Abstract
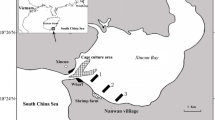
The origin and temporal variation in composition of sedimented particulate organic matter (POM) in the Gulf of Trieste (northern Adriatic) was studied over the year with special reference to the composition and sedimentation of macroaggregates in summer of 1991 using sediment traps.
Suspended and sedimented POM, comprising a minor part of the largely inorganic total particulate matter, was prevalently of marine origin and composed mostly of humic substances followed by carbohydrates and proteins. Seasonal variations of particulate proteins and carbohydrates were correlated with variations of phytoplankton biomass. ‘New’ production, occurring in late spring as a consequence of massive riverine inputs of N, Si and P nutrients in the surface layer of the Gulf, produced high particulate carbohydrate and protein concentrations. Subsequent depletion of introduced nutrients caused the decrease of particulate protein concentration but not that of particulate carbohydrate. The prolonged plankton biosynthesis of carbohydrates successively produced marine snow and later macroaggregates. The macroaggregates were characterized by δ13C value of −19.9‰. and their carbohydrates were mostly composed of glucose followed in decreasing order by mannose, fructose, galactose, arabinose, ribose, xylose and fucose, suggesting a prevalent origin from phytoplankton structural heteropolysaccharides. Sedimentation of particulate organic constituents in the summertime, characterized by the massive presence of macroaggregates in the surface layer above the pycnocline, was the highest at a depth of 10 m at the end of this phenomenon, about six weeks after its first appearance. Sedimented macroaggregates were clearly traced by a characteristic δ13C signal and higher carbohydrate concentrations. The monosaccharide composition was influenced by selective degradation in the water column. Sedimented POM in the bottom layer was, on the other hand, more affected by sediment resuspension. The mean yearly decrease of particulate protein-C and carbohydrate-C by 40–50% in the water column between the depths of 10 and 20 m indicates the preferential utilization of these constituents by microorganisms. The decrease of particulate humic-C is probably more the result of the export of particulate matter from the Gulf. This study also indicates that the macroaggregate formation has little impact on the annual C and N budget in such coastal areas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azam F & Smith DC (1991) Bacterial influence on the variability in the ocean's biogeochemical state: A mechanistic view, pp. 213–236. In: Demers S (Ed) Particles analysis in oceanography. NATO ASI Series, Series G, Vol. 27. Springer Verlag, Berlin
Blomqvist S & Kofoed C (1981). Sediment trapping — a subaquatic in situ experiment. Limnology and Oceanography 26: 585–590
Burney CM & McSeiburth JN (1977) Dissolved carbohydrates in sea water. II. A spectrophotometric procedure for total carbohydrate analysis and polysaccharide determination. Marine Chemistry 5: 15–28
Cowie GL, Hedges JH & Calvert SE (1992) Sources and relative reactivities of amino acids, neutral sugars and lignin in an intermittently anoxic marine environment. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 56: 1963–1978
Craig H (1953) The geochemistry of the stable carbon isotopes. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 3: 53–92
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA & Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for the determination of sugars and related substances. Analytical Chemistry 28: 350–356
Faganeli J (1989) Sedimentation of particulate nitrogen and amino acids in shallow coastal waters (Gulf of Trieste, northern Adriatic). Marine Chemistry 26: 67–80
Faganeli J, Fanuko N, Stegnar P & Vukovič (1982) Studies on primary pelagic bioproduction in the Gulf of Trieste. Acta Adriatica 23: 53–60
Faganeli J, Malej A, Pezdič & Malačič V (1988). C:N:P and stable C isotopic ratios as indicators of sources of organic matter in the Gulf of Trieste (northern Adriatic). Oceanologica Acta 11: 373–382
Faganeli J, Pezdič J & Fanuko N (1989) Chemical and isotopic composition of some phytoplankton species. Biološki Vestnik 37: 9–18
Faganeli J, Planinc R, Pezdič J. Smodiš B, Stegnar P & Ogorelec B (1991) Marine geology of the Gulf of Trieste (northern Adriatic): geochemical aspects. Marine Geology 99: 93–108
Fanuko N & Turk V (1990) The oceanologic properties of the sea water in the Gulf of Trieste before and during the ‘mare sporco’ phenomenon (summer 1988). Bollettino di Oceanologia Teorica ed Applicata 8: 3–11
Fonda-Umani S, Ghirardelli E & Specchi M (1989) Gli episodi di ‘mare sporco’ nell' Adriatico da 1729 ai nostri giomi. Regione autonoma Friuli-Venezia Giulia, Trieste
Fontugne M (1983) Les isotopes stable du carbonne organique dans l'ocean. Application á la paléoclimatologie. Thèse Doct. Sci., Univ. Paris sud Orsay
Grasshoff K, Ehrhardt M & Kremling K (1983) Methods of seawater analysis. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim
Hama J & Handa N (1992) Diel variations of water — extractable carbohydrate composition of natural phytoplankton populations in Kinu-Ura Bay. Journal of experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 162: 159–176
Handa N (1969) Carbohydrate metabolism in the marine diatom Skeletonema costatum. Marine Biology 4: 208–214
Handa N & Yanagi K (1969) Studies on water-extractable carbohydrates of particulate matter from the northwest Pacific Ocean. Marine Biology 4: 197–207
Haug A & Myklestad S (1976) Polysaccharides of marine diatoms with special reference to Chaetoceros species. Marine Biology 34: 217–222
Herndl GJ (1992) Marine snow in the northern Adriatic Sea: possible causes and consequences for a shallow ecosystem. University of Vienna, Habilitationschrift
Ittekkot V, Degens ET & Brockmann V (1982) Monosaccharide composition of acidhydrolizable carbohydrates in particulate matter during a plankton bloom. Limnology and Oceanography 27: 770–776
Kiørboe T, Andersen KP & Dam HG 1990. Coagulation efficiency and aggregate formation in marine phytoplankton. Marine Biology 107: 235–243
Lee C & Wakeham SG (1992) Organic matter in the water column. Future Research Challenges. Marine Chemistry 39: 95–115
Mayer LM, Schick LL & Setchell FW (1986) Measurements of protein in nearshore marine sediments. Marine Ecology Progress Series 30: 159–165
Michaels AF, Silver MW, Gowing RM & Knauer GA (1990) Cryptic zooplankton ‘swimmers’ in upper ocean sediment traps. Deep-Sea Research 37: 1285–1296
Mopper K (1977) Sugars and uronic acids in sediment and water from the Black Sea and North Sea with emphasis on analytical techniques. Marine Chemistry 5: 585–603
Mopper K, Dawson R, Liebezeit G, Ittekkot V (1980) The monosaccharide spectra of natural waters. Marine Chemistry 10: 55–66
Neeser JR & Schweizer TF (1984) A quantitative determination by capillary gas-liquid chromatography of neutral and amino sugars (as O-methyloxime acetates), and a study of hydrolytic conditions for glycoproteins and polysaccharides in order to increase sugar recoveries. Analytical Biochemistry 142: 58–67
Pakulski JD & Benner R (1992) An improved method for the hydrolysis and MBTH analysis of dissolved and particulate carbohydrates in seawater. Marine Chemistry 40: 143–160
Percival E (1970) Algal carbohydrates, pp. 537–568. In: Pigman W & Horton D (Eds) The carbohydrates: Chemistry and Biochemistry, 2nd ed., Vol. IIB, Academic Press, London
Plechanov N (1983) Studies of molecular weight distributions of fulvic and humic acids by gel permeation chromatography. Examination of the solute molecular composition using RI, UV, fluorescence and weight measurement as detection technique. Organic Geochemistry 5: 143–149
Posedel N & Faganeli J (1991) Nature and sedimentation of suspended particulate matter during density stratification in shallow coastal waters (Gulf of Trieste, northern Adriatic). Marine Ecology Progress Series 77: 135–145
Ranke U (1976) The sediments of the Gulf of Piran (northern Adriatic sea). Senckenbergiana Maritima 8: 91–162
Rausch T (1981) The estimation of micro-algal biomass. I. Comparison of methods for extracting protein. Hydrobiologia 78: 237–251
Setchell FW (1981) Particulate protein measurements in oceanographic samples by dye binding. Marine Chemistry 10: 301–313
Stachowitsch M, Fanuko N & Richter M (1990) Mucus aggregates in the Adriatic sea: An overview of stages and occurrences. P.S.Z.N. I: Marine Ecology 11: 327–350
Tanoue E, Handa N (1987) Monosaccharide composition of marine particles and sediments from the Bering Sea and northern North Pacific. Oceanologica Acta 10: 91–99
Tegelaar EW, deLeeuw JW, Derenne S & Largau C (1989) A reappraisal of kerogen formation. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 53: 3103–3106
Wakeham SG & Lee C (1989) Organic geochemistry of particulate matter in the Ocean: The role of particles in oceanic sedimentary cycles. Organic Geochemistry 14: 83–96
Willis DE (1983) GC analysis of C4-C7 carbohydrates as trimethylsilyl-oxime derivatives on packed and capillary columns. Journal of Chromatographic Science 21: 132–138
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faganeli, J., Kovač, N., Leskovšek, H. et al. Sources and fluxes of particulate organic matter in shallow coastal waters characterized by summer macroaggregate formation. Biogeochemistry 29, 71–88 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00002595
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00002595