Abstract
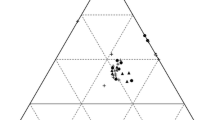
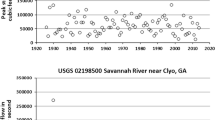
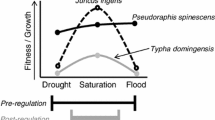
During 1993 the Upper Mississippi River System experienced floods of exceptional magnitude and duration, especially at its more downstream reaches. The flood had widespread effects on the vegetation. Submerged species such as Potamogeton pectinatus significantly decreased in abundance, especially at sites with more severe flooding. However, many species were able to regenerate in 1994 from seeds or storage organs. Emergent species such as Scirpus fluviatilis were similarly affected, but in the upstream reaches were able to regrow in the autumn following the flood and at many sites showed exceptionally high productivity in the following year, probably due to nutrient-rich sediment deposition by the flood. Many tree species were very severely impacted, although Acer saccharinum and Populus deltoides have shown some seedling regeneration on newly deposited sediment beneath stands of mature trees, which would have out-shaded the seedlings if they had not been killed by the flood.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barko, J. W. & R. M. Smart, 1983. Effects of organic matter additions to sediments on the growth of aquatic plants. J. Ecol 71: 161–175.
Chen, Y. H. & D. B. Simons, 1986. Hydrology, hydraulics, and geomorphology of the Upper Mississippi River System. Hydrobiologia 136: 5–20.
Coutts, M. P. & W. Armstrong, 1976. Role of oxygen transport in the tolerance of trees to waterlogging. In Cannell, M. G. R. & F. T. Last (eds), Tree Physiology and Yield Improvement. Academic Press, London: 361–385.
Dieterman, D., 1993. Major river survey. Backwaters of the Mississippi River, Pools 3, 5, 5A & 6. Minnesota Department of Natural Resources, Division of Fish & Wildlife, 14.
Goolsby, D. A., W. A. Battaglin & E. M. Thruman, 1993. Occurrence and transport of agricultural chemicals in the Mississippi River basin, July through August 1993. United States Geological Survey Circular 1120-C. pp 22.
IFMRC (Interagency Floodplain Management Review Committee), 1994. Sharing the Challenge: Floodplain Management into the 21st Century. US Government Printing Office, Washington DC. 189 pp.
Madsen, J. D. & M. S. Adams, 1988. The seasonal biomass and productivity of the submerged macrophytes in a polluted Winsconsin stream. Freshwat. Biol. 20: 41–50.
Nichols, S. A. & B. H. Shaw, 1986. Ecological life history of three aquatic nuisance plants, Myriophyllum spicatum, Potamogeton crispus and Elodea canadensis. Hydrobiologia 131: 3–21.
Nielsen, S. L., 1993. A comparison of aerial and submerged photosynthesis in some Danish amphibious plants. Aquat. Bot. 45: 27–40.
Peck, J. H. & M. M. Smart, 1986. An assessment of the aquatic and wetland vegetation of the Upper Mississippi River. Hydrobiologia 136: 57–76.
Sparks, R. E., P. B. Bayley, S. L. Kohler & L. L. Osborne, 1990. Disturbance and recovery of large floodplain rivers. Envir. Mgmt 14: 699–709.
Spink, A. J., 1992 The ecological strategies of aquatic Ranunculus species. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Glasgow: 360.
Tanner, L. C., J. S. Clayton & R. D. S. Wells, 1993. Effects of suspended solids on the establishment and growth of Egeria densa. Aquat. Bot. 45: 299–310.
Van Dijk, G. M., 1992 Impact of light climate history on seasonal dynamics of Potamogeton pectinatus L. during a three year period (1986–1988). Aquat. Bot. 43: 17–42.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spink, A., Rogers, S. The effects of a record flood on the aquatic vegetation of the Upper Mississippi River System: some preliminary findings. Hydrobiologia 340, 51–57 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00012734
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00012734