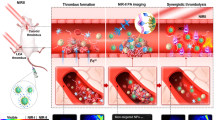
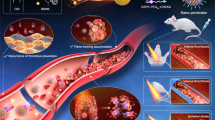
Abstract
Fibrinolytic therapy for arterial or venous thrombotic disorders involves the systemic administration of thrombolytics such as streptokinase, which is associated with serious bleeding complications. With this study, we provide a proof-of-concept of photothermal thrombus ablation with gold nanorods exposed to near-infrared irradiation, both in vitro using materials generated from purified fibrinogen or plasma and in vivo in murine blood vessels. This is the first report of the application of photothermal therapy as an anti-thrombotic measure. Remarkably, the addition of streptokinase had a multimodal additive effect with regard to acceleration of photothermal lysis of thrombi even at a dose significantly below the therapeutic concentration, thus minimizing the life-threatening side effects and adverse complications. This combinatorial approach exhibits great promise for lysing pathological clots while effectively overcoming the drawbacks of existing therapies.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Canto, J. G.; Rogers, W. J.; Goldberg, R. J.; Peterson, E. D.; Wenger, N. K.; Vaccarino, V.; Kiefe, C. I.; Frederick, P. D.; Sopko, G.; Zheng, Z.-J. et al. Association of age and sex with myocardial infarction symptom presentation and in-hospital mortality. JAMA 2012, 307, 813–822.
Weitz, J. I. Antiplatelet, anticoagulant, and fibrinolytic drugs. In Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine. Longo, D. L.; Fauci, A. S.; Kasper, D. L.; Hauser, S. L.; Jameson, J. L.; Loscalzo, J., Eds.; McGraw-Hill: New Delhi, 2011; Vol. 1, pp 1001–1003.
Tsai, M. F.; Chang, S. H. G.; Cheng, F. Y.; Shanmugam, V.; Cheng, Y. S.; Su, C. H.; Yeh, C. S. Au nanorod design as light-absorber in the first and second biological near-infrared windows for in vivo photothermal therapy. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 5330–5342.
Mosesson, M. W. Fibrinogen and fibrin structure and functions. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 3, 1894–1904.
Hethershaw, E. L.; Cilia La Corte, A. L.; Duval, C.; Ali, M.; Grant, P. J.; Ariëns, R. A. S.; Philippou, H. The effect of blood coagulation factor XIII on fibrin clot structure and fibrinolysis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2014, 12, 197–205.
Chernysh, I. N.; Everbach, C. E.; Purohit, P. K.; Weisel, J. W. Molecular mechanisms of the effect of ultrasound on the fibrinolysis of clots. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2015, 13, 601–609.
Walters, M. I. An evaluation of hemoglobin concentrations obtained with frozen altered Drabkin’s reagents. Clin. Chem. 1968, 14, 682–691.
Chernysh, I. N.; Nagaswami, C.; Purohit, P. K.; Weisel, J. W. Fibrin clots are equilibrium polymers that can be remodeled without proteolytic digestion. Sci. Rep. 2012, 2, 879.
Gersh, K. C.; Zaitsev, S.; Cines, D. B.; Muzykantov, V.; Weisel, J. W. Flow-dependent channel formation in clots by an erythrocyte-bound fibrinolytic agent. Blood 2011, 117, 4964–4967.
Westrick, R. J.; Winn, M. E.; Eitzman, D. T. Murine models of vascular thrombosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 2079–2093.
Liopo, A.; Conjusteau, A.; Tsyboulski, D.; Ermolinsky, B.; Kazansky, A.; Oraevsky, A. Biocompatible gold nanorod conjugates for preclinical biomedical research. J. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. 2012, 6, 274.
Falati, S.; Gross, P.; Merrill-Skoloff, G.; Furie, B. C.; Furie, B. Real-time in vivo imaging of platelets, tissue factor and fibrin during arterial thrombus formation in the mouse. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1175–1180.
Nagai, N.; Vanlinthout, I.; Collen, D. Comparative effects of tissue plasminogen activator, streptokinase, and staphylokinase on cerebral ischemic infarction and pulmonary clot lysis in hamster models. Circulation 1999, 100, 2541–2546.
Small, W.; Wilson, T. S.; Benett, W. J.; Loge, J. M.; Maitland, D. J. Laser-activated shape memory polymer intravascular thrombectomy device. Opt. Express 2005, 13, 8204–8213.
Kuo, W. T.; Odegaard, J. I.; Louie, J. D.; Sze, D. Y.; Unver, K.; Kothary, N.; Rosenberg, J. K.; Hovesepian, D. M.; Hwang, G. L.; Hofmann, L. V. Photothermal ablation with the excimer laser sheath technique for embedded inferior vena cava filter removal: Initial results from a prospective study. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2011, 22, 813–823.
Kharlamov, A. N.; Gabinsky, J. L. Plasmonic photothermic and stem cell therapy of atherosclerotic plaque as a novel nanotool for angioplasty and artery remodeling. Rejuvenation Res. 2012, 15, 222–230.
Walker, J. M.; Zaleski, J. M. Non-enzymatic remodeling of fibrin biopolymers via photothermally triggered radicalgenerating nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 5120–5130.
Choi, J.; Yang, J.; Jang, E.; Suh, J. S.; Huh, Y. M.; Lee, K.; Haam, S. Gold nanostructures as photothermal therapy agent for cancer. Anti-Cancer Agents Med. Chem. 2011, 11, 953–964.
Green, H. N.; Martyshkin, D. V.; Rodenburg, C. M.; Rosenthal, E. L.; Mirov, S. B. Gold nanorod bioconjugates for active tumor targeting and photothermal therapy. J. Nanotechnol. 2011, 2011, Article ID 631753.
Gaffney, P. J.; Whitaker, A. N. Fibrin crosslinks and lysis rates. Thromb. Res. 1979, 14, 85–94.
McDonagh Jr, R. P.; McDonagh, J.; Duckert, F. The influence of fibrin crosslinking on the kinetics of urokinase-induced clot lysis. Br. J. Haematol. 1971, 21, 323–332.
Banerjee, A.; Chisti, Y.; Banerjee, U. C. Streptokinase—A clinically useful thrombolytic agent. Biotechnol. Adv. 2004, 22, 287–307.
Collen, D.; de Cock, F.; Stassen, J. M. Comparative immunogenicity and thrombolytic properties toward arterial and venous thrombi of streptokinase and recombinant staphylokinase in baboons. Circulation 1993, 87, 996–1006.
Betancourt, B. Y.; Marrero-Miragaya, M. A.; Jiménez-López, G.; Valenzuela-Silva, C.; García-Iglesias, E.; Hernández-Bernal, F.; Debesa-García, F.; González-López, T.; Alvarez-Falcón, L.; López-Saura, P. A. et al. Pharmacovigilance program to monitor adverse reactions of recombinant streptokinase in acute myocardial infarction. BMC Clin. Pharmacol. 2005, 5, 5.
Kunitada, S.; FitzGerald, G. A.; Fitzgerald, D. J. Inhibition of clot lysis and decreased binding of tissue-type plasminogen activator as a consequence of clot retraction. Blood 1992, 79, 1420–1427.
Katori, N.; Tanaka, K. A.; Szlam, F.; Levy, J. H. The effects of platelet count on clot retraction and tissue plasminogen activator-induced fibrinolysis on thrombelastography. Anesth. Analg. 2005, 100, 1781–1785.
Leung, J. P.; Wu, S.; Chou, K. C.; Signorell, R. Investigation of sub-100 nm gold nanoparticles for laser-induced thermotherapy of cancer. Nanomaterials 2013, 3, 86–106.
Kennedy, L. C.; Bickford, L. R.; Lewinski, N. A.; Coughlin, A. J.; Hu, Y.; Day, E. S.; West, J. L.; Drezek, R. A. A new era for cancer treatment: Gold-nanoparticle-mediated thermal therapies. Small 2011, 7, 169–183.
Dickerson, E. B.; Dreaden, E. C.; Huang, X. H.; El-Sayed, I. H.; Chu, H. H.; Pushpanketh, S.; McDonald, J. F.; El-Sayed, M. A. Gold nanorod assisted near-infrared plasmonic photothermal therapy (PPTT) of squamous cell carcinoma in mice. Cancer Lett. 2008, 269, 57–66.
Rengan, A. K.; Bukhari, A. B.; Pradhan, A.; Malhotra, R.; Banerjee, R.; Srivastava, R.; De, A. In vivo analysis of biodegradable liposome gold nanoparticles as efficient agents for photothermal therapy of cancer. Nano Lett. 2015, 15, 842–848.
Hudson, D. E.; Hudson, D. O.; Wininger, J. M.; Richardson, B. D. Penetration of laser light at 808 and 980 nm in bovine tssue samples. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2013, 31, 163–168.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
These authors contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, N., Varma, A., Verma, A. et al. Relief from vascular occlusion using photothermal ablation of thrombus with a multimodal perspective. Nano Res. 9, 2327–2337 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1119-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-016-1119-5