Abstract
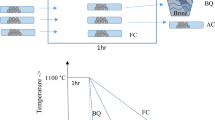
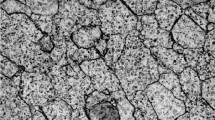
We investigated the influence of heat treated microstructures, namely, equiaxed, bimodal and lamella types of Ti–6Al–4V alloy on the dynamic deformation characteristics. Four different heat treatment conditions were employed for the development of the microstructures. Static tensile and compressive deformation tests were preliminarily performed with hydraulic test equipment. Dynamic deformation tests at a high level of strain rate, 2700 s−1 ∼ 6400 s−1, together with high velocity impact tests were, respectively, conducted on the specimens through a compressive Split Hopkinson pressure bar (SHPB) and a high pressure gas gun system. The dependence of flow stress on the strain rate associated with the corresponding microstructure was examined. The microstructural factors on the dynamic fracture characteristics were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy. The static compressive tests showed that the flow stress was greatest in the lamella microstructure and decreased in the order of lamella, bimodal and equiaxed microstructures, whereas the ductility was largest in the bimodal microstructure and smallest in the lamellar microstructure. In dynamic compressive tests, a similar dependency of the flow stress on microstructures was observed: highest in the lamellar microstructure and lowest in the equiaxed microstructure. The ductility, such as strain at maximum stress or at failure, was highest in the equiaxed microstructure and lowest in the lamellar structure. In addition, the ductility for individual microstructure decreased as the strain rate increased. Every microstructure exhibited ductile fracture surfaces, and it seems that a large shear crack on the lateral surface in the specimen was the main factor inducing the final failure. The result of high velocity impact test exhibited that the resistance to fracture of equiaxed microstructure with superior dynamic toughness was much higher than that of lamella microstructure with inferior dynamic toughness. The results obtained help provide a fundamental idea and guide to improve the dynamic mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V alloy through the microstructure control.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. A. Greenfield and H. Margolin, Mechanism of void formation, void growth, and tensile fracture in an alloy consisting of two ductile phases, Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 3 (1972) 2649–2659.
D. Eylon, J. A. Hall, C. M. Pierce and D. L. Ruckel, Microstructure and mechanical properties relationships in the Ti-11 alloy at room and elevated temperatures, Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 7 (1976) 1817–1826.
A. Gysler and G. Lütjering, Influence of test temperature and microstructure on the tensile properties of titanium alloys, Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 13 (1982) 1435–1443.
W. Lee and C. Lin, Plastic deformation and fracture behaviour of Ti-6Al-4V alloy loaded with high strain rate under various temperatures, Materials Science and Engineering A, 241 (1998) 48–59.
S. L. Semiatin and T. R. Bieler, Effect of texture changes on flow softening during hot working of Ti-6Al-4V, Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 32 (2001) 1871–1875.
B. K. Kad, S. E. Schoenfeld and M. S. Burkins, Through thickness dynamic impact response in textured Ti-6Al-4V plates, Materials Science and Engineering A, 322 (2002) 241–251.
K. Suzuki and M. Yao, Simulation of mold filling and solidification during centrifugal precision casting of Ti-6Al-4V alloy, Metals and Materials International, 10 (2004) 33–38.
S. P. Timothy and I. M. Hutchings, The structure of adiabatic shear bands in a titanium alloy, Acta Metallurgica, 33 (1985) 667–676.
H. T. Li, Y. M. Zhang and D. Z. Yang, Micro-damage of Ti–6Al-4V alloy under hypervelocity projectile impact, Materials Science and Engineering A, 292 (2000) 130–132.
S. Nemat-Nasser, W-G. Guo, V. Nesterenko, S. S. Indrakanti and Y. B. Gu, Dynamic response of conventional and hot isostatically pressed Ti-6Al-4V alloys: experiments and modeling, Mechanics of Materials, 33 (2001) 425–439.
D. G. Lee, S. Lee and C. S. Lee, Quasi-static and dynamic deformation behavior of Ti-6Al-4V alloy containing fine 2-Ti3Al precipitates, Materials Science and Engineering A, 366 (2004) 25–37.
D. Bhattacharyya, G. B. Viswanathan, S. C. Vogel, D. J. Williams, V. Venkatesh and H. L. Fraser, A study of the mechanism of a to b phase transformation by tracking texture evolution with temperature in Ti–6Al–4V using neutron diffraction, Scripta Materialia, 54 (2006) 231–236.
B. D. Venkatesh, D. L. Chen and S. D. Bhole, Effect of heat treatment on mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-4V ELI alloy, Materials Science and Engineering A, 506 (2009) 117–124.
B. B. Singh, G. Sukumar, A. Bhattacharjee, K. S. Kumar, T. B. Bhat and A. K. Gogia, Effect of heat treatment on ballistic impact behavior of Ti-6Al-4V against 7.62 mm deformable projectile, Materials & Design, 36 (2012) 640–649.
H. Kolsky, An investigation of the mechanical studies in plastic wave propagation, J. of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids, 10 (1949) 195–223.
C. Ruiz and R. A. W. Mines, The hopkinson pressure bar: an alternative to the instrumented pendulum for charpy tests, International J. of Fracture, 29 (1985) 101–109.
F. S. Lin, E. A. Starke, S. B. Chakrabortty and A. Gysler, The effect of microstructure on the deformation modes and mechanical properties of Ti-6Al-2Nb-1Ta-0.8Mo: Part I. Widmanstätten structures, Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 15 (1982) 1229–1246.
H. A. Rastegari, S. Asgari and S. M. Abbasi, Producing Ti–6Al-4V/TiC composite with good ductility by vacuum induction melting furnace and hot rolling process, Materials & Design, 32 (2011) 5010–5014.
J. X. Li et al., The effect of heat treatment on thermal stability of Ti matrix composite, J. of Alloys and Compounds, 509 (1) (2009) 52–56.
D. J. Mceldowney, S. Tamirisakandala and D. B. Miracle, Heat-treatment effects on the microstructure and tensile properties of powder metallurgy Ti-6Al-4V alloys modified with boron, Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 41 (2010) 1003–1015.
J. Luo, M. Li, W. Yu and H. Li, The variation of strain rate sensitivity exponent and strain hardening exponent in isothermal compression of Ti-6Al-4V alloy, Materials & Design, 31 (2010) 741–748.
P. K. Jena, B. Mishra, K. Siva Kumar and T. B. Bhat, An experimental study on the ballistic impact behavior of some metallic armour materials against 7.62 mm deformable projectile, Materials & Design, 31 (2010) 3308–3316.
B. Srivathsa and N. Ramakrishnan, Ballistic performance for thick metallic armour, J. Mater. Process Technol., 96 (1999) 81–91.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Recommended by Associate Editor Youngseog Lee
Yongseok Seo earned a B.S. of Mechanical Engineering from Chonnam national University in 1987. He was awarded a M.S. Degree in Mechanical Engineering from Chonnam National University in 1990. He currently serves as a Principle Researcher in Agency for Defense Development. He is interesting in the area of impact mechanics and hydrodynamics.
YoungShin Lee received a B.S. degree in Mechanical Engineering from Yonsei University, Korea in 1972. He received master and Ph.D. in Mechanical Engineering from Yonsei University, Korea in 1974 and 1980, respectively. He is currently professor of Department of Mechanical Design Engineering at Chungnam National University, Korea. Prof. Lee's research interests are in area of impat mechnics, optimal design, biomechanical nanlysis and shell structure analysis.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, Y., Woo, SC., Kim, TW. et al. Influence of heat treated microstructures on the dynamic deformation characteristics of Ti-6Al-4V alloy. J Mech Sci Technol 29, 5223–5232 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-015-1122-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12206-015-1122-x