Abstract
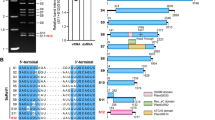
Molecular cloning of 30 cDNAs and subsequent characterization of the corresponding SRP RNA from four cultivars of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) revealed altogether 14 sequence variants, which could be ordered into six groups. The expression of five representatives from these groups was examined by reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) in different cultivars and different tissues. Although one cultivar-specific SRP RNA variant could be detected in the leaf SRP RNA population, identical SRP RNA populations seem to be present in the four different cultivars as well as in different tissues, such as leaves, flowers, fruits, stems and roots. Sequence comparison revealed that several variants might have evolved by recombination of two different SRP RNA sequences. On the basis of five SRP RNA variants, the current secondary structure model was refined and a new conserved structural element was detected. Comparative sequence analysis of domain II from all known SRP RNA homologues reveals a remarkable conservation of this element. As demonstrated previously, the corresponding area overlaps with a region that interact with the SRPp68/p72 heterodimer and/or with ribosomes. Based on structural and functional considerations, we propose that the domain IV structure together with the highly conserved area of domain II constitutes the essential core of the SRP RNA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amasino RM: Acceleration of nucleic acid hybridization rate by polyethylene glycol. Anal Biochem 152: 304–307 (1986).
Andreazzoli M, Gerbi SA: Changes in 7SL RNA conformation during signal recognition particle cycle. EMBO J 10: 767–777 (1991).
Brennwald PJ, Liao X, Holm K, Porter G, Wise JA: Identification of an essential Schizosaccharomyces pombe RNA homologous to the 7SL component of signal recognition particle. Mol Cell Biol 8: 1580–1590 (1988).
Brennwald PJ, Siegel V, Walter P, Wise JA: Sequence and structure of Tetrahymena SRP RNA. Nucl Acids Res 19: 1942 (1991).
Campos N, Palau J, Torrent M, Ludevid D: Signal recognition-like particles are present in maize. J Biol Chem 263: 9646–9650 (1988).
Campos N, Palau J, Zwieb C: Diversity of 7SL RNA from signal recognition particle of maize endosperm. Nucl Acids Res 17: 1573–1588 (1989).
Chung CT, Miller RA: Rapid and convenient method for the preparation and storage of competent bacterial cells. Nucl Acids Res 16: 3580 (1988).
Collasius M, Falk H, Ciesler C, Valet G: How to build an inexpensive cyclotherm instrument for automated polymerase chain-reaction. Anal Biochem 181: 163–166 (1989).
Devereux J: The GCG Sequence analysis software package, Version 7.0. Genetics Computer Group (GCG), University Research Park, Madison, WI 53711 (1991).
Fox G, Woese CR: 5S secondary structure. Nature 256: 505–507 (1975).
Haas B, Klanner A, Ramm K, Sänger HL: The 7S RNA from tomato leaf tissue resembles a signal recognition particle RNA and exhibits a remarkable sequence complementarity to viroids. EMBO J 7: 4063–4074 (1988).
Hann BC, Walter P: The signal recognition particle in S. cerevisiae. Cell 67: 131–144 (1991).
He F, Beckerich JM, Gaillardin C: A mutant of 7SL RNA in Yarrowia lipolytica affecting the synthesis of a secreted protein. J Biol Chem 267: 1932–1937 (1992).
James BD, Olson G, Pace N: Phylogenetic comparison of RNA secondary structure. Meth Enzymol 180: 227–239 (1989).
Krieg UC, Walter P, Johnson AE: Photocrosslinking of the signal sequence of nascent preprolactin to the 54-kilodalton polypeptide of the signal recognition particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 8604–8608 (1986).
Kurzchalia TV, Wiedmann M, Girshovich AS, Bochkareva ES, Bielka H Rapoport TA: The signal sequence of nascent preprolactin interacts with the 54K polypeptide of the signal recognition particle. Nature 320: 634–636 (1986).
Larsen N, Zwieb C: SRP-RNA sequence alignment and secondary structure. Nucl Acids Res 19: 209–215 (1991).
Liao X, Brennwald P, Wise JA: Genetic analysis of Schizosaccharomyces pombe RNA: a structural motif that induces a conserved tetranucleotide loop is important for function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 4137–4141 (1989).
Liao X, Selinger D, Althoff S, Chiang A, Hamilton D, Ma M, Wise JA: Random mutagenesis of Schizosaccharomyces pombe SRP RNA: lethal or conditional lesions cluster in presumptive protein binding sites. Nucl Acids Res 20: 1607–1615 (1992).
Marques JP, Gualberto JM, Palme K: Sequence of the Arabidopsis thaliana 7SL RNA gene. Nucl Acids Res 21: 3581 (1993).
Marshallsay C, Prehn S, Zwieb C: cDNA cloning of the wheat germ SRP 7S RNAs. Nucl Acids Res 17: 1771 (1989).
Mühlbach H-P, Sänger HL: Multiplication of cucumber pale fruit viroid in oculated tomato leaf protoplasts. J Gen Virol 35: 377–386 (1977).
Noller HF: Structure of ribosomal RNA. Ann Rev Biochem 55: 119–162 (1984).
Noma Y, Sideras P, Naito T, Bergstedt-Lindquist S, Azuma C, Severinson E, Tanabe T, Kinashi T, Matsuda F, Yaoita Y, Honjo T: Cloning of cDNA encoding the murine IgG1 induction factor by a novel strategy using SP6 promoter. Nature 319: 640–646 (1986).
Öfverstedt L-G, Hammarström K, Balgobin N, Hjerten S, Pettersson U, Chattopadhyaya J: Rapid and quantitative recovery of DNA fragments from gels by displacement electrophoresis (isotachophoresis). Biochim Biophys Acta 782: 120–126 (1984).
Okayama H, Berg P: High-efficiency cloning of full-length cDNA. Mol Cell Biol 2: 161–170 (1982).
Poritz M A, Siegel V, Hansen W, Walter P: Small ribonucleoproteins in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Yarrowia lipolytica homologous to signal recognition particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 4315–4319 (1988).
Poritz MA, Strub K, Walter P: Human SRP RNA and E. coli 4.5S RNA contain a highly homologous structural domain. Cell 55: 4–6 (1988).
Poritz MA, Bernstein HD, Strub K, Zopf D, Wilhelm H, Walter P: An E. coli ribonucleoprotein containing 4.5 S RNA resembles mammalian signal recognition particle. Science 250: 1111–1116 (1990).
Prehn S, Wiedmann M, Rapoport TA, Zwieb C: Protein translocation across wheat germ microsomal membranes requieres an SRP-like component. EMBO J 6: 2093–2097 (1987).
Rapoport TA: Transport of proteins across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Science 258: 931–936 (1992).
Ribes V, Römisch K, Giner A, Dobberstein B, Tollervey D: E. coli 4.5S RNA is part of a ribonucleoprotein particle that has properties related to signal recognition particle. Cell 63: 591–600 (1990).
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T: Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press. Cold Spring Harbor, NY (1989).
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR: DNA sequencing with chain termination inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci, USA 74: 5463–5467 (1977).
Selinger D, Liao X, Wise JA: Functional interchangeability of the structurally similar tetranucleotide loops GAAA and UUCG in fission yeast signal recognition particle RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 5409–5413 (1993).
Siegel V, Walter P: Removal of the Alu structural domain from signal recognition particle leaves its proteintranslocation activity intact. Nature 320: 81–84 (1986).
Siegel V, Walter P: Each of the activities of signal recognition particle (SRP) is contained within a distinct domain: analysis of biochemical mutants of SRP. Cell 52: 39–49 (1988).
Siegel V, Walter P: Binding sites of the 19-kda and 68/72-kda signal recognition particle (SRP) proteins on SRP RNA as determined by protein-RNA ‘footprinting’. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85: 1801–1805 (1988).
Stellwag ET, Dahlberg AE: Electrophoretic transfer of DNA, RNA and protein onto diazobenzylomethyl (DBM)-paper. Nucl Acids Res 8: 299–317 (1980).
Strub K, Moss J, Walter P: Binding sites of the 9- and 14-kilodalton heterodimeric protein subunit of the signal recognition particle (SRP) are contained exclusively in the Alu domain of the SRP RNA and contain a sequence motif that is conserved in evolution. Mol Cell Biol 11: 3949–3959 (1991).
Struck JCR, Toschka HY, Specht T, Erdmann VA: Common structural features between eukaryotic 7SL RNAs, eubacterial 4.5S RNA and scRNA and archaebacterial 7S RNA. Nucl Acids Res 16: 7740 (1988).
Symons B: Pathogenesis by antisense. Nature 338: 542–543 (1989).
Ullu E, Melli M: Cloning and characterization of cDNA copies of the 7S RNAs of HeLa cells. Nucl Acids Res 10: 2209–2223 (1982).
Ullu E, Weiner AM: Human genes and pseudogenes for the 7SL RNA component of signal recognition particle. EMBO J 3: 3303–3310 (1984).
Walter P, Blobel G: Purification of a membrane-associated protein complex requiered for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77: 7112–7116 (1980).
Walter P, Blobel G: Signal recognition particle contains a 7S RNA essential for protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum. Nature 299: 691–698 (1982).
Walter P, Blobel G: Disassembly and reconstitution of signal recognition particle. Cell 34: 525–533 (1983).
Walter P, Lingappa VR: Mechanism of protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Annu Rev Cell Biol 2: 499–516 (1986).
Wolin SL, Walter P: Signal recognition particle mediates a transient elongation arrest of preprolactin in reticulocyte lysate. J Cell Biol 109: 2617–2622 (1989).
Yanisch-Perron C, Vieira J, Messing J: Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequence of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 33: 103–119 (1985).
Zopf D, Bernstein HD, Walter P: GTPase domain of the 54-kD subunit of the mammalian signal recognition particle is required for protein translocation but not for signal sequence binding. J Cell Biol 120, 1113–1121 (1993).
Zuker M: On finding all suboptimal foldings of an RNA molecule. Science 244: 48–52 (1989).
Zwieb C, Schüler D: Low resolution three-dimensional models of the 7SL RNA of the signal recognition particle, based on an intramolecular cross-link introduced by mild irradiation with ultraviolet light. Biochem Cell Biol 67: 434–442 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riedel, L., Pütz, A., Hauser, MT. et al. Characterization of the signal recognition particle (SRP) RNA population of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum). Plant Mol Biol 27, 669–680 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00020221
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00020221