Abstract
Introduction and objective
Although the effectiveness of single-fraction brain stereotactic radiosurgery has been extensively demonstrated, recent evidence is suggesting that when skull base lesions are the targets, radiation near critical structures (e.g., optic nerves, and brainstem) should be reduced to avoid radiotoxic effects, with the risk of treatment inefficacy. Hence, in these tumors, hypofractionated stereotactic radiosurgery (HSRS) would offer a therapeutical opportunity. Here, we present our experience with this modality in the management of patients with skull base tumors.
Methods
A series of patients with skull base tumors was retrospectively analyzed to evaluate the treatment with HSRS. The primary endpoint was tumor control in post-treatment imaging. Age, sex, tumor histology, tumor volume, type of radiation protocol, pre-treatment Karnofsky performance status (KPS), previous neurosurgery, and prior radiotherapy were analyzed.
Results
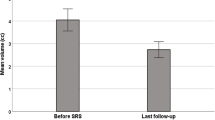
A total of 84 patients were treated between January/2009 to January/2017. Median age: 51.5 years. Female gender: 53.6%. There was 92.7% of non-progression after HSRS, with a median f/u of 36 months. Main tumors treated were pituitary adenomas, acoustic schwannomas, and skull base meningioma. Most of the patients were treated with a 5-day fraction scheme of a 25 Gy total dose. No late radiotoxicity was observed. In multivariate analysis, a high KPS was associated with non-progression.
Conclusions
In our series of patients, the high incidence of non-progression of tumors indicated that HSRS could be a therapeutic option in some cases of skull base lesions, mainly residuals or tumoral recurrences of pituitary adenomas, schwannomas, and meningiomas.






Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Hormone-secreting pituitary adenomas were excluded given that the appropriate outcome, in this case, is not the tumor non-progression, but the biochemical normalization of hormone secretion.
References
Amichetti M, Amelio D, Minniti G (2012) Radiosurgery with photons or protons for benign and malignant tumours of the skull base: a review. Radiat Oncol 7:210
Anker CJ, Shrieve DC (2009) Basic principles of radiobiology applied to radiosurgery and radiotherapy of benign skull base tumors. Otolaryngol Clin N Am 42(4):601–621
De Witte O, Hassid S, Massager N (2009) Tumors involving the base of the skull: diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. Curr Opin Oncol 21(3):238–231
Ding D, Yen CP, Starke RM, Lee CC, Sheehan JP (2014) Unyielding progress: recent advances in the treatment of central nervous system neoplasms with radiosurgery and radiation therapy. J Neuro-Oncol 119(3):513–529
Fernandez-Miranda JC, Gardner PA, Snyderman CH, Devaney KO, Mendenhall WM, Suárez C et al (2014) Clival chordomas: a pathological, surgical, and radiotherapeutic review. Head Neck 36(6):892–906
Prabhu SS, Demonte F (2003) Treatment of skull base tumors. Curr Opin Oncol 15(3):209–212
Suh JH, Saxton JP (2000) Conventional radiation therapy for skull base tumors: an overview. Neurosurg Clin N Am 11(4):575–586
Abdelaziz OS, Kandil A, El-Assaal S, Abdelaziz A, Rostom Y, Rashed Y (2011) Linear accelerator-based stereotactic radiosurgery of intracranial meningiomas: results of the first 5 years of clinical practice. Neurosurg Rev 34(1):87–99
Conley GS, Hirsch BE (2010) Stereotactic radiation treatment of vestibular schwannoma: indications, limitations, and outcomes. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 18(5):351–356
Deinsberger R, Tidstrand J (2005) Linac radiosurgery as a tool in neurosurgery. Neurosurg Rev 28(2):79–88
Friedman WA, Foote KD (2003) Linear accelerator-based radiosurgery for vestibular schwannoma. Neurosurg Focus 14(5):e2
Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2008) The principles of skull base radiosurgery. Neurosurg Focus 24(5):E11
McCutcheon IE (2013) Stereotactic radiosurgery for malignant extracerebral intracranial tumors: patient selection, efficacy, and technical nuances. Acta Neurochir Suppl 116:71–83
Pollock BE, Foote RL (2004) The evolving role of stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with skull base tumors. J Neuro-Oncol 69(1–3):199–207
Betti O, Derechinsky V (1983) Multiple-beam stereotactic irradiation. Neurochirurgie 29(4):295–298 French
Betti OO, Derechinsky VE (1984) Hyperselective encephalic irradiation with linear accelerator. Acta Neurochir Suppl 33:385–390
Betti OO, Galmarini D, Derechinsky V (1991) Radiosurgery with a linear accelerator. Methodol Aspects Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 57(1–2):87–98
Emami B (2013) Tolerance of normal tissue to therapeutic radiation. Reports of Radiother Oncol 1(1):35–48
Leavitt JA, Stafford SL, Link MJ, Pollock BE (2013) Long-term evaluation of radiation-induced optic neuropathy after single-fraction stereotactic radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 87(3):524–527
Killory BD, Kresl JJ, Wait SD, Ponce FA, Porter R, White WL (2009) Hypofractionated CyberKnife radiosurgery for perichiasmatic pituitary adenomas: early results. Neurosurgery 64(2 Suppl):A19–A25
Astradsson A, Wiencke AK, Munck AF, Rosenschold P, Engelholm SA, Ohlhues L, Roed H, Juhler M (2014) Visual outcome after fractionated stereotactic radiation therapy of benign anterior skull base tumors. J Neuro-Oncol 118(1):101–108
Chun SG, Nedzi LA, Choe KS, Abdulrahman RE, Chen SA, Yordy JS, Timmerman RD, Kutz JW, Isaacson B (2014) A retrospective analysis of tumor volumetric responses to five fraction stereotactic radiotherapy for paragangliomas of the head and neck (glomus tumors). Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 92(3):153–159
Coppa ND, Raper DM, Zhang Y, Collins BT, Harter KW, Gagnon GJ, Collins SP, Jean WC (2009) Treatment of malignant tumors of the skull base with multi-session radiosurgery. Hematol Oncol 2:16
Tuniz F, Soltys SG, Choi CY, Chang SD, Gibbs IC, Fischbein NJ, Adler JR Jr (2009) Multisession cyberknife stereotactic radiosurgery of large, benign cranial base tumors: preliminary study. Neurosurgery 65(5):898–907
Combs SE, Adeberg S, Dittmar JO, Welzel T, Rieken S, Habermehl D, Huber PE, Debus J (2013) Skull base meningiomas: Long-term results and patient self-reported outcome in 507 patients treated with fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy (FSRT) or intensity modulated radiotherapy (IMRT). Radiother Oncol 106(2):186–191 2012 Aug 18
Litré CF, Colin P, Noudel R, Peruzzi P, Bazin A, Sherpereel B, Bernard MH, Rousseaux P (2009) Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy treatment of cavernous sinus meningiomas: a study of 100 cases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74(4):1012–1017
McGregor JM, Sarkar A (2009) Stereotactic radiosurgery and stereotactic radiotherapy in the treatment of skull base meningiomas. Otolaryngol Clin N Am 42(4):677–688
Minniti G, Amichetti M, Enrici RM (2009) Radiotherapy and radiosurgery for benign skull base meningiomas. Radiat Oncol 4:42
Minniti G, Clarke E, Cavallo L, Osti MF, Esposito V, Cantore G, Cappabianca P, Enrici RM (2011) Fractionated stereotactic conformal radiotherapy for large benign skull base meningiomas. Radiat Oncol 6:36
Solberg TD, Selch MT, Smathers JB, DeSalles AA (1998 Fall) Fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy: rationale and methods. Med Dosim 23(3):209–219
De Salles AA, Gorgulho AA, Pereira JL, McLaughlin N (2013) Intracranial stereotactic radiosurgery: concepts and techniques. Neurosurg Clin N Am 24(4):491–498
Benghiat H, Heyes G, Nightingale P, Hartley A, Tiffany M, Spooner D, Geh JI, Cruickshank G, Irving RM, Sanghera P (2014) Linear accelerator stereotactic radiosurgery for vestibular schwannomas: a UK series. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 26(6):309–315
Combs SE, Ganswindt U, Foote RL, Kondziolka D, Tonn JC (2012) State-of-the-art treatment alternatives for base of skull meningiomas: complementing and controversial indications for neurosurgery, stereotactic and robotic based radiosurgery or modern fractionated radiation techniques. Radiat Oncol 7:226
Han J, Girvigian MR, Chen JC, Miller MJ, Lodin K, Rahimian J, Arellano A, Cahan BL, Kaptein JS (2014) A comparative study of stereotactic radiosurgery, hypofractionated, and fractionated stereotactic radiotherapy in the treatment of skull base meningioma. Am J Clin Oncol 37(3):255–260
Ho JC, Phan J (2017 Oct 28) Reirradiation of skull base tumors with advanced highly conformal techniques. Curr Oncol Rep 19(12):82
Barnett GH, Linskey ME, Adler JR, Cozzens JW, Friedman WA, Heilbrun P et al (2007) Stereotactic radiosurgery—an organized neurosurgery sanctioned definition. J Neurosurg 106:1–5
Navarria P, Pessina F, Cozzi L, Clerici E, Villa E, Ascolese AM, De Rose F, Comito T, Franzese C, D'Agostino G, Lobefalo F, Fogliata A, Reggiori G, Fornari M, Tomatis S, Bello L, Scorsetti M (2015) Hypofractionated stereotactic radiation therapy in skull base meningiomas. J Neuro-Oncol 124(2):283–289
Patibandla MR, Lee CC, Sheehan J Stereotactic radiosurgery of central skull base meningioma’s - volumetric evaluation and long-term outcomes. World Neurosurg. 2017
Meijer OW, Weijmans EJ, Knol DL, Slotman BJ, Barkhof F, Vandertop WP et al (2008) Tumor-volume changes after radiosurgery for vestibular schwannoma: implications for follow-up MR imaging protocol. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:906–910
Hauptman JS, Barkhoudarian G, Safaee M, Gorgulho A, Tenn S, Agazaryan N, Selch M, De Salles AA (2012) Challenges in linear accelerator radiotherapy for chordomas and chondrosarcomas of the skull base: focus on complications. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 83(2):542–551
Kano H, Lunsford LD (2013) Stereotactic radiosurgery of intracranial chordomas, chondrosarcomas, and glomus tumors. Neurosurg Clin N Am 24(4):553–560
Klinger DR, Flores BC, Lewis JJ, Barnett SL (2013) The treatment of cavernous sinus meningiomas: evolution of a modern approach. Neurosurg Focus 35(6):E8
Somers T, Van Havenbergh T (2012) Multidisciplinary management of vestibular schwannomas: state of the art. B-ENT 8(4):235–240
Collen C, Ampe B, Gevaert T, Moens M, Linthout N, De Ridder M, Verellen D, D’Haens J, Storme G (2011) Single fraction versus fractionated linac-based stereotactic radiotherapy for vestibular schwannoma: a single institution experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81(4):e503–e509
Stelzer KJ (2000) Acute and long-term complications of therapeutic radiation for skull base tumors. Neurosurg Clin N Am 11(4):597–604
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Our Institutional Review Board approved the execution of the study.
Conflict of interest
Author Diego A. Hernández declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Juan M Zaloff Dakoff declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Cynthia Auad declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author Victor E. Derechinsky declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Roberto Rosler declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Julio García declares that he has no conflict of interest. Author Luisa Rafailovici declares that she has no conflict of interest. Author María L. Filomia declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study. During the processing of data at the time of analysis, the patient’s identity remained anonymous.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hernández, D.A., Zaloff Dakoff, J.M., Auad, C. et al. Experience with hypofractionated stereotactic radiosurgery in a series of patients with skull base tumors. J Radiat Oncol 7, 307–315 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13566-018-0365-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13566-018-0365-4