Abstract
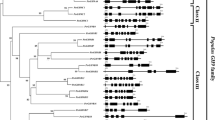
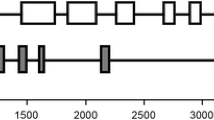
Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) genes and cDNA sequences have so far been isolated from a broad range of angiosperm but not from gymnosperm species. We constructed a cDNA library from seedlings of Norway spruce (Picea abies) and identified cDNAs coding for PEPC. A full-length PEPC cDNA was sequenced. It consists of 3522 nucleotides and has an open reading frame (ORF) that encodes a polypeptide (963 amino acids) with a molecular mass of 109 551. The deduced amino acid sequence revealed a higher similarity to the C3-form PEPC of angiosperm species (86–88%) than to the CAM and C4 forms (76–84%). The putative motif (Lys/Arg-X-X-Ser) for serine kinase, which is conserved in all angiosperm PEPCs analysed so far, is also present in this gymnosperm sequence. Southern blot analysis of spruce genomic DNA under low-stringency conditions using the PEPC cDNA as a hybridization probe showed a complex hybridization pattern, indicating the presence of additional PEPC-related sequences in the genome of the spruce. In contrast, the probe hybridized to only a few bands under high-stringency conditions. Whereas this PEPC gene is highly expressed in roots of seedlings, a low-level expression can be detected in cotyledons and adult needles. A molecular phyiogeny of plant PEPC including the spruce PEPC sequence revealed that the spruce PEPC sequence is clustered with monocot and dicot C3-form PEPCs including the only dicot C4 form characterized so far.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albert HA, Martin T, Sun SSM: Structure and expression of a sugarcane gene encoding a housekeeping phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase. Plant Mol Biol 20: 663–671 (1992).
Bachmann B, Lüke W, Hunsmann G: Improvement of PCR amplified DNA sequencing with the aid of detergens. Nucl Acids Res 18: 1309 (1990).
Bandurski RS, Greiner CM: The enzymatic synthesis of oxaloacetate from phosphoenolpyruvate and carbon dioxide. J Biol Chem 204: 781–786 (1953).
Bauer S, Galliano H, Pfeiffer F, Meßner B, Sandermann H, Ernst D: Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone encoding a novel short-chain alcohol dehydro- genase from Norway spruce (Picea abies L. Karst.). Plant Physiol 103: 1479–1480 (1993).
Birnboim HC, Doly J: A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucl Acids Res 7: 1513–1523 (1979).
Bousquet J, Strauss SH, Doerksen AH and Price RA: Extensive variation in evolutionary rate of rbcL gene sequences among seed plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 7844–7848 (1992).
Cavener DR, Stuart CR: Eukaryotic start and stop translation sites. Nucl Acids Res 19: 3185–3192 (1991).
Chardot TP, Wedding R: Role of cysteine in activation and allosteric regulation of maize phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase. Plant Physiol 98: 780–783 (1992).
Chomczynski P: One-hour downward alkaline capilary transfer for blotting of DNA and RNA. Anal Biochem 201: 134–139 (1992).
Clapham DH, vonArnold S, Dormling I Ekberg I, Eriksson G, Larsson C-T, Norrell L, Qamaruddin M: Variation in total and specific RNA during inwintering of two contrasting populations of Picea abies. Physiol Plant 90: 504–512 (1994).
Crétin C, Santi S, Keryer E, Lepiniee L, Tagu D, Vidal J, Gadal P: The phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene family of Sorghum: promotor structures, amino acid sequences and expression of genes. Gene 99: 87–94 (1991).
Cushman JC, Meyer G, Michalowski CB, Schmitt JM, Bohnert HJ: Salt stress leads to differential expression of two isogenes of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase during crassulacean acid metabolism induction in the common ice plant. Plant Cell 1: 715–725 (1989).
Cushman JC, Bohnert HJ: Nucleotide sequence of the ppc2 gene encoding a house-keeping isoform of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from Mesembryanthemum crystallinum. Nucl Acids Res 17: 6743–6744 (1989).
Cushman JC, Bohnert HJ: Nucleotide sequence of a gene encoding a CAM specific isoform of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from Mesembryanthemum crystallinum Nucl Acids Res 17: 6745–6746 (1989).
Duff SMG, Chollet R: In vivo regulation of wheat-leaf phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase by reversible phosphorylation. Plant Physiol 107: 775–782 (1995).
Eikmanns BJ, Follettie MT, Griot MU, Sinskey AJ: The phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene of Corynebacterium glutamicum Mol Gen Genet 218: 330–339 (1989).
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B: A technique for radiolabelling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132: 6–13 (1983).
Felsenstein J: Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39: 783–791 (1985).
Fujita N, Miwa T, Ishijama K, Katsuki H: The primary structure of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase of E. coli J Biochem 95: 909–916 (1984).
Galliano H, Cabané M, Eckerskorn C, Lottspeich F, Sandermann H, Ernst D: Molecular cloning, sequence analysis and elicitor-l ozone-induced accumulation of cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase from Norway spruce (Picea abies L.). Plant Mol Biol 23: 145–156 (1993).
Hermans J, Westhoff P: Homologous genes for the C4 isoform of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in a C3 and a C4 Flaveria species. Mol Gen Genet 234: 275–284 (1992).
Hudspeth RL, Glackin CA, Bonner J, Grula JW: Genomic and and cDNA clones for maize phosphenolpyruvate carboxylase and pyruvate, orthophosphate dikinase: Expression of different genes-family members in leaves and roots. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 2884–2888 (1986).
Izui K, Ishijima S, Yamaguchi Y, Katagiri F, Murata T, Shigesata K, Sugiyama T, Katsuki H: Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA encoding active phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase of the C4-pathway from maize. Nucl Acids Res 14: 1615–1628 (1986).
Jiao JA, Chollet R: Regulatory phosphorylation of serine-15 in maize phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase by a C4-leaf protein-serine kinase. Arch Biochem Biophys 283: 300–305 (1990).
Katagiri F, Kodaki T, Fujita N, Izui K, Katsuki H: Nucleotide sequence of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene of the cyanobacterium Anacystis nidulans. Gene 38: 265–269 (1985).
Kawamura T, Shigesada K, Toh H, Okumura S, Yanagisawa S, Izui K: Molecular evolution of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase for C4 photosynthesis in maize: Comparison of its cDNA sequence with a newly isolated cDNA encoding an isozyme involved in the anaplerotic function. J Biochem 112: 147–154 (1992).
King BJ, Layzell DB, Canvin DT: The role of dark carbon dioxide fixation in root nodules of soybean. Plant Physiol 81: 200–205 (1986).
Koizumi N, Sato F, Terano Y, Yamada Y: Sequence analysis of cDNA encoding phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from cultured tobbacco cells. Plant Mol Biol 17: 535–539 (1991).
Kozak M: Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eukaryotes and organelles. Microbiol Rev 47: 1–45 (1983).
Kozak M: Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucl Acids Res 12: 857–872 (1984).
Kozak M: Selection of initiation sites by eukaryotic ribosomes: effect of inserting AUG triplets upstream from the coding sequence for preproinsulin. Nucl Acids Res 12: 3873–3893 (1984).
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M: Mega: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis, Version 1.0. The Pennsylvania State University, Stata University, PA 16802, USA.
Kvarnheden A Tandre K, Engström P: A cdc2 homologue and related processed retropseudogenes from Norway spruce. Plant Mol Biol 27: 391–403 (1995).
Latzko E, Kelly GJ: The many-faceted function of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in C3 plants. Physiol Vég 21: 805–815 (1983).
Lepiniec L; Santi S, Kéryer E, Amiet V, Vidal J, Gadal P, Crétin C: Complete nucleotide sequence of one member of the Sorghum phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene family. Plant Mol Biol 17: 1077–1079 (1991).
Lepiniec L, Kéryer E, Philippe H, Gadal P, Crétin C: Sorghum phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene family: structure function and molecular evolution. Plant Mol Biol 21: 487–502 (1993).
Lepiniec L, Vidal J, Chollet R, Gadal P, Crétin P: Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase: structure, regulation and evolution. Plant Sci 99: 111–124 (1994).
Lütcke HA, Chow KC, Mickel FS, Moss KA, Kern HF, Scheele GA: Selection of AUG initiation codons differ in plants and animals. EMBO J 6: 43–48 (1987).
Luinenburg I, Coleman JR: Identification, characterization and sequence analysis of the gene encoding phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in Anabaena sp. PCC7120. J Gen Microbiol 138: 685–691 (1992).
Mac Kay JJ, Liu W, Whetten R, Sederoff RR and O'Malley DM: Genetic analysis of cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase in loblolly pine: single gene inheritance, molecular characterization and evolution. Mol Gen Genet 247: 537–545 (1995).
Martin F, Chemardin M, Gadal P: Nitrate assimilation and nitrogen circulation in Austrian pine. Physiol Plant 53: 105–110 (1981).
Martin W, Lydiate D, Brinkmann H, Forkmann G, Saedier H and Cerff R: Molecular phylogenies in angiosperm evolution. Mol Biol Evol 10: 140–162 (1993).
Matsuoka M, Hata S: Comparative studies of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase from C3 and C4 plants. Plant Physiol 85: 947–951 (1987).
Merkelbach S, Gehlen J, Denecke M, Hirsch H-J, Kreuzaler F: Cloning, sequence analysis and expression of a cDNA encoding active phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase of the C3 plant Solanum tuberosum Plant Mol Biol 23: 881–888 (1993).
Murray MG, Thompson WF: Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucl Acids Res 8: 4321–4325 (1980).
O'Reagan M, Thierbach G, Bachmann B, Villeval D, Lepage P, Viret J-F, Lemoine Y: Cloning and nucieotide sequence of the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase-coding gene of Corynebacterium glutamicum ATCC13032. Gene 77: 237–251 (1989).
Pasternak JJ, Glick BR: Molecular evolutionary analyses of the small and large subunits of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. Can J Bot 70: 715–723 (1992).
Pathirana SM, Vance CP, Miller SS, Gantt JS: Aflalfa nodule phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase: characterization of the cDNA and expression in effective and plant-controlled ineffective nodules. Plant Mol Biol 20: 437–450 (1992).
Relle M, Sutter A, Wild A: A method to isolate cDNA-quality RNA from adult conifer needles and a psbA cDNA from Norway spruce. J Plant Physiol 149: 225–228 (1996).
Rosendahl L, Vance CP, Pedersen WB: Products of dark CO2 fixation in pea root nodules support bacteroid metabolism. Plant Physiol 93: 12–19 (1990).
Saitou N, Nei M: the neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4 406–425 (1987).
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1989).
Schuller KA, Werner D: Phosphorylation of soybean (Glycine max L.) nodule phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in vitro decreases sensivity to inhibition by L-malate. Plant Physiol 101: 1267–1273 (1993).
Schulz M, Hunte C, Schnabl H: Multiple forms of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in mesophyll, epidermal and guard cells of Vicia faba. Physiol Plant 86: 315–321 (1992).
Sugiharto B, Nakamoto H, Sasakawa H, Sugiyama T: Regulation of expression of carbon-assimilating enzymes by nitrogen in maize leaf. Plant Physiol 92: 963–969 (1990).
Sugimoto T, Kawasaki T, Kato T, Whittier RF, Shibata D, Kawamura Y: cDNA sequence and expression of a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase gene from soybean. Plant Mol Biol 20: 743–747 (1992).
Sundås A, Tandre K, Holmstedt E, Engström P: Differential gene expression during germination and after the induction of adventitious bud formation in Norway spruce embryos. Plant Mol Biol 18: 713–724 (1992).
Toh H, Kawamura T, Izui K: Molecular evolution of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase. Plant Cell Envir 17: 31–43 (1994).
Thompson JD, Higgins DG, Gibson TJ: Clustal W: Improving the sensivity of progressive multiple sequence alignment through sequence weighting, position-specific gap penalties and weight matrix choice. Nucl Acids Res 22: 4673–4680 (1994).
Troitsky AV, Melekhovets YF, Rakhimova GM, Bobrova VK, Valiejo-Roman KM, Antonov AS. Angiosperm origin and early stages of seed plant evolution deduced from rRNA sequence comparisons. J Mol Evol 32: 253–261 (1991).
Wingler A, Einig W, Schaeffer C, Wallenda T, Hampp R, Wallander H, Nylund J-E: Influence of different nutrient regimes on the regulation of carbon metabolism in Norway spruce [Picea abies (L.) Karst.] seedlings. New Phytol 128: 323–330 (1994).
Woese CR: Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev 51: 221–271 (1987).
Yang D, Oyaizu Y, Oyaizu H, Olsen GJ, Woese CR: Mitochondrial origins. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82: 4443–4447 (1985).
Yokoyama S, Harry DE: Molecular phylogeny and evolutionary rates of alcohol dehydrogenases in vertebrates and plants. Mol Biol Evol 10: 1215–1226 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Relle, M., Wild, A. Molecular characterization of a phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase in the gymnosperm Picea abies (Norway spruce). Plant Mol Biol 32, 923–936 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00020489
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00020489