Abstract
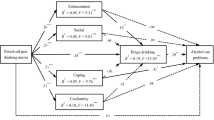
The present research continues to test the hypothesis from Akers’ Social Structure-Social Learning Theory (1998) that the effects of structural variables will be mediated by social learning processes. The present research uses Core Alcohol and Drug Survey data from eight diverse college campuses throughout the United States to study binge drinking. This research examines 13 structural features for a full range of college students. The results indicate the social learning variables (rewards, punishments and definitions) mediated most of the structural effects of binge drinking. There were significant interactions, which are not predicted by Akers. The paper discusses the implication of these findings for Akers’ mediation hypothesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnew, R. (1992). Foundation for a general strain theory of crime and delinquency. Criminology, 30, 47–88.
Akers, R. L. (1973). Deviant behavior: A social learning approach (Wadsworth, Ed.). Belmont: Wadsworth.
Akers, R. L. (1977). Deviant behavior: A social learning approach (2nd ed.). Belmont: Wadsworth.
Akers, R. L. (1985). Deviant behavior: A social learning approach (3rd ed.). Belmont: Wadsworth.
Akers, R. L. (1994). Criminological theories: Introduction and evaluation. Los Angeles: Roxbury.
Akers, R. L. (1998). Social learning and social structure: A general theory of crime and deviance. Boston: Northeastern University Press.
Akers, R. L. (1999). Social learning and social structure: Reply to Sampson. Morash, and Krohn, Theoretical Criminology, 3, 477–493.
Akers, R. L. (2000). Criminological theories: Introduction and evaluation (2nd ed.). Los Angeles: Roxbury.
Akers, R. L., Krohn, M. D., Lanza-Kaduce, L., & Radosevich, M. (1979). Social learning and deviant behavior: A specific test of a general theory. American Sociological Review, 44, 635–655.
Akers, R. L., La Greca, A. J., Cochran, J., & Sellers, C. (1989). Social learning theory and alcohol behavior among the elderly. Sociological Quarterly, 30, 625–638.
Akers, R. L., & Lee, G. (1996). A longitudinal test of social learning theory: Adolescent smoking. Journal of Drug Issues, 26, 317–343.
Bachman, J. G., O’Malley, P. M., & Johnston, L. D. (1984). Drug use among young adults: The impacts of role status and social environment. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 47(3), 629–645.
Baer, J. S., Kiviahan, D. R., & Mariatt, G. A. (1995). High-risk drinking across the transition from high school to college. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 19, 54–61.
Baron, R. M., & Kenny, D. A. (1986). The moderator-mediator variable distinction in social psychological research: Conceptual, strategic, and statistical considerations. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 51, 1173–1182.
Bartusch, D., Jeglum, R., Lyman, D. R., Moffitt, T. E., & Silva, P. A. (1997). Is age important? Testing a general versus a developmental theory of antisocial behavior. Criminology, 35, 13–48.
Burgess, R. L., & Akers, R. L. (1966). A differential association-reinforcement theory of criminal behavior. Social Problems, 14, 128–147.
Department of Health and Human Services. (2000). Healthy people 2010: Understanding and improving health and objectives for improving health. Washington: GPO.
Dowdall, G. W., Lee, H., Kuo, M., & Weschler, H. (2000). Environmental correlates of underage alcohol use and related problems of college students. Journal of Preventative Medicine, 19(1), 24–29.
Elliot, D. S., Huizinga, D., & Ageton, S. S. (1985). Explaining delinquency and drug use. Beverly Hills: Sage.
Frintner, M. P., & Rubinson, L. (1993). Acquaintance rape: The influence of alcohol, fraternity membership and sports team membership. Journal of Sex Education and Therapy, 19(4), 272–284.
Geller, E. S., & Kalsher, M. J. (1990). Environmental determinants of party drinking: Bartenders verses self-service. Environment and Behavior, 22(1), 74–90.
Grucza, R. A., Norberg, M. D., & Bierut, L. J. (2009). Binge drinking among youths and adults in the United States. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 48, 692–702.
Harrington, N. G., Brigham, N. L., & Clayton, R. R. (1997). Differences in alcohol use and alcohol-related problems among fraternity and sorority members. Drug and Alcohol Dependence, 47, 237–246.
Knight, J. R., Wechsler, H., Kuo, M., Seibring, M., Weitzman, E. R., & Schuckit, M. A. (2002). Alcohol abuse and dependence among United States college students. Journal of Studies of Alcohol, 63(3), 263–270.
Koss, M. P., & Gaines, J. S. (1993). The prediction of sexual aggression by alcohol use, athletic participation and fraternity affiliation. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 8(1), 94–108.
Krohn, M. (1999). Social learning theory: The continuing development of a perspective. Theoretical Criminology, 3, 462–476.
Krohn, M. D., Lanza-Kaduce, L., & Akers, R. L. (1984). Community context and theories of criminal behavior: An examination of social learning and social bonding theories. Sociological Quarterly, 25, 353–371.
Krohn, M. D., Skinner, W. F., Massey, J. L., & Akers, R. L. (1985). Social learning theory and adolescent cigarette smoking: A longitudinal study. Social Problems, 32, 455–473.
Lanza-Kaduce, L., Akers, R. L., Krohn, M. D., & Radosevich, M. (1982). Conceptual and analytical models in testing social learning theory: Reply to Stafford, Ekland-Olsen and Strictland. American Sociological Review, 47, 169–173.
Lanza-Kaduce, L., & Capece, M. (2003). Social structure/social learning theory (SSSL) and binge drinking: A specific test of an integrated general theory. In R. L. Akers & G. F. Jensen (Eds.), Social learning theory and the explanation of crime: A guide for the new century. Advances in Criminological Theory (11) (pp. 179–196). Newark, NJ: Transaction Publishing.
Lanza-Kaduce, L., Capece, M., & Alden, H. (2006). Liquor is quicker: Gender and social learning among college students. Criminal Justice Policy Review, 7, 127–143.
Lanza-Kaduce, L., & Klug, M. (1986). Learning to cheat: The interaction of moral-development and social learning theories. Deviant Behavior, 7, 243–259.
Lee, G., Akers, R. L., & Borg, M. J. (2004). Social learning and structural factors in adolescent substance use. Western Criminology Review., 5, 17–34.
Lieberman, J. I. (2002). Under the influence: The binge drinking epidemic on college campuses. United States Senate, Committee on Governmental Affairs. Washington, D.C.: USGOP.
Liska, A. E., Krohn, M. D., & Messner, S. F. (1989). Strategies and requisites for the theoretical integration in the study of crime and deviance. In S. F. Messner, M. D. Krohn, & A. E. Liska (Eds.), Theoretical integration in the study of deviance and crime (pp. 1–20). Albany: State University of New York Press.
Miller, M. E., Melnick, M. J., Farrell, M. P., Sabo, D. F., & Barnes, G. M. (2006). Jocks, gender, binge drinking, and adolescent violence. Journal of Interpersonal Violence, 21, 105–120.
Morris, R. G., & Higgins, G. E. (2010). Criminological theory in the digital age: The case of social learning theory and digital piracy. Journal of Criminal Justice, 38, 470–480.
Naimi, T. S., Brewer, R. D., Mokdad, A., Denny, C., Serdula, M. K., & Marks, J. S. (2003). Binge drinking among U.S. adults. Journal of the American Medical Association, 289(1), 70–75.
O’Malley, P. M., & Johnston, L. D. (2002). Epidemiology of alcohol and other drug use among American college students. Journal for Study of Alcohol, 14, 23–39.
Perkins, W. H. (2002). Surveying the damage: A review of research on consequences of alcohol misuse in college populations. Journal for the Study of Alcohol, 14, 91–100.
Plant, M. A., Plant, M. L., Miller, P., Gmel, G., & Kuntsche, S. (2009). The social consequences of binge drinking: A comparison of young adults in six European countries. Journal of Addictive Diseases, 28, 294–308.
Powell, L. M., Czart-Ciecierski, C. U., Chaloupka, F. J., & Weschler, H. (2002). Binge drinking and violence among college students: Sensitivity to correlation in the unobservable. Research Paper Series No. 20. ImpacTeen.
Sampson, R. J., & Laub, J. H. (1993). Crime in the making: Pathways and turning points through life. Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
Shalala, D. E. (1995). Alcohol alert—message from Secretary of Health and Human Services. Department of Health and Human Services. Washington, D.C.: National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism.
Simpson, S., & Ellis, L. (1995). Doing gender: Sorting out the caste and crime conundrum. Criminology, 33, 47–82.
Tampke, D. R. (1990). Alcohol behavior, risk perception, and fraternity and sorority membership. National Association of Student Personnel Administrators Journal, 28, 71–77.
Thornberry, T. P. (1987). Towards an interactional theory of delinquency. Criminology, 25, 863–891.
Wechsler, H. (1996). Alcohol and the american college campus: A report from the Harvard School of Public Health. Change, 28, 20–25. 60.
Wechsler, H., Davenport, A., Dowdall, G., Moeykens, B., & Castillo, S. (1994). Health and behavioral consequences of binge drinking in college: A national survey of students on 140 campuses. Journal of the American Medical Association, 272, 1672–77.
Wechsler, H., Dowdall, G. W., Maenner, G., Gledhill-Hoyt, J., & Lee, H. (1998). Changes in binge drinking and related problems among American college students between 1993 and 1997: Results of the Harvard School of Public Health College Alcohol Study. Journal of American College Health, 47, 57–68.
Wechsler, H., Kuh, G., & Davenport, A. E. (1996). Fraternities, sororities and binge drinking: Results from a national study of American colleges. National Association of Student Personnel Administrators Journal, 33, 260–279.
Wechsler, H., Lee, J. E., Kuo, M., & Lee, H. (2000). College binge drinking in the 1990s: A continuing problem. Results of the Harvard School of Public Health 1999 College Alcohol Study. Journal of American College Health, 48, 199–210.
Wechsler, H., Lee, J. E., Kuo, M., Seibring, M., Nelson, T. F., & Lee, H. (2002). Trends in college binge drinking during a period of increased prevention efforts: Findings from four Harvard School of Public Health College Alcohol Study surveys: 1993–2001. Journal of American College Health, 50, 203–217.
Wechsler, H., Moeykens, B., Davenport, A., Castillo, S., & Hansen, J. (1995). The adverse impact of heavy episodic drinkers on other college students. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 56(6), 628–634.
Wechsler, H., Nelson, T. F., Lee, J. E., Seibring, M., Lewis, C., & Keeling, R. P. (2003). Perception and reality: A national evaluation of social norms marketing interventions to reduce college students’ heavy alcohol use. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 64(4), 484.
Wechsler, H., & Wuethrich, B. (2002). Dying to drink: Binge drinking on college campuses. Pennsylvania: Rodale Books.
Weitzman, E. R., Nelson, T. F., & Wechsler, H. (2003). Taking up binge drinking in college: The influences of person, social group, and environment. Journal of Adolescent Health, 32(1), 26–35.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Capece, M., Lanza-Kaduce, L. Binge Drinking Among College Students: A Partial Test of Akers’ Social Structure-Social Learning Theory. Am J Crim Just 38, 503–519 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12103-013-9208-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12103-013-9208-4