Abstract
Method for delivery remains a central component of stem cell-based cardiovascular research. Comparative studies have demonstrated the advantages of administering cell therapy directly into the myocardium, as distinct from infusing cells into the systemic or coronary vasculature. Intramyocardial delivery can be achieved either transepicardially or transendocardially. The latter involves percutaneous, femoral arterial access and the retrograde passage of specially designed injection catheters into the left ventricle, making it less invasive and more relevant to wider clinical practice. Imaging-based navigation plays an important role in guiding catheter manipulation and directing endomyocardial injections. The most established strategy for three-dimensional, intracardiac navigation is currently endoventricular, electromechanical mapping, which offers superior spatial orientation compared to simple x-ray fluoroscopy. Its provision of point-by-point, electrophysiologic and motion data also allows characterization of regional myocardial viability, perfusion, and function, especially in the setting of ischemic heart disease. Integrating the mapping catheter with an injection port enables this diagnostic information to facilitate the targeting of intramyocardial stem cell delivery. This review discusses the diagnostic accuracy and expanding therapeutic application of electromechanical navigation in cell-based research and describes exciting developments which will improve the technology’s sensing capabilities, image registration, and delivery precision in the near future.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amado, L. C., Saliaris, A. P., Schuleri, K. H., St John, M., Xie, J. S., Cattaneo, S., et al. (2005). Cardiac repair with intramyocardial injection of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells after myocardial infarction. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(32), 11474–11479.
Beeres, S. L., Bax, J. J., Dibbets-Schneider, P., Stokkel, M. P., Fibbe, W. E., van der Wall, E. E., et al. (2006). Sustained effect of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cell injection in patients with refractory angina pectoris and chronic myocardial ischemia: twelve-month follow-up results. American Heart Journal, 152(4), 684.e11–684.e16.
Beeres, S. L., Zeppenfeld, K., Bax, J. J., Dibbets-Schneider, P., Stokkel, M. P., Fibbe, W. E., et al. (2007). Electrophysiological and arrhythmogenic effects of intramyocardial bone marrow cell injection in patients with chronic ischemic heart disease. Heart Rhythm, 4(3), 257–265.
Behfar, A., Faustino, R. S., Arrell, D. K., Dzeja, P. P., Perez-Terzic, C., & Terzic, A. (2008). Guided stem cell cardiopoiesis: discovery and translation. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology, 45(4), 523–529.
Ben-Haim, S. A., Osadchy, D., Schuster, I., Gepstein, L., Hayam, G., & Josephson, M. E. (1996). Nonfluoroscopic, in vivo navigation and mapping technology. Natural Medicines, 2(12), 1393–1395.
Botker, H. E., Lassen, J. F., Hermansen, F., Wiggers, H., Sogaard, P., Kim, W. Y., et al. (2001). Electromechanical mapping for detection of myocardial viability in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy. Circulation, 103(12), 1631–1637.
Chazaud, B., Hittinger, L., Sonnet, C., Champagne, S., Le Corvoisier, P., Benhaiem-Sigaux, N., et al. (2003). Endoventricular porcine autologous myoblast transplantation can be successfully achieved with minor mechanical cell damage. Cardiovascular Research, 58(2), 444–450.
Cheng, Y., Sherman, W., Yi, G., Conditt, G., Sheehy, A., Martens, T., et al. (2009). Real time 3D echo guided intramyocardial delivery of mesenchymal precursor cells in a chronic myocardial infarct ovine model using a novel catheter. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 53(10 Suppl A), A41.
Corti, R., Badimon, J., Mizsei, G., Macaluso, F., Lee, M., Licato, P., et al. (2005). Real time magnetic resonance guided endomyocardial local delivery. Heart, 91(3), 348–353.
de Leeuw, N., Ruiter, D. J., Balk, A. H., de Jonge, N., Melchers, W. J., & Galama, J. M. (2001). Histopathologic findings in explanted heart tissue from patients with end-stage idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. Transplant International, 14(5), 299–306.
de Silva, R., Gutierrez, L. F., Raval, A. N., McVeigh, E. R., Ozturk, C., & Lederman, R. J. (2006). X-ray fused with magnetic resonance imaging (XFM) to target endomyocardial injections: validation in a swine model of myocardial infarction. Circulation, 114(22), 2342–2350.
Dib, N., Dinsmore, J., Lababidi, Z., White, B., Moravec, S., Campbell, A., et al. (2009). One-year follow-up of feasibility and safety of the first U.S., randomized, controlled study using 3-dimensional guided catheter-based delivery of autologous skeletal myoblasts for ischemic cardiomyopathy (CAuSMIC study). JACC Cardiovascular Interventions, 2(1), 9–16.
Dick, A. J., Guttman, M. A., Raman, V. K., Peters, D. C., Pessanha, B. S., Hill, J. M., et al. (2003). Magnetic resonance fluoroscopy allows targeted delivery of mesenchymal stem cells to infarct borders in Swine. Circulation, 108(23), 2899–2904.
Dohmann, H. F., Perin, E. C., Takiya, C. M., Silva, G. V., Silva, S. A., Sousa, A. L., et al. (2005). Transendocardial autologous bone marrow mononuclear cell injection in ischemic heart failure: postmortem anatomicopathologic and immunohistochemical findings. Circulation, 112(4), 521–526.
Erbs, S., Linke, A., Adams, V., Lenk, K., Thiele, H., Diederich, K. W., et al. (2005). Transplantation of blood-derived progenitor cells after recanalization of chronic coronary artery occlusion: first randomized and placebo-controlled study. Circulation Research, 97(8), 756–762.
Fernandes, M. R., Silva, G., Cardoso, C. O., Zheng, Y., Baimbridge, F., Cabreira, M. G., et al. (2009). The impact of timing on the safety of transendocardial delivery of mesenchymal precursor stem cells following acute myocardial infarction. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 53(10 Suppl A), A311.
Fernandes, M. R., Silva, G. V., Zheng, Y., Oliveira, E. M., Cardoso, C. O., Canales, J., et al. (2008). Validation of QwikStar catheter for left ventricular electromechanical mapping with NOGA XP system. Texas Heart Institute Journal, 35(3), 240–244.
Fischer-Rasokat, U., Assmus, B., Seeger, F. H., Honold, J., Leistner, D., Fichtlscherer, S., et al. (2009). A pilot trial to assess potential effects of selective intracoronary bone marrow-derived progenitor cell infusion in patients with non-ischemic dilated cardiomyopathy: Final 1-year results of the TOPCARE-DCM trial. Circulation Heart Failure, 2, 417–423.
Freyman, T., Polin, G., Osman, H., Crary, J., Lu, M., Cheng, L., et al. (2006). A quantitative, randomized study evaluating three methods of mesenchymal stem cell delivery following myocardial infarction. European Heart Journal, 27(9), 1114–1122.
Fuchs, S., Hendel, R. C., Baim, D. S., Moses, J. W., Pierre, A., Laham, R. J., et al. (2001). Comparison of endocardial electromechanical mapping with radionuclide perfusion imaging to assess myocardial viability and severity of myocardial ischemia in angina pectoris. American Journal of Cardiology, 87(7), 874–880.
Fuchs, S., Kornowski, R., Shiran, A., Pierre, A., Ellahham, S., & Leon, M. B. (1999). Electromechanical characterization of myocardial hibernation in a pig model. Coronary Artery Disease, 10(3), 195–198.
Fuchs, S., Kornowski, R., Weisz, G., Satler, L. F., Smits, P. C., Okubagzi, P., et al. (2006). Safety and feasibility of transendocardial autologous bone marrow cell transplantation in patients with advanced heart disease. American Journal of Cardiology, 97(6), 823–829.
Gavira, J. J., Nasarre, E., Abizanda, G., Perez-Ilzarbe, M., de Martino-Rodriguez, A., Garcia de Jalon, J. A., et al. (2009). Repeated implantation of skeletal myoblast in a swine model of chronic myocardial infarction. European Heart Journal, (in press).
Gavira, J. J., Perez-Ilzarbe, M., Abizanda, G., Garcia-Rodriguez, A., Orbe, J., Paramo, J. A., et al. (2006). A comparison between percutaneous and surgical transplantation of autologous skeletal myoblasts in a swine model of chronic myocardial infarction. Cardiovascular Research, 71(4), 744–753.
Gepstein, L., Hayam, G., & Ben-Haim, S. A. (1997a). A novel method for nonfluoroscopic catheter-based electroanatomical mapping of the heart. In vitro and in vivo accuracy results. Circulation, 95(6), 1611–1622.
Gepstein, L., Hayam, G., Shpun, S., & Ben-Haim, S. A. (1997b). Hemodynamic evaluation of the heart with a nonfluoroscopic electromechanical mapping technique. Circulation, 96(10), 3672–3680.
Gnecchi, M., He, H., Liang, O. D., Melo, L. G., Morello, F., Mu, H., et al. (2005). Paracrine action accounts for marked protection of ischemic heart by Akt-modified mesenchymal stem cells. Natural Medicines, 11(4), 367–368.
Gnecchi, M., Zhang, Z., Ni, A., & Dzau, V. J. (2008). Paracrine mechanisms in adult stem cell signaling and therapy. Circulation Research, 103(11), 1204–1219.
Graf, S., Gyongyosi, M., Khorsand, A., Nekolla, S. G., Pirich, C., Kletter, K., et al. (2004). Electromechanical properties of perfusion/metabolism mismatch: comparison of nonfluoroscopic electroanatomic mapping with 18F-FDG PET. Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 45(10), 1611–1618.
Grossman, P. M., Han, Z., Palasis, M., Barry, J. J., & Lederman, R. J. (2002). Incomplete retention after direct myocardial injection. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions, 55(3), 392–397.
Gyongyosi, M., Lang, I., Dettke, M., Beran, G., Graf, S., Sochor, H., et al. (2009). Combined delivery approach of bone marrow mononuclear stem cells early and late after myocardial infarction: the MYSTAR prospective, randomized study. Nature Clinical Practice Cardiovascular Medicine, 6(1), 70–81.
Heng, B. C., Hsu, S. H., Cowan, C. M., Liu, A., Tai, J., Chan, Y., et al. (2009). Trans-catheter injection induced changes in human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Transplant (in press).
Hou, D., Youssef, E. A., Brinton, T. J., Zhang, P., Rogers, P., Price, E. T., et al. (2005). Radiolabeled cell distribution after intramyocardial, intracoronary, and interstitial retrograde coronary venous delivery: implications for current clinical trials. Circulation, 112(9 Suppl), I150–I156.
Hsia, H. H., & Marchlinski, F. E. (2002). Characterization of the electroanatomic substrate for monomorphic ventricular tachycardia in patients with nonischemic cardiomyopathy. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology, 25(7), 1114–1127.
Ince, H., Petzsch, M., Rehders, T. C., Chatterjee, T., & Nienaber, C. A. (2004). Transcatheter transplantation of autologous skeletal myoblasts in postinfarction patients with severe left ventricular dysfunction. Journal of Endovascular Therapy, 11(6), 695–704.
Kaye, D. M., Preovolos, A., Marshall, T., Byrne, M., Hoshijima, M., Hajjar, R., et al. (2007). Percutaneous cardiac recirculation-mediated gene transfer of an inhibitory phospholamban peptide reverses advanced heart failure in large animals. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 50(3), 253–260.
Keck, A., Hertting, K., Schwartz, Y., Kitzing, R., Weber, M., Leisner, B., et al. (2002). Electromechanical mapping for determination of myocardial contractility and viability. A comparison with echocardiography, myocardial single-photon emission computed tomography, and positron emission tomography. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 40(6), 1067–1074.
Kornowski, R., Fuchs, S., Shiran, A., Summers, N., Pietrusewicz, M., Ellahham, S., et al. (2001). Catheter-based electromechanical mapping to assess regional myocardial function: a comparative analysis with transthoracic echocardiography. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions, 52(3), 342–347.
Kornowski, R., Hong, M. K., Gepstein, L., Goldstein, S., Ellahham, S., Ben-Haim, S. A., et al. (1998a). Preliminary animal and clinical experiences using an electromechanical endocardial mapping procedure to distinguish infarcted from healthy myocardium. Circulation, 98(11), 1116–1124.
Kornowski, R., Hong, M. K., & Leon, M. B. (1998b). Comparison between left ventricular electromechanical mapping and radionuclide perfusion imaging for detection of myocardial viability. Circulation, 98(18), 1837–1841.
Kornowski, R., Leon, M. B., Fuchs, S., Vodovotz, Y., Flynn, M. A., Gordon, D. A., et al. (2000). Electromagnetic guidance for catheter-based transendocardial injection: a platform for intramyocardial angiogenesis therapy. Results in normal and ischemic porcine models. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 35(4), 1031–1039.
Krause, K., Jaquet, K., Schneider, C., Haupt, S., Lioznov, M. V., Otte, K. M., et al. (2009). Percutaneous intramyocardial stem cell injection in patients with acute myocardial infarction: first-in-man study. Heart, 95(14), 1145–1152.
Lau, G. T., Yoneyama, R., Kawase, Y., Ly, H. Q., Hoshino, K., Pomerantseva, I., et al. (2009). Accuracy of non-fluoroscopic cather based electromechanically-guided (NOGA) mononuclear cell endocardial injection in a swine myocardial infarction model assessed by MRI. Heart, Lung and Circulation, 18(Suppl 3), S73.
Leon, M. B., Kornowski, R., Downey, W. E., Weisz, G., Baim, D. S., Bonow, R. O., et al. (2005). A blinded, randomized, placebo-controlled trial of percutaneous laser myocardial revascularization to improve angina symptoms in patients with severe coronary disease. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 46(10), 1812–1819.
Leri, A., Kajstura, J., & Anversa, P. (2005). Cardiac stem cells and mechanisms of myocardial regeneration. Physiological Reviews, 85(4), 1373–1416.
Losordo, D. W., Schatz, R. A., White, C. J., Udelson, J. E., Veereshwarayya, V., Durgin, M., et al. (2007). Intramyocardial transplantation of autologous CD34+ stem cells for intractable angina: a phase I/IIa double-blind, randomized controlled trial. Circulation, 115(25), 3165–3172.
Martens, T. P., Godier, A. F., Parks, J. J., Wan, L. Q., Koeckert, M. S., Eng, G. M., et al. (2009). Percutaneous cell delivery into the heart using hydrogels polymerizing in situ. Cell Transplantation, 18(3), 297–304.
Menasche, P., Alfieri, O., Janssens, S., McKenna, W., Reichenspurner, H., Trinquart, L., et al. (2008). The myoblast autologous grafting in ischemic cardiomyopathy (MAGIC) trial: first randomized placebo-controlled study of myoblast transplantation. Circulation, 117(9), 1189–1200.
Opie, S. R., & Dib, N. (2006). Surgical and catheter delivery of autologous myoblasts in patients with congestive heart failure. Nature Clinical Practice Cardiovascular Medicine, 3(Suppl 1), S42–S45.
Perin, E. C., Dohmann, H. F., Borojevic, R., Silva, S. A., Sousa, A. L., Mesquita, C. T., et al. (2003). Transendocardial, autologous bone marrow cell transplantation for severe, chronic ischemic heart failure. Circulation, 107(18), 2294–2302.
Perin, E. C., Dohmann, H. F., Borojevic, R., Silva, S. A., Sousa, A. L., Silva, G. V., et al. (2004). Improved exercise capacity and ischemia 6 and 12 months after transendocardial injection of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells for ischemic cardiomyopathy. Circulation, 110(11 Suppl 1), II213–II218.
Perin, E. C., Silva, G. V., Assad, J. A., Vela, D., Buja, L. M., Sousa, A. L., et al. (2008). Comparison of intracoronary and transendocardial delivery of allogeneic mesenchymal cells in a canine model of acute myocardial infarction. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology, 44(3), 486–495.
Perin, E. C., Silva, G. V., Fernandes, M. R., Munger, T., Pandey, A., Sehra, R., et al. (2007). First experience with remote left ventricular mapping and transendocardial cell injection with a novel integrated magnetic navigation-guided electromechanical mapping system. Eurointervention, 3(1), 142–148.
Perin, E. C., Silva, G. V., Sarmento-Leite, R., Sousa, A. L., Howell, M., Muthupillai, R., et al. (2002). Assessing myocardial viability and infarct transmurality with left ventricular electromechanical mapping in patients with stable coronary artery disease: validation by delayed-enhancement magnetic resonance imaging. Circulation, 106(8), 957–961.
Poh, K. K., Sperry, E., Young, R. G., Freyman, T., Barringhaus, K. G., & Thompson, C. A. (2007). Repeated direct endomyocardial transplantation of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells: safety of a high dose, “off-the-shelf”, cellular cardiomyoplasty strategy. International Journal of Cardiology, 117(3), 360–364.
Pompilio, G., Steinhoff, G., Liebold, A., Pesce, M., Alamanni, F., Capogrossi, M. C., et al. (2008). Direct minimally invasive intramyocardial injection of bone marrow-derived AC133+ stem cells in patients with refractory ischemia: preliminary results. Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgeon, 56(2), 71–76.
Poppas, A., Sheehan, F. H., Reisman, M., Harms, V., & Kornowski, R. (2004). Validation of viability assessment by electromechanical mapping by three-dimensional reconstruction with dobutamine stress echocardiography in patients with coronary artery disease. American Journal of Cardiology, 93(9), 1097–1101.
Psaltis, P. J., Carbone, A., Nelson, A., Lau, D. H., Manavis, J., Finnie, J., et al. (2008a). An ovine model of toxic, nonischemic cardiomyopathy—assessment by cardiac magnetic resonance imaging. Journal of Cardiac Failure, 14(9), 785–795.
Psaltis, P. J., Gronthos, S., Worthley, S. G., & Zannettino, A. C. W. (2008b). Cellular therapy for cardiovascular disease part 2—delivery of cells and clinical experience. Clinical Medicine: Cardiology, 2, 139–151.
Psaltis, P. J., Nelson, A. J., Carbone, A., Lau, D. H., Jantzen, T., Williams, K., et al. (2009). Cardiac repair with intramyocardial injection of allogeneic mesenchymal precursor cells for experimental nonischaemic cardiomyopathy. Heart, Lung and Circulation, 18(Suppl 3), S74.
Psaltis, P. J., & Worthley, S. G. (2009). Endoventricular electromechanical mapping—the diagnostic and therapeutic utility of the NOGA® XP Cardiac Navigation System. Journal of Cardiovascular Translational Research, 2(1), 48–62.
Psaltis, P. J., Zannettino, A. C., Worthley, S. G., & Gronthos, S. (2008c). Concise review: mesenchymal stromal cells: potential for cardiovascular repair. Stem Cells, 26(9), 2201–2210.
Rezaee, M., Yeung, A. C., Altman, P., Lubbe, D., Takeshi, S., Schwartz, R. S., et al. (2001). Evaluation of the percutaneous intramyocardial injection for local myocardial treatment. Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions, 53(2), 271–276.
Schachinger, V., Erbs, S., Elsasser, A., Haberbosch, W., Hambrecht, R., Holschermann, H., et al. (2006). Intracoronary bone marrow-derived progenitor cells in acute myocardial infarction. New England Journal of Medicine, 355(12), 1210–1221.
Siminiak, T., Fiszer, D., Jerzykowska, O., Grygielska, B., Rozwadowska, N., Kalmucki, P., et al. (2005). Percutaneous trans-coronary-venous transplantation of autologous skeletal myoblasts in the treatment of post-infarction myocardial contractility impairment: the POZNAN trial. European Heart Journal, 26(12), 1188–1195.
Smeets, J. L., Ben-Haim, S. A., Rodriguez, L. M., Timmermans, C., & Wellens, H. J. (1998). New method for nonfluoroscopic endocardial mapping in humans: accuracy assessment and first clinical results. Circulation, 97(24), 2426–2432.
Smits, P. C., van Geuns, R. J., Poldermans, D., Bountioukos, M., Onderwater, E. E., Lee, C. H., et al. (2003). Catheter-based intramyocardial injection of autologous skeletal myoblasts as a primary treatment of ischemic heart failure: clinical experience with six-month follow-up. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 42(12), 2063–2069.
Smits, P. C., van Langenhove, G., Schaar, M., Reijs, A., Bakker, W. H., van der Giessen, W. J., et al. (2002). Efficacy of percutaneous intramyocardial injections using a nonfluoroscopic 3-D mapping based catheter system. Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy, 16(6), 527–533.
Steendijk, P., Smits, P. C., Valgimigli, M., van der Giessen, W. J., Onderwater, E. E., & Serruys, P. W. (2006). Intramyocardial injection of skeletal myoblasts: long-term follow-up with pressure-volume loops. Nature Clinical Practice Cardiovascular Medicine, 3(Suppl 1), S94–S100.
Takahashi, K., & Yamanaka, S. (2006). Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell, 126(4), 663–676.
Theiss, H. D., David, R., Engelmann, M. G., Barth, A., Schotten, K., Naebauer, M., et al. (2007). Circulation of CD34+ progenitor cell populations in patients with idiopathic dilated and ischaemic cardiomyopathy (DCM and ICM). European Heart Journal, 28(10), 1258–1264.
Tse, H. F., Thambar, S., Kwong, Y. L., Rowlings, P., Bellamy, G., McCrohon, J., et al. (2007). Prospective randomized trial of direct endomyocardial implantation of bone marrow cells for treatment of severe coronary artery diseases (PROTECT-CAD trial). European Heart Journal, 28(24), 2998–3005.
Vale, P. R., Losordo, D. W., Milliken, C. E., Maysky, M., Esakof, D. D., Symes, J. F., et al. (2000). Left ventricular electromechanical mapping to assess efficacy of phVEGF(165) gene transfer for therapeutic angiogenesis in chronic myocardial ischemia. Circulation, 102(9), 965–974.
Vale, P. R., Losordo, D. W., Tkebuchava, T., Chen, D., Milliken, C. E., & Isner, J. M. (1999). Catheter-based myocardial gene transfer utilizing nonfluoroscopic electromechanical left ventricular mapping. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 34(1), 246–254.
van Ramshorst, J., Bax, J. J., Beeres, S. L., Dibbets-Schneider, P., Roes, S. D., Stokkel, M. P., et al. (2009). Intramyocardial bone marrow cell injection for chronic myocardial ischemia: a randomized controlled trial. Journal of the American Medical Association, 301(19), 1997–2004.
Vulliet, P. R., Greeley, M., Halloran, S. M., MacDonald, K. A., & Kittleson, M. D. (2004). Intra-coronary arterial injection of mesenchymal stromal cells and microinfarction in dogs. Lancet, 363(9411), 783–784.
Wiggers, H., Botker, H. E., Sogaard, P., Kaltoft, A., Hermansen, F., Kim, W. Y., et al. (2003). Electromechanical mapping versus positron emission tomography and single photon emission computed tomography for the detection of myocardial viability in patients with ischemic cardiomyopathy. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 41(5), 843–848.
Wolf, T., Gepstein, L., Dror, U., Hayam, G., Shofti, R., Zaretzky, A., et al. (2001). Detailed endocardial mapping accurately predicts the transmural extent of myocardial infarction. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 37(6), 1590–1597.
Acknowledgements
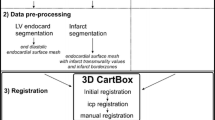
The authors thank Dr. Emerson Perin and Mr. Fred Baimbridge (Texas Heart Institute, Houston, TX, USA) for kindly providing the image in Fig. 3. The authors have no financial conflicts to report. Dr. Psaltis is supported by a Postgraduate Medical Scholarship from the National Health and Medical Research Council of Australia (ID 390711) and the National Heart Foundation of Australia (PB 05A 2312) and a Dawes Scholarship from the Royal Adelaide Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Psaltis, P.J., Zannettino, A.C.W., Gronthos, S. et al. Intramyocardial Navigation and Mapping for Stem Cell Delivery. J. of Cardiovasc. Trans. Res. 3, 135–146 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-009-9138-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12265-009-9138-1