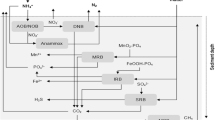
Abstract
The effect of redox potential and pH on the phosphate mobility in two sediments were investigated using both consolidated and suspended sediments from the area where the Parana Medio long reservoir (Atgentina) is to be built (Smirnov, 1984). In addition to direct chemical sediment analysis, extraction techniques were carried out with a stepwise NH4Cl-NaOH-HCl shaking method, the latter supposedly separating the weakly bound, the Fe- and Al- bound and the Ca- bound phosphates in the sediments.
Phosphate released into water depends upon redox potential and pH, which both were modified in an experimental setup. The source of the phosphate was the fraction of Fe and/or Al bound phosphate present both in the sediment and in the suspended solids.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- cm:
-
centimeter
- km:
-
kilometer
- gg:
-
gram
- l:
-
liter
- ¬m:
-
micrometer
- °C:
-
grade centigrades
- km2 :
-
square kilometer
- m.s−1 :
-
meter per second
- m3.s−1 :
-
cubic meter per second
- mg.1‐1 :
-
miligram per liter
References
Ahlgren, I., 1980. A dilution model applied to a system of shallow eutrophic lakes after diversion of sewage effluents. Arch. Hydrobiol. 89: 17–32.
Bates, M. & N. Neafus, 1980. Phosphorus release from sediments from Lake Carl Blackwell, Oklahoma. Wat. Res. 14: 1477–1481.
Bostrom, B., M. Jansson & C. Forsberg,1982. Phosphorus release from lake sediments. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. 18: 6–54.
Bostrom, B., 1984. Potential mobiligy of Phosphorus in Lake Sediment. Hydrobiol. 69: 457–474.
Chang, S. C. & M. L. Jackson, 1957. Fractionation of soil phosphorus. Soil Sci. 84: 133–144.
De Groot, C. J. & H. L. Golterman, 1990. Sequential fractionation of sediment phosphate. Hydrobiologia 192: 143–148.
Depetris, P. J. & A. M. Lenardon, 1982. Particulate and Dissolved Phases in the Parana River. Mitt. Geol. 5: 385–395.
Groterman, H. L., 1988. The calcium- and iron bound phosphate phase diagram.Hydrobiologia 159: 149–151.
Grobbelaar, J. V., 1983. Availability to algae of N and P adsorbed on suspended solids in turbid waters of the Amazon River. Arch. Hydrioiol. 96: 302–316.
Harrison, M. J., R. W. Pacha & R. Y. Morita, 1972. Solubilization of inorganic phosphate by bacteria isolated from Upper Klemath lake sediment. Limnol. Oceanogr. 17: 50–57.
Hieltjes, A. H. M. & L. Lijklema, 1980. Fractionation of inorganic phosphates in calcareous sediments. J. envir. Qual. 9: 405–407.
Kamp-Nielsen, L., 1974. Mud-water exchange of phosphates and other ions in undisturbed sediments cores and factors affecting the exchange rates. Arch. Hydrobiol. 73: 218–237.
Lijklema, L., 1977. The role of iron in the exchange of phosphate between water and sediments. In: H. L. Golterman (ed.), Interactions between sediments and fresh water: 313–317. Dr W. Junk, The Hague.
Lorenzen, M. W., 1974. Predicting the effects of nutrient diversion on lake recovery. In: E. J. Middlebrooks, D. H. Falkenborg & T. E. Maloney (eds), Modeling the Eutrophication Process. pp. 205–210. Ann Arbor Science Publishers, Ann Arbor.
Murphy, J. & J. Riley, 1962. A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Anal. Chim. Acta 27: 31–36.
Ohle, W., 1937.Kolloidgele als Nahrstoffregulanten der Gewassen Naturwissenschaften. 25: 471–474.
Ohle, 1964. Interstitiallosung der sediments, Nahrstoffgehalt des phytoplanktons in seen. Helgol. Wiss Meeresunters. 10: 411–429.
Smirnov, N. N., 1984. Attempt at ecological prognosis of plankton in the man-made lake ‘Parana Medio (Chapeton transect)’, Argentina, Hydrobiol. 113: 159–163.
Sridharan, N. & G. F. Lee, 1974. Phosphorus studies in lower Green Bay Lake Michigan. J. Wat. Pollut. control. Fed. 46: 684–696.
Standard Methods for the examination of water and Wastewater, 1975. 14th Edition American Public Health Association.
Stumm, W. & J. J. Morgan, 1970. Aquatic Chemistry, Wiley-Interscience New York.
Vollenweider, R.AA., 1975. Input-Output models. Schweiz. T. Hydrol. 37: 53–84.
Welch, E. B., C. A. Rock, J. D. Krull, 1974. Long-term lake recovery related to available phosphorus. In: E. J. Middlebrooks, D. H. Falkenborg and T. E. Maloney (eds), Modeling the Eutrophication Process. pp. 5–13. Ann Arbor Science Publishers, Ann Arbor.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maine, M.A., Hammerly, J.A., Leguizamon, M.S. et al. Influence of the pH and redox potential on phosphate activity in the Parana Medio system. Hydrobiologia 228, 83–90 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00006479
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00006479