Abstract
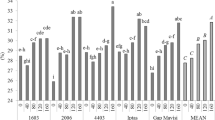
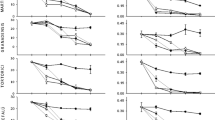
The effects of salinity, temperature, and N-fertilization on growth and yield of Rhodes grass were investigated. High levels of all three factors had a negative effect on tillering and consequently on the total yield. Though high salt-stress lowered the yields, it also lowered the content of free-NO3 − in the shoots, thus, raising the quality of the crops obtained.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnett, N. M. and Naylor, A. W., Amino acid and protein synthesis during water stress. Plant Physiol. 41, 1222–1230 (1966).
Bogdan, A. V., Rhodes grass. Herb. Abstr. 39(1), 1–10 (1969).
Bustenai, M., Waisel, Y., Kuller, Z., Guggenheim, J. and Tillman, G., The use of saline water for growing Rhodes grass on coastal sand dunes. Hassadeh 51, 603–605 (1971).
Dixon, W. J. and Massey, F. J. Jr., Introduction to statistical analysis. Mc Graw Hill Book Company. Third edition (International Student Edition) pp. 150–192 (1969).
Dovrat, A. and Cohen, Y., Regrowth potential of Rhodes grass (Chloris gayana Kunth) as affected by nitrogen and defoliation. 1. Dry matter production and tillering. Neth. J. Agric. Sci. 19, 94–101 (1970).
Downes, R. W., The effect of temperature on tillering of grain Sorghum seedlings. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 19, 59–64 (1968).
Hoagland, D. R. and Arnon, D. I., The water culture method for growing plants with soil. Calif. Agr. Exp. Sta. Circ. 347 (1950).
Horrocks, R. D. and Washko, J. B., Studies of tiller formation in Reed Canary grass (Phalaris arundinaceae L.) and ‘Climax’ Timothy (Phleum pratense) Crop. Sci. 11, 41–44 (1971).
Kahane, I. and Poljakoff-Mayber, A., Effect of substrate salinity on ability for protein synthesis in pea roots. Plant Physiol. 43, 1115–1119 (1968).
Langdale, G. W. and Thomas, J. R., Soil salinity effects on absorption of nitrogen, phosphorus and protein synthesis by Coastal Bermuda-grass. Agron. J. 63, 708–711 (1971).
Liphschitz, N., Ilan, A., Eshel, A. and Waisel, Y., Salt glands on leaves of Rhodes grass (Chloris gayana Kth.). Ann. Bot. 38, 459–462 (1974).
Magistad, O. C., Plant growth relations on saline and alkali soils. Bot. Rev. 2, 181–230 (1945).
Richards, L. A., Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils, U.S.D.A. Agricultural handbook No. 60. (1954).
Scheffe, H., The analysis of variance. A Wiley Publication. pp. 66–72 (1959).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
In partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of M.Sc. at The Tel Aviv University.
In partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of M.Sc. at The Tel Aviv University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guggenheim, J., Waisel, Y. Effects of salinity, temperature and nitrogen fertilization on growth and composition of Rhodes grass (Chloris gayana Kunth.). Plant Soil 47, 431–440 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011501
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00011501