Abstract
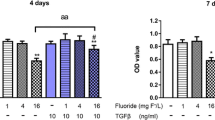
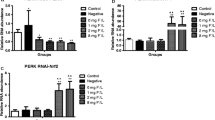
The role of insulin signaling on the mechanism underlying fluoride induced osteopathology was studied. We analyzed the expression of genes related with bone turnover and insulin signaling in rats treated by varying dose of fluoride with or without streptozotocin (STZ) in vivo. Furthermore, insulin receptor (InR) expression in MC3T3-E1 cells (pre-osteoblast cell line) was interfered with small interfering RNA (siRNA), and genes related with osteoblastic and osteoclastic differentiation were investigated in cells exposed to fluoride in vitro for 2 days. The in vivo study indicated the possible role of insulin in bone lesion induced by excessive amount of fluoride. Fluoride activated the InR and Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) signaling, which were involved in the mechanism underlying fluoride induced bone turnover. The TGFβ1 and Wnt10/β-catenin pathway took part in the mechanism of bone lesion induced by fluoride, and insulin probably modulated the TGFβ1 and β-catenin to exert action on bone turnover during the development of bone lesion. The in vitro study showed the concomitant decrease of OPG, osterix and OCN with inhibition of InR expression in osteoblast, and three genes still was low in cells co-treated with fluoride and InR siRNA, which suggested that fluoride probably stimulated the expression of OPG, osterix and OCN through InR signaling. In conclusion, insulin played the important role in bone lesion induced by excessive amount of fluoride through mediating InR receptor signaling, and IGF1 signaling probably exerted action on bone turnover caused by overdose of fluoride.








Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Christie DP (1980) The spectrum of radiographic bone changes in children with fluorosis. Radiology 136(1):85–90
Wang W, Kong L, Zhao H, et al. (2007) Thoracic ossification of ligamentum flavum caused by skeletal fluorosis. Eur Spine J 16(8):1119–1128
Faienza MF, Luce V, Ventura A, et al. (2015) Skeleton and glucose metabolism: a bone-pancreas loop. Int J Endocrinol 2015:758148
Pramojanee SN, Phimphilai M, Chattipakorn N, et al. (2014) Possible roles of insulin signaling in osteoblasts. Endocr Res 39(4):144–151
Lupo M, Buzalaf MA, Rigalli A (2011) Effect of fluoridated water on plasma insulin levels and glucose homeostasis in rats with renal deficiency. Biol Trace Elem Res 140(2):198–207
Hu CY, Ren LQ, Li XN, et al. (2012) Effect of fluoride on insulin level of rats and insulin receptor expression in the MC3T3-E1 cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 150(1–3):297–305
Yang C, Zhang M, Li Y, et al. (2015) Streptozotocin aggravated osteopathology and insulin induced osteogenesis through co-treatment with fluoride. Biol Trace Elem Res. doi:10.1007/s12011-015-0374-8
Strunecka A, Patocka J, Blaylock RL, et al. (2007) Fluoride interactions: from molecules to disease. Curr Signal Transduct Ther 2007; 2(3):190–213
Sun F, Li X, Yang C, Lv P, et al. (2014) A role for PERK in the mechanism underlying fluoride-induced bone turnover. Toxicology 325:52–66
Fulzele K, Clemens TL (2012) Novel functions for insulin in bone. Bone 50(2):452–456
Pun KK, Lau P, Ho PW (1989) The characterization, regulation, and function of insulin receptors on osteoblast-like clonal osteosarcoma cell line. J Bone Miner Res 4(6):853–862
Lau KH, Goodwin C, Arias M, et al. (2002) Bone cell mitogenic action of fluoroaluminate and aluminum fluoride but not that of sodium fluoride involves upregulation of the insulin-like growth factor system. Bone 30(5):705–711
Fulzele K, Riddle RC, DiGirolamo DJ, et al. (2010) Insulin receptor signaling in osteoblasts regulates postnatal bone acquisition and body composition. Cell 142(2):309–319
Sims NA, Martin TJ (2014) Coupling the activities of bne formation and resorption: a multitude of signals within the basic multicellular unit. Bonekey Rep 3:481
Saidak Z, Le Henaff C, Azzi S, et al. (2015) Wnt/β-catenin signaling mediates osteoblast differentiation triggered by peptide-induced α5β1 integrin priming in mesenchymal skeletal cells. J Biol Chem 290(11):6903–6912
Kobayashi Y, Uehara S, Koide M, et al. (2015) The regulation of osteoclast differentiation by Wnt signals. Bonekey Rep 4:713
Ferron M, Wei J, Yoshizawa T, et al. (2010) Insulin signaling in osteoblasts integrates bone remodeling and energy metabolism. Cell 2010; 142(2):296–308
Randhawa RS (2008) The insulin-like growth factor system and fetal growth restriction. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev 6(2):235–240
Thrailkill K, Bunn RC, Lumpkin Jr C, et al. (2014) Loss of insulin receptor in osteoprogenitor cells impairs structural strength of bone. J Diabetes Res 2014:703589
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant for skeletal fluorosis research from National Natural Science Foundation of China [81072249], the Norman Bethune Program of Jilin University [2012222] and Doctoral Fund of Ministry of Education of China [20130061110084].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Liu, H., Yu, X. et al. Analysis of the Role of Insulin Signaling in Bone Turnover Induced by Fluoride. Biol Trace Elem Res 171, 380–390 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0555-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-015-0555-5