Abstract
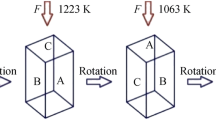
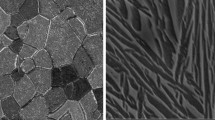
The effects of temperature and thermomechanical loading on the tensile strength and hardness were studied for a rolled, low-cost metastable β titanium alloy, Ti-13Cr-1Fe-3Al (wt.%). Tensile tests were performed at temperatures between room temperature (RT) and 410°C. The results indicated that the ultimate tensile strength (UTS) decreased with increasing temperatures up to 300°C. However, the UTS was 1400 MPa at 410°C, which was approximately 150% higher than the RT UTS. It is believed that the formation of nanoscale ω and α precipitates, identified using transmission electron microscopy, hindered the dislocation motion, which resulted in the exceptionally high UTS at 410°C. However, ductility was maintained, as the elongation-to-failure (εf) was ~ 10% at 410°C. Dynamic mechanical analysis suggested that phase transformations occurred between 370°C–475°C. To evaluate the effect of the phase transformations on the hardness, the as-received material was heat treated at 400°C, 450°C, and 500°C for 2 h, which resulted in hardness values of approximately 340 Hv, 380 Hv, and 470 Hv, respectively. However, the greatest hardness value (500 Hv) was exhibited by the as-received material after it was tensile tested at 410°C. This suggested that both temperature and loading history affected the phase transformations. As all the samples exhibited a ductile fracture mode, this work indicates that it is possible to maintain both high strength and adequate εf for Ti-13Cr-1Fe-3Al (wt.%).










Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Brozek, F. Sun, P. Vermaut, Y. Millet, A. Lenain, D. Embury, and F. Prima, Scr. Mater. 114, 60 (2016).
T. Gloriant, G. Texier, F. Sun, I. Thibon, F. Prima, and J. Soubeyroux, Scr. Mater. 58, 271 (2008).
T. Grosdidier, Y. Combres, E. Gautier, and M. Phillipe, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 31, 1095 (2000).
F. Sun, F. Prima, and T. Gloriant, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 527, 4262 (2010).
M. Marteleur, F. Sun, T. Gloriant, P. Vermaut, P. Jaccques, and F. Prima, Scr. Mater. 66, 749 (2012).
F. Sun, J. Zhang, M. Marteleur, T. Gloriant, P. Vermaut, D. Laille, and F. Prima, Acta Mater. 61, 6406 (2013).
F. Sun, J.Y. Zhang, P. Vermaut, D. Choudhuri, T. Alam, S.A. Mantri, P. Svec, T. Gloriant, P.J. Jacques, R. Banerjee, and F. Prima, Mater. Res. Lett. 5, 547 (2017).
O.M. Ivasishin, P. Markovsky, Y. Matviychuk, S.L. Semiaitin, C. Ward, and S. Fox, J. Alloys Compd. 457, 296 (2008).
S. Ankem and C.A. Greene, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 263, 127 (1999).
G. Lütjering and J.C. Williams, Titanium (Berlin: Springer, 2003).
I. Weiss and S.L. Semiatin, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 243, 46 (1998).
G.S. Rohrer, Structure and Bonding in Crystalline Materials (Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2001).
J.I. Qazi, V. Tsakiris, B. Marquardt, and H.J. Rack, JAI 2, 1 (2005).
S. Nag, R. Banerjee, R. Srinivasan, J.Y. Hwang, M. Harper, and H.L. Fraser, Acta Mater. 57, 2136 (2009).
O.M. Ivasishin, P.E. Markovsky, Y.V. Matviychuk, and S.L. Semiatin, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 34, 147 (2003).
Z. Liu and G. Welsch, Metall. Trans. A 19, 527 (1988).
Y. Chen, Z. Du, S. Xiao, L. Xu, and J. Tian, J. Alloys Compd. 586, 588 (2014).
A. Dehghan-Manshadi and R.J. Dippenaar, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 528, 1833 (2011).
M.J. Donachie, Titanium: A Technical Guide, 2nd ed. (Materials Park: ASM International, 2000).
O.M. Ivasishin, P.E. Markovsky, S.L. Semiatin, and C.H. Ward, Mater. Sci. Eng., A 405, 296 (2005).
R. Prakash Kolli, W.J. Joost, and S. Aankem, JOM 67, 1273 (2015).
J.D. Cotton, R.D. Briggs, R.R. Boyer, S. Tamirisakandala, P. Russo, N. Shchetnikov, and J.C. Fanning, JOM 67, 1281 (2015).
H. Liu, M. Niinomi, M. Nakai, K. Cho, and H. Fujii, Scr. Mater. 130, 27 (2017).
H. Liu, M. Niinomi, M. Nakai, X. Cong, K. Cho, C.J. Boehlert, and V. Khademi, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 48, 139 (2017).
M. Hida, E. Sukedai, C. Henmi, K. Sakaue, and H. Terauchi, Acta Metall. 30, 1471 (1982).
B.S. Hickman, J. Mater. Sci. 4, 554 (1969).
A. Devaraj, S. Nag, R. Srinivasan, R. Williams, R. Banerjee, and H.L. Fraser, Acta Mater. 60, 596 (2012).
F. Prima, J. Debuigne, M. Boliveau, and D. Ansel, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 19, 2219 (2000).
A. Gysler, G. Lutjering, and V. Gerold, Acta Metall. 22, 901 (1974).
F. Sun, S. Nowak, T. Gloriant, P. Laheurte, A. Eberhardt, and F. Prima, Scr. Mater. 63, 1053 (2010).
Y. Zheng, D. Banerjee, and H.L. Fraser, Scr. Mater. 116, 131 (2016).
S. Dubinskiy, A. Korotitskiy, S. Prokoshkin, and V. Brailovski, Mater. Lett. 168, 155 (2016).
T.S. Kuan, R.R. Ahrens, and S.L. Sass, Metall. Trans. A 6, 1767 (1975).
S. Li, Y. Hao, R. Yang, Y. Cui, and M. Niinomi, Mater. Trans. 43, 2964 (2002).
M. Ogawa, T. Shimizu, T. Noda, and M. Ikeda, Mater. Trans. 48, 390 (2007).
V. Khademi, C.J. Boehlert, and M. Ikeda, in Proceedings of the Twenty-Fourth International Symposium on Processing and Fabrication of Advanced Materials (PFAM XXIV), ed. by M. Ikeda, T. Haruna, M. Niinomi, T.S. Srivatsan (Kansai University, Osaka, 2016), pp. I–X.
H. Li, D.E. Mason, T.R. Bieler, C.J. Boehlert, and M.A. Crimp, Acta Mater. 61, 7555 (2013).
A. Chakkedath, J. Bohlen, S. Yi, D. Letzig, Z. Chen, and C.J. Boehlert, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 45, 3254 (2014).
H. Li, C.J. Boehlert, T.R. Bieler, and M.A. Crimp, Philos. Mag. 95, 691 (2015).
H. Li, D.E. Mason, Y. Yang, T.R. Bieler, M.A. Crimp, and C.J. Boehlert, Philos. Mag. 93, 2875 (2013).
G. Welsch, R. Boyer, and E.W. Collings, Materials Properties Handbook: Titanium Alloys (Materials Park: ASM International, 1993).
V. Khademi, M. Ikeda, and C.J. Boehlert, in Proceedings of the 13th World Conference on Titanium (Wiley-Blackwell, 2016), p. 1109.
V. Khademi, in An Experimental–Computational Study on the Plastic Deformation Behavior of Body-Centered Cubic Titanium Alloys, PhD Dissertation, Michigan State University (2018).
S.A. Mantri, D. Choudhuri, A. Behera, J.D. Cotton, N. Kumar, and R. Banerjee, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 46, 2803 (2015).
C.J. Boehlert and V. Khademi, Michigan State University, Titanium Alloy and Method of Forming a Titanium Alloy, International Patent Application number PCT/US2018/014246, International Publication Number WO 2018/136641 A3, International Publication Date: July 26, 2018.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the US Department of Energy, Office of Basic Energy Science through Grant No. DE-FG02-09ER46637. Some of the microscopy conducted at Oak Ridge National Laboratory’s (ORNL) Center for Nanophase Materials Sciences (CNMS), which is a U.S. Department of Energy, Office of Science User Facility. The authors are grateful to Professors Thomas Bieler, Philip Eisenlohr, and Martin Crimp of Michigan State University (MSU) for helpful discussions and Professor Andre Lee of MSU for assistance with the DMA analysis. The authors are also grateful to Dr. Karren More of ORNL and Dr. Huihong Liu of Osaka University for TEM assistance. The authors are also grateful to Mrs Dorothy Coffey of ORNL for TEM sample preparation assistance. The authors acknowledge that material was prepared by Daido Steel Co. Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khademi, V., Ikeda, M., Hernández-Escobar, D. et al. The Elevated-Temperature Strength Enhancement of a Low-Cost β Titanium Alloy Through Thermomechanically-Induced Phase Transformation. JOM 71, 3621–3630 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03598-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11837-019-03598-2