Abstract
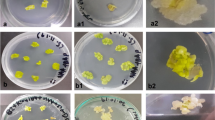
Single and multiple infections of carrot discs were carried out with Agrobacterium strains harbouring different segments of pRi1855 TL-DNA cloned in the binary vector Bin 19 and with a strain carrying the TR-DNA from the same Ri plasmid. Roots induced by the various co-inoculations were cultured and their growth patterns were followed. Abundant roots could be induced by TL-DNA rol genes A, B and C as a single insert (rolA+B+C) and by rolB alone provided an extended segment beyond its 5′ noncoding region was included in the construction. A depression of rooting capability was caused by the inclusion of rolC together with rolB (rolB+C). In all cases co-inoculation with the Agrobacterium carrying TR-DNA-borne auxin genes was necessary for root induction since none of the rol constructions was in itself capable of eliciting any response; an exceeding majority of these roots were however shown to contain rol genes but no TR-DNA. Rooting was also elicited if rol constructions were co-inoculated with a strain carrying TL-DNA genes 13 and 14 (ORF13+14) instead of the TR-DNA strain. These roots were shown to contain both rol genes and ORF13+14. Striking differences in growth properties were shown by roots containing different complements of TL-DNA genes. Typical hairy root traits, high growth rate, branching and, most noticeably, absence of geotropism, were shown by roots containing rolB alone, while roots with rolA+B+C were geotropic as normal carrot roots. Hairy root traits were conferred to rolA+B+C roots by the concomitant presence of ORF13+14 and by the addition of auxin to the culture medium. A model is presented which attempts to rationalize the growth patterns by assigning interplaying roles to the various TL-DNA genes involved.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Elliot C: Manual of Bacterial Plant Pathogens, 2nd rev. ed. Chronica Botanica, Waltham, MA (1951).
Chilton MD, Tepfer DA, Petit A, David C, Casse-Delbart F, Tempé J: Agrobacterium rhizogenes inserts T-DNA into the genome of host plant root cells. Nature 295: 432–434 (1982).
White FF, Ghidossi G, Gordon MP, Nester EW: Tumor induction by Agrobacterium rhizogenes involves the transfer of plasmid DNA to the plant genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79: 3193–3197 (1982).
Willmitzer L, Sanchez-Serrano J, Buschfeld E, Schell J: DNA from Agrobacterium rhizogenes is transferred to and expressed in axenic hairy root plant tissues. Mol Gen Genet 186: 16–22 (1982).
Spanò L, Pomponi M, Costantino P, VanSlogteren GMS, Tempé J: Identification of T-DNA in the root-inducing plasmid of the agropine type Agrobacterium rhizogenes 1855. Plant Mol Biol 1: 291–300 (1982).
David C, Chilton MD, Tempé J: Conservation of T-DNA in plants regenerated from hairy root cultures. Biotechnology 2: 73–76 (1984).
White FF, Taylor BH, Huffman GA, Gordon MP, Nester EW: Molecular and genetic analysis of the transferred DNA regions of the root inducing plasmid of Agrobacterium rhizogenes. J Bacteriol 164: 33–34 (1985).
Slightom JL, Durand-Tardif M, Jouanin L, Tepfer D: Nucleotide sequence analysis of TL-DNA of Agrobacterium rhizogenes agropine type plasmid: identification of open-reading frames. J Biol Chem 261: 108–121 (1986).
DePaolis A, Mauro ML, Pomponi M, Cardarelli M, Spanò L, Costantino P: Localization of agropine synthesizing functions in the TR region of the root inducing plasmid of Agrobacterium rhizogenes 1855. Plasmid 13: 1–7 (1985).
Cardarelli, Spanò L, Mariotti D, Mauro ML, Costantino P: The role of auxin in hairy root induction. Mol Gen Genet 208: 457–463 (1987).
Cardarelli M, Mariotti D, Pomponi M, Spanò L, Capone I, Costantino P: Agrobacterium rhizogenes T-DNA genes capable of inducing hairy root phenotype. Mol Gen Genet 209: 475–480 (1987).
Vilaine F, Charbonnier C, Casse-Delbart: Further insight concerning the TL region of the Ri plasmid of Agrobacterium rhizogenes strain A4: transfer of a 1.9 kb fragment is sufficient to induce transformed roots on tobacco leaf fragments. Mol Gen Genet 210: 111–115 (1987).
Spena A, Schmulling T, Koncz C, Schell J: Independent and synergistic activity of rol A, B and C loci in stimulating abnormal growth in plants. EMBO J 6: 3891–3899 (1987).
Spanò L, Mariotti D, Cardarelli M, Branca C, Costantino P: Morphogenesis and auxin sensitivity of transgenic tobacco with different complements of Ri T-DNA. Plant Physiol 87: 479–483 (1988).
Schmulling T, Schell J, Spena A: Single genes from Agrobacterium rhizogenes influence plant development. EMBO J 7: 2621–2629 (1988).
Sinkar VP, Pythoud F, White FF, Nester EW, Gordon MP: rol A locus of the Ri plasmid directs developmental abnormalities in transgenic tobacco plants. Genes and Develop 2: 688–697 (1988).
Shen WH, Petit A, Guern J, Tempé J: Hairy roots are more sensitive to auxin than normal roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 3417–3421 (1988).
Hooykaas PJJ, Klapwijck P, Nuti MP, Schilperoort RA, Rorsch A: Transfer of the Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid to avirulent Agrobacteria and to Rhizobium enplanta. J Gen Microbiol 98: 477–484 (1977).
Pomponi M, Spanò L, Sabbadini MG, Costantino P: Restriction endonuclease mapping of the root-inducing plasmid of Agrobacterium rhizogenes 1855. Plasmid 10: 119–129 (1983).
Bevan M: Agrobacterium vectors for plant transformation. Nucleic Acids Res 12: 8711–8721 (1984).
Petit A, David C, Dahl G, Ellis GJ, Guyon P, Casse-Delbart F, Tempé J: Further extention of theopine concept: plasmids in Agrobacterium rhizogenes cooperate for opine degradation. Mol Gen Genet 190: 204–214 (1983).
Capone I, Cardarelli M, Trovato M, Costantino P: Upstream non-coding region which confers polar expression to Ri plasmid root inducing gene rolB. Mol Gen Genet, in press.
Durand-Tardif M, Broglie R, Slightom J, Tepfer D: Structure and expression of Ri T-DNA from Agrobacterium rhizogenes in Nicotiana tabacum: organ and phenotypic specificity. J Mol Biol 186: 557–564 (1986).
Petit A, Berkaloff A, Tempé J: Multiple transformation of plant cells by Agrobacterium may be responsible for the complex organization of T-DNA in crown gall and hairy roct. Mol Gen Genet 190: 204–214 (1986).
Filetici P, Spanò L, Costantino P: Conserved regions in the T-DNA of different Agrobacterium rhizogenes root-inducing plasmids. Plant Mol Biol 9: 19–26 (1987).
Brevet J, Tempé J: Homology mapping of T-DNA regions of three Agrobacterium rhizogenes Ri plasmids by electron microscope heteroduplex studies. Plasmid 19: 75–83 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Capone, I., Spanò, L., Cardarelli, M. et al. Induction and growth properties of carrot roots with different complements of Agrobacterium rhizogenes T-DNA. Plant Mol Biol 13, 43–52 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00027334
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00027334