Abstract
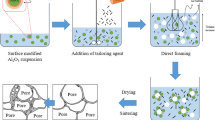
This study reports on the wet-foam stability of porous ceramics that are formed from a particle-stabilized colloidal suspension for which the direct-foaming method is used. To stabilize the wet foam, an initial colloidal suspension of silicon carbide (SiC) was partially hydrophobized by the surfactant octylamine (12.5 wt.%). The influence of the binder content on the wet-foam stability in terms of the air content, bubble size, contact angle, surface tension, surface-free energy, Laplace pressure, and relative bubble size is described in this paper. The results show a wet-foam stability of more than 95% that corresponds to an air content of 87.8%, an increase of the adsorption free energy from 3.0 × 10−5 to nearly 7.5 × 10−5 J, a Laplace pressure increase from 0.16 to 0.20 mPa, and a relative bubble size of 1.3 for the colloidal particles with a 20 wt% binder content. The uniform distribution of the highly open/interconnected pores could be controlled with thick struts and an increasing of the binder content up to 20 wt%, leading to the achievement of a higher-stability wet foam with respect to the porous ceramic.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamada, K., and Mohri, M.: Properties and applications of silicon carbide ceramics. Silicon Carbide Ceramics—1 Ch 2, pp 13–44 (1991)
Zum Gahr, K.H., Blattner, R., Hwang, D.H., Pohlmann, K.: Micro- and macro-tribological properties of SiC ceramics in sliding contact. Wear. 250(1–12), 299–310 (2001)
Eom, J.H., Kim, Y.W., Song, I.H., Kim, H.D.: Processing and properties of polysiloxane-derived porous silicon carbide. J. Eur. Cer. Soc. 28, 1029–1035 (2008)
Fukushima, M., Colombo, P.: Processing of polysiloxane-derived porous ceramics: a review. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 11, 044303 (2010) (16pp)
Scheffler, M., Colombo, P.: Cellular ceramics: structure, manufacturing, properties and applications, p. 645. Wiley-VCH, Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim (2005)
Eom, J.H., Kim, Y.K., Raju, S.: Processing and properties of macroporous silicon carbide ceramics: a review. Jor Asian Cer Soc. 1(3), 220–242 (2013)
Studart, A.R., Gonzenbach, U.T., Tervoort, E., Gauckler, L.J.: Processing routes to Macroporous ceramics: a review. J Am Ceram Soc. 89(6), 1771–1789 (2006)
Wong, J.C.H., Tervoort, E., Busato, S., Gonzenbach, U.T., Studart, A.R., Ermanni, P., Gauckler, L.J.: Designing macroporous polymers from particle-stabilized foams. J Mater Chem. 20, 5628–5640 (2010)
Lee, J.S., Lee, S.H., Choi, S.C.: Improvement of porous silicon carbide filters by growth of silicon carbide nanowires using modified carbothermal reduction process. J Alloys and Comp. 467, 543–549 (2009)
Mouazer, R., Mullens, S., Thijs, I., Luyten, J., Buekenhoudt, A.: Silicon carbide foams by polyurethane replica technique. Adv Eng Matr. 7(12), 1124–1128 (2005)
Li, F., Kanga, Z., Huanga, X., Wang, X.G., Zhang, G.J.: Preparation of zirconium carbide foam by direct foaming method. J Eur Cer Soc. 34, 3513–3520 (2014)
Bhaskar, S., Park, J.G., Kim, S.W., Kim, H.T., Kim, I.J.: Micro porous ceramics using partially hydrophobized SiO2–SiC particle by direct foaming. J Cer Soc Jp. 123(6), 1–5 (2015)
Zhang, L.Y., Zhou, D.-l., Chen, Y., Liang, B., Zhou, J.B.: Preparation of high open porosity ceramic foams via direct foaming molded and dried at room temperature. Journal of the J Eur Cer Soc. 34, 2443–2452 (2014)
Pokhrel, A., Nam, S.D., Lee, S.T., Kim, I.J.: Processing of porous ceramics by direct foaming: a review. J Kr Ceram Soc. 50(2), 93–102 (2013)
Murray, B.S.: Stabilization of bubbles and foams. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sc. 12, 231–241 (2007)
Horozov, T.S.: Foams and foam films stabilized by solid particles. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sc. 13, 134–140 (2008)
Zibouche, F., Kerdjoudj, H.: Rheological properties of the Tamazert kaolin. Eur J Sci Res. 13, 22–30 (2006)
Sarkar, N., Park, J.G., Mazumder, S., Seo, D.N., Kim, I.J.: Effect of Amphiphile chain length on wet foam stability of porous ceramics. Cer Intr. 41, 4021–4027 (2015)
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by Hanseo University, and it was conducted under the framework of the research and development program of the Korea Institute of Energy Research (B6-2455).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, W.Y., Park, J.G., Basnet, B. et al. Highly porous SiC ceramics from particle-stabilized suspension. J Aust Ceram Soc 53, 657–665 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-017-0077-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s41779-017-0077-z