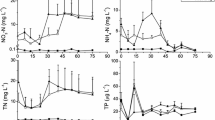
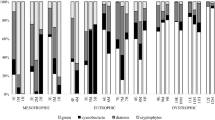
Abstract
The small, polyhumic lake, Mekkojärvi (southern Finland), is bordered by a moss vegetation zone (Warnstorfia and Sphagnum species) which provides a habitat-rich and productive environment for many planktonic and periphytic animals. Impacts of moss on the metabolism of bacterioplankton, phytoplankton and zooplankton in polyhumic water were investigated in laboratory throughflow systems. Growing Warnstorfia (together with epiphytic algae and bacteria) suppressed the production of planktonic algae but had no clear effect on leucine uptake, and hence bacterial production, or on the decomposition of humic substances. Phenol uptake and mineralization rates, however, were lower in the littoral water than in the pelagial water. Excretion of organic carbon by Warnstorfia algae or Daphnia longispina (the predominant crustacean in the pelagial water) provided only a minor contribution to bacterial production; therefore, a major contribution had to be from humic substances. A bacterial production efficiency of 31–38% could account for the microbial respiration in the water. The results indicated that bacterial, or detrital matter (originating largely from the littoral zone), could not obviate the need for algal food, and that a great deal of particulate matter in the water was poor or useless food for Daphnia. In all, the bulk of dissolved organic matter in Lake Mekkojärvi was biochemically highly recalcitrant. Our results indicate that humic substances (from watershed or littoral area) which, through bacterial degradation, enter the planktonic food web of the lake are mainly lost through respiration by microorganisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arvola, L. & P. Kankaala, 1989. Winter and spring variability in phyto- and bacterioplankton in lakes with different water colour. Aqua fern. 19: 29–39.
Bergström, I., A. Heinänen & K. Salonen, 1986. Comparison of acridine orange, acriflavine, and bisbenzimide strains for enumaration of bacteria in clear and humic waters. Appl. Envir. Microbiol. 51: 664–667.
Boers, P. C. M. & J. J. Boon, 1988. Unmasking the particulate organic matter in a lake ecosystem: Origin and fate of POM in the shallow eutrophic Loodsdrecht Lakes (The Netherlands). Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol. 31: 27–34.
Bratbak, G., 1985. Bacterial biovolume and biomass estimations. Appl. Envir. Microbiol. 49: 1488–1493.
Chin-Leo, G. & D. L. Kirchman, 1988. Estimating bacterial production in marine waters from the simultaneous incorporation of thymidine and leucine. Appl. Envir. Microbiol. 54: 1934–1939.
Downing, J. A., 1981. In situ foraging responses of three species of littoral cladocerans. Ecol. Monographs 51: 85–103.
Gadel, F. & A. Bruchet, 1987. Application of pyrolysis-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry to the characterization of humic substances resulting from decay of aquatic plants in sediments and waters. Wat. Res. 21: 1195–1206.
Glime, J. M., R. G. Wetzel & B. J. Kennedy, 1982. The effects of bryophytes on succession from alkaline marsh to Sphagnum bog. Am. Midl. Nat. 108: 209–223.
Hessen, D. O., 1989. Factors determining the nutritive status and production of zooplankton in a humic lake. J. Plankton Res. 11: 649–664.
Jones, R. I., 1990. Phosphorus transformations in the epilimnion of humic lakes: biological uptake of phosphorus. Freshwat. Biol. 23: 323–337.
Jumars, P. A., D. L. Penry, J. A. Baross, M. J. Perry & B. W. Frost, 1989. Closing the microbial loop: dissolved pathway to heterotrophic bacteria from incomplete ingestion, digestion and absorption in animals. Deep-Sea Res. 36: 483–495.
Kairesalo, T., 1984. The seasonal succession of epiphytic communities within an Equisetum fluviatile L. stand in Lake Paäjarvi, southern Finland. Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 69: 475–505.
Kairesalo, T. & P. Saukkonen, 1990. Thymidine incorporation by littoral and pelagial bacterioplankton in a mesohumic lake. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 24: 677–681.
Kairesalo, T., G. S. Jónsson, K. Gunnarsson, C. Lindegaard & P. M. Jónasson, 1992. Metabolism and community dynamics within Nitella opaca (Charophyceae) beds in Thingvallavatn. Oikos 64.
Kankaala, P., 1988. The relative importance of algae and bacteria as food for Daphnia longispina (Cladocera) in a polyhumic lake. Freshwat. Biol. 19: 285–296.
Kankaala, P. & P. Eloranta, 1987. Epizooic ciliates (Vorticella sp.) compete for food with their host Daphnia longispina in a small polyhumic lake. Oecologia (Berlin) 73: 203–206.
Kieber, D. J., J. McDaniel & K. Moppet, 1989. Photochemical source of biological substrates in sea water: implications for carbon cycling. Nature 341: 637–639.
Koroleff, F., 1979. Methods for the chemical analysis of seawater. Meri 7: 1–60 (in Finnish).
Lampert, W., 1978. Release of dissolved organic carbon by grazing zooplankton. Linmol. Oceanogr. 23: 831–834.
Moran, M. A., T. Legovic, R. Benner & R. E. Hodson, 1988. Carbon flow from lignocellulose: a simulation analysis of a detritus-based ecosystem. Ecology 6: 1525–1536.
Murphy, J. & J. P. Riley, 1962. A modified single-solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analyt. Chim. Acta 27: 31–36.
Münster, U., P. Einiö & J. Nurminen, 1989. Evaluation of the measurements of extracellular enzyme activities in a polyhumic lake by means of studies with 4-methylum-belliferylsubstrates. Arch. Hydrobiol. 115: 321–337.
Münster, U., P. Einiö, J. Nurminen & J. Overbeck, 1992. Extracellular enzymes in a polyhumic lake: important regulators in detritus processing. In K. Salonen, T. Kairesalo & R. I. Jones (eds), Dissolved Organic Matter in Lacustrine Ecosystems: Energy Source and System Regulator. Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Olsen, Y., K. M. Varum & A. Jensen, 1986. Some characteristics of the carbon compounds-released by Daphnia. J. Plankton Res. 8: 505–517.
Riemann, B., P. Simonsen & L. Stensgaard, 1989. The carbon and chlorophyll content of phytoplankton from various nutrient regimes. J. Plankton Res. 11: 1037–1045.
Salonen, K., 1979. A versatile method for the rapid and accurate determination of carbon by high temperature combustion. Limnol. Oceanogr. 24: 127–129.
Salonen, K., 1981. Rapid and precise determination of total inorganic carbon and some gases in aqueous solutions. Water Research 15: 403–406.
Salonen, K. & S. Jokinen, 1988. Flagellate grazing on bacteria in a small dystrophic lake. Hydrobiologia 161: 203–209.
Salonen, K. & A. Lehtovaara, 1992. Migrations of haemoglobin-rich Daphnia longispina in a small, steeply stratified humic lake with an anoxic hypolimnion. In K. Salonen, T. Kairesalo & R. I. Jones (eds), Dissolved Organic Matter in Lacustrine Ecosystems: Energy Source and System Regulator. Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Sanders, R. W., K. G. Porter, S. J. Bennett & A. E. DeBiase, 1989. Seasonal patterns of bactivory by flagellates, ciliates, rotifers, and cladocerans in a freshwater planktonic community. Limnol. Oceanogr. 34: 673–687.
Sherr, B. F. & E. B. Sherr, 1984. Role of heterotrophic protozoa in carbon and energy flow in aquatic ecosystems. In M. Klug & C. A. Reddy (eds), Current Perspectives in Microbial Ecology. Am. Soc. Microbial. (Wash. D.C.).
Solorzano, L., 1969. Determination of ammonia in natural waters by the phenolhypochlorite method. Limnol. Oceanogr. 14: 799–801.
Søndergaard, M., 1983. Heterotrophic utilization and decomposition of extracellular carbon released by the aquatic angiosperm Littorella uniflora (L.) Aschers. Aquat. Bot. 16: 59–73.
Stich, H.-B. & W. Lampert, 1984. Growth and reproduction of migrating and non-migrating Daphnia species under simulated food and temperature conditions of diurnal vertical migration. Oecologia (Berlin) 61: 192–196.
Tranvik, L. J. & J. McN. Sieburth, 1989. Effects of flocculated humic matter on free and attached pelagic microorganisms. Limnol. Oceanogr. 34: 688–699.
Tuomikoski, R., 1973. New combinations in mosses; Loeskypnum wickesii, Scorpidium vernicosum and Warn-storfia procera. Ann. Bot. fern. 10: 216.
Wetzel, R. G., 1992. Gradient dominated ecosystems: sources and regulatory functions of dissolved organic matter in freshwater ecosystems. In K. Salonen, T. Kairesalo & R. 1. Jones (eds), Dissolved Organic Matter in Lacustrine Ecosystems: Energy Source and System Regulator. Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Wetzel, R. G. & H. L. Allen, 1972. Functions and interactions of dissolved organic matter and the littoral zone in lake metabolism and eutrophication. In Z. Kajak & A. Hillbricht-Ilkowska (eds), Productivity Problems of Freshwaters. Warszawa-Krakow 1972: 333–347.
Wood, E. D., F. A. J. Armstrong & F. A. Richards, 1967. Determination of nitrate in sea water by cadmium-copper reduction to nitrite. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 47: 23–31.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kairesalo, T., Lehtovaara, A. & Saukkonen, P. Littoral-pelagial interchange and the decomposition of dissolved organic matter in a polyhumic lake. Hydrobiologia 229, 199–224 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00007001
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00007001