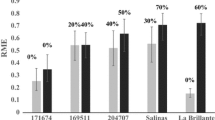
Summary
Resistance to lettuce mosaic virus (LMV) is derived either from cv. Gallega (g gene) or the wild accession PI251245 (mo gene). Previous studies indicated that these two genes were identical. Breeders in Europe produced numerous resistant cultivars utilisingg while in the USAmo was used. The resistance has been effective for over 20 years. However, recently there have been reports of LMV isolates causing unusually severe and sometimes necrotic symptoms on cultivars with these resistance genes. Investigations of these ‘severe’ isolates have distinguished three new pathotypes in addition to the common pathotype (II) and identified a novel dominant gene for resistance. Themo/g genes confer resistance to pathotypes I and II but pathotype III possesses virulence for cultivars withg but not for those withmo. These two genes are therefore not identical but are probably either closely linked genes or alleles. Pathotype IV possesses virulence for all lettuce lines so far tested. Some isolates of this pathotype are seed transmitted in cultivars possessingmo org and have caused severe crop losses in southern France. The durability of the resistance conditioned by these two genes is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dinant, S. & H., Lot, 1992. Lettuce mosaic virus: a review. Plant Pathol. 41: 528–542.
Kyriakopoulou, P.E., 1985. A lethal strain of lettuce mosaic virus in Greence. Phytoparasitica 13: 271.
Pink, D.A.C., D., Kostova & D.G.A., Walkey, 1992. Differentiation of pathotypes of lettuce mosaic virus. Plant Pathol. 41: 5–12.
Ryder, E.J., 1968. Evaluation of lettuce varieties and breeding lines for resistance to common lettuce mosaic. USDA Tech. Bull. 1391, 8 pp
Ryder, E.J., 1970. Inheritance of resistance to common lettuce mosaic. J. Amer. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 95: 378–379.
Ryder, E.J., 1973. Seed transmission of LMV in mosaic resistant lettuce. J. Amer. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 98: 610–614.
Ryder, E.J., 1976. The nature of resistance to LMV. Eucarpia Meeting of Leafy Vegetables, Wageningen, Holland 15–18 March.
Tomlinson, J.A., 1962. Control of lettuce mosaic by the use of healthy seed. Plant. Pathol. 11: 61–64.
Tomlinson, J.A., 1970. Lettuce mosaic virus. CMI/AAB Descriptions of Plant Viruses No. 9.
Von der, Pahlen, A. & J., Crnko, 1965. El virus del mosaico de la lechuga (Marmer lactucae) en Menoza y Buenos Aires. Rev. Invest. Agropecuarias 11: 25–31.
Walkey, D.G.A., C.M., Ward & K., Phelps, 1985. Studies on lettuce mosaic virus resistance in commercial lettuce cultivars. Plant Pathol. 34: 545–551.
Walkey, D.G.A., A.A., Allubaishi & J.W., Webb, 1990. Plant virus diseases in the Yemen Arab Republic. Tropical Disease Management 36: 195–206.
Zink, F.W., J.E., Duffus & K.A., Kimble, 1973. Relationship of a non-lethal reaction to a virulent isolate of lettuce mosaic virus and turnip mosaic susceptibility in lettuce. J. Amer. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 98: 41–45.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pink, D.A.C., Lot, H. & Johnson, R. Novel pathotypes of lettuce mosaic virus — breakdown of a durable resistance?. Euphytica 63, 169–174 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023921
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00023921