Journal of Applied Mechanics 58 (1991) 104–110.
N.P. O'Dowd, C.F. Shih and R.H. Dodds, Jr., The Role of Geometry and Crack Growth on Constraint and Implications for Ductile/Brittle Fracture, Constraint Effects in fracture, Theory and Applications, ASTM STP 1244, M. Kirk and A. Bakker, (eds.), American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadephia, (1995) 134–159.
R.H. Dodds, M., Jr. Tang and T.L. Anderson, Effects of Prior Tearing on Cleavage Fracture Toughness in the Transition Region, Constraint Effects in Fracture, Theory and Applications, ASTM STP 1244 M. Kirk and A. Bakker, Eds., American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadephia, (1995) 100–133.
L. Xia and C.F. Shih, Ductile Crack Growth — I. A Numerical Study Using Computational Cells with Microstructurally-Based Length Scales. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 43 (1995) 233–259.
A. G. Varias and C.F. Shih, Quasi-Static Crack Advance Under A Range of Constraints - Steady-State Fields Based on a Characteristic Length. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 41 (1993) 835–861.
A.G. Varias and C.F. Shih, Dynamic Steady Crack Growth in Elastic-Plastic Solids - Propagation of Strong Discontinuities. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 42 (1995) 1817–1848.
J.W. Hutchinson, Singular Behavior at the End of a Tensile Crack in a Hardening Material. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 16 (1968) 13–31.
J.R. Rice and G.F. Rosengren, Plane Strain Deformation Near a Crack Tip in a Power Law Hardening Material. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 16 (1968) 1–12.
L. Xia, C.F. Shih and J.W. Hutchinson, A Computational Approach to Ductile Crack Growth under Large Scale Yielding Conditions. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 43 (1995) 389–413.
X. Gao, C.F. Shih, V. Tvergaard and A. Needleman, Constraint Effects on the Ductile-Brittle Transition in Small Scale Yielding. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 44 (1996) 1255–1282.
L. Xia and C.F. Shih, Ductile Crack Growth — III. Transition to Cleavage Fracture Incorporating Statistics. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 44 (1996) 603–639.
L.B. Freund and J.W. Hutchinson. High Strain-Rate Crack Growth in Rate-Dependent Plastic Solids. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 33 (1985) 169–191.
R.J. Clifton, High Strain Rate Behavior of Metals. Applied Mechanics Reviews 43 (1990) S9-S22.
D. Pierce, C.F. Shih and A. Needleman, A Tangent Modulus Method for Rate Dependent Solid. Computer & Structure 18 (1984) 875–887.
M.L. Williams, On the Stress Distribution at the Base of a Stationary Crack. Journal of Applied Mechanics 24 (1957) 109–114.
R.H. Dean and J.W. Hutchinson, Quasi-Static Steady Crack Growth in Small-Scale Yielding, Fracture Mechanics: Twelfth Conference, ASTM STP 700, American Society for Testing and Materials, (1980) 383–405.
D.M. Parks, P.S. Lam and R.M. McMeeking, Some effects of Inelastic Constitutive Models on Crack Tip Fields in Steady Quasistatic Growth, Advances in Fracture Research, 5th Int. Conf. on Frac., D. Francois, Ed., Cannes, France, 5 (1981) 2607–2614.
C.F. Shih, N.P. O'Dowd and M.T. Kirk, A Framework for Quantifying Crack Tip Constraint, Constraint Effects in Fracture, ASTM STP 1171. E.M. Hackett, K.-H Schewalbe, and R.H. Dodds, Eds., American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, (1993) 2–20.
W.J. Drugan, J.R. Rice and T.-L. Sham, Asymptotic Analysis of Growing Plane Strain Tensile Cracks in Elastic-Ideally Plastic Solids. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 30 (1982) 447–473.
K.C. Hwang and X.F. Luo, Near-Tip Fields of Growing Cracks and Resistance Curves. Mechanics of Materials 7 (198) 271–278.
R.O. Ritchie, J.F. Knott and J.R. Rice, On the Relationship between Critical Tensile Stress and Fracture Toughness in Mild Steel. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 21 (1973) 395–410.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xia, L., Cheng, L. Quasi-statically steady crack growth in rate dependent solids-one-parameter field encompassing different constraints. Int J Fract 82, 97–114 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00034658
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00034658