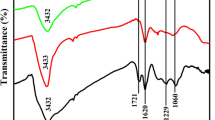
Abstract
An ultrasensitive label-free electrochemical immunosensor of okadaic acid (OA) was studied based on electrodimerization of p-aminobenzoic acid (p-ABA)-modified gold three-dimensional nanoelectrode ensembles (3DNEEs) which were prepared by electroless gold plating and etching using polycarbonate as template. Staphylococcus protein A (SPA) was introduced to immobilize okadaic acid antibody (anti-OA). The morphology and composition of 3DNEEs were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy-dispersive X-ray spectrometer (EDX). The polydimer (p-aminobenzoic acid) (pPABA) film was measured by Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FTIR). The concentration of OA was measured by EIS and SWV. The detection limit of EIS is lower than that of SWV (6.47 × 10−3 ng mL−1 vs. 9.15 × 10−3 ng mL−1), but the linear OA detection range of the latter is wider (0.01–1.0 ng mL−1 vs. 0.01–0.8 ng mL−1). The average recovery of OA in oyster samples is 99.81%. The OA recovery test in oyster samples demonstrated potential application value of the electrochemical immunosensor.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Satoshi I, Shota T, Yuta M et al (2015) Okadaic acid is taken-up into the cells mediated by human hepatocytes transporter OATP1B3[J]. Food Chem Toxicol 83:229–236
Morimoto Y, Morimoto H, Kobayashi S et al (1999) The protein phosphatase inhibitors, okadaic acid and calyculin a, induce apoptosis in human submandibular gland ductal cell line HSG cells [J]. Oral Dis 5(2):104–110
Verma M, Chaudhary M, Singh A et al (2020) Naphthalimide-gold-based nanocomposite for the ratiometric detection of okadaic acid in shellfish [J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B 8(36):8405–8413
Karaseva NA, Farafonova OV, Ermolaeva TN (2016) Highly sensitive detection of okadaic acid in seafood products via the unlabeled piezoelectric sensor [J]. Food Anal Methods 9(6):1495–1501
Creppy EE, Traore A, Baudrimont I et al (2002) Recent advances in the study of epigenetic effects induced by the phycotoxin okadaic acid [J]. Toxicology 181:433–439
Pan L, Chen J, He X et al (2020) Aqueous photodegradation of okadaic acid and dinophysistoxin-1: persistence, kinetics, photoproducts, pathways, and toxicity evaluation [J]. Science of The Total Environment 743:140593
Hayat A, Barthelmebs L, Sassolas A et al (2011) An electrochemical immunosensor based on covalent immobilization of okadaic acid onto screen printed carbon electrode via diazotization-coupling reaction [J]. Talanta 85(1):513–518
Lin C, Liu Z, Tan C et al (2015) Contamination of commercially available seafood by key diarrhetic shellfish poisons along the coast of China[J]. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22:1545–1553
Antunes J, Justino C, Da CJP et al (2018) Graphene immunosensors for okadaic acid detection in seawater [J]. Microchem J 138:465–471
Zou L, Tian Y, Zhang X et al (2017) A competitive love wave immunosensor for detection of okadaic acid based on immunogold staining method [J]. Sens Actuators, B Chem 238:1173–1180
Prassopoulou E, Katikou P, Georgantelis D et al (2009) Detection of okadaic acid and related esters in mussels during diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) episodes in Greece using the mouse bioassay, the PP2A inhibition assay and HPLC with fluorimetric detection [J]. Toxicon 53(2):214–227
Louppis AP, Badeka AV, Katikou P et al (2010) Determination of okadaic acid, dinophysistoxin-1 and related esters in Greek mussels using HPLC with fluorometric detection, LC-MS/MS and mouse bioassay [J]. Toxicon 55(4):724–733
Pang L, Quan H, Sun Y et al (2019) A rapid competitive ELISA assay of okadaic acid level based on epoxy-functionalized magnetic beads [J]. Food Hydrocolloids 30(1):1286–1302
Eissa S, Zourob M (2012) A graphene-based electrochemical competitive immunosensor for the sensitive detection of okadaic acid in shellfish [J]. Nanoscale 4(23):7593
Paz B (2008) Identification of a new diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxin, 19-epi-okadaic acid by liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry detection [J]. Mar Drugs 6(3):489–495
Huang H, Lin H, Li X et al (2014) Determination of okadaic acid and dinophysistoxin-1 in mussels by high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry [J]. Anal Lett 47(12):1987–1994
Garthwaite I (2000) A brief review of shellfish toxins [J]. Trends Food Sci Technol 11(11):235–244
Dorantes AJJ, Campbell K, Bradbury A et al (2017) Comparative performance of four immunological test kits for the detection of paralytic shellfish toxins in tasmanian shellfish [J]. Toxicon 125:110–119
Chinnappan R, Alzabn R, Mir TA et al (2019) Fluorometric determination of okadaic acid using a truncated aptamer [J]. Microchim Acta 186(7):397–406
Grieshaber D, Mackenzie O, OS J V, et al (2008) Electrochemical biosensors - sensor principles and architectures [J]. Sensors 8:1400–1458
Hayat A, Barthelmebs L, Marty J (2019) Electrochemical impedimetric immunosensor for the detection of okadaic acid in mussel sample [J]. Sens Actuators, B Chem 171–172:810–815
Cao LX, Yan PS, Sun KN et al (2008) Nanoelectrode ensembles and arrays [J]. Progress in Chemistry 20(9):1276–1282
Cao LX, Yan PS, Sun KN et al (2007) Development and evaluation of gold 3D cylindrical nanoelectrode ensembles [J]. Chin J Chem 25(11):1754–1757
De LM, Kuhn A, Ugo P (2007) 3D-ensembles of gold nanowires: preparation, characterization and electroanalytical peculiarities [J]. Electroanalysis 19(2–3):227–236
Menon VP, Martin CR (1995) Fabrication and evaluation of nanoelectrode ensembles [J]. Anal Chem 67(13):1920–1928
Beluomini MA, Karimian N, Stradiotto NR et al (2019) Tailor-made 3D-nanoelectrode ensembles modified with molecularly imprinted poly(O-phenylenediamine) for the sensitive detection of L-arabitol [J]. Sens Actuators, B Chem 284:250–257
Hong Y, Wang Y, Zhu Y (2020) Highly sensitive immunosensor based on polydopamine-nanofilm modified 3D gold nanoelectrode for A-fetoprotein detection [J]. Electrochimica Acta 364:137328
Fu X, Chen X, Guo Z et al (2010) Three-dimensional gold micro-/nanopore arrays containing 2-mercaptobenzothiazole molecular adapters allow sensitive and selective stripping voltammetric determination of trace mercury (II)[J]. Electrochim Acta 56(1):463–469
Kotkar RM, Srivastava AK (2006) Voltammetric determination of para-aminobenzoic acid using carbon paste electrode modified with macrocyclic compounds [J]. Sens Actuators, B Chem 119(2):524–530
Zhang Y, Wang J, Xu M (2010) A sensitive DNA biosensor fabricated with gold nanoparticles/ploy (P-aminobenzoic acid)/carbon nanotubes modified electrode [J]. Colloids Surf, B 75(1):179–185
Qu J, Lou T, Kang GS et al (2013) Preparation of poly-(P-aminobenzoic acid)/multiwall carbon nanotubes composite film modified glassy carbon electrode and application to detect catechol and hydroquinone simultaneously [J]. Electrochemistry 81(2):82–85
Thiemann C, Brett CMA (2001) Electrosynthesis and properties of conducting polymers derived from aminobenzoic acids and from aminobenzoic acids and anilinE [J]. Synth Met 123(1):1–9
Yang L, Zhao F, Zeng B (2016) Electrochemical determination of eugenol using a three-dimensional molecularly imprinted poly (P-aminothiophenol-Co-P-aminobenzoic acids) film modified electrode [J]. Electrochim Acta 210:293–300
Xu F, Gao M, Wang L et al (2001) Sensitive determination of dopamine on poly(aminobenzoic acid) modified electrode and the application toward an experimental Parkinsonian animal model [J]. Talanta 55(2):329–336
Derkus B, Cebesoy EK, Mazi H et al (2014) Protein a immunosensor for the detection of immunoglobulin G by impedance spectroscopy [J]. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 37(5):965–976
Hu H, Cao L, Li Q et al (2015) Fabrication and modeling of an ultrasensitive label free impedimetric immunosensor for aflatoxin B1 based on poly(O-phenylenediamine) modified gold 3D nano electrode ensembles [J]. RSC Adv 5(68):5529–55217
Li X, Cao L, Zhang Y et al (2017) Fabrication and modeling of an ultrasensitive label free impedimetric immunosensor for aflatoxin B1 based on protein a self-assembly modified gold 3D nanotube electrode ensembles [J]. Electrochim Acta 247:1052–1059
Sun X, Zhu Y, Wang X (2011) Amperometric immunosensor based on a protein A/deposited gold nanocrystals modified electrode for carbofuran detection [J]. Sensors 11(12):11679–11691
Krishnamoorthy K, Zoski CG (2005) Fabrication of 3D gold nanoelectrode ensembles by chemical etching [J]. Anal Chem 77(15):5068–5071
Li R, Cao L, Liang C et al (2020) Development and modeling of an ultrasensitive label-free electrochemical immunosensor for okadaic acid based on polythionine-modified three-dimensional gold nanoelectrode ensembles [J]. Ionic 26(9):4661–4670
Brett CMA, Thiemann C (2002) Conducting polymers from aminobenzoic acids and aminobenzenesulphonic acids: influence of pH on electrochemical behaviour [J]. J Electroanal Chem 538–539:215–222
Benyoucef A, Huerta F, Vazquez JL et al (2005) Synthesis and in situ FTIRS characterization of conducting polymers obtained from aminobenzoic acid isomers at platinum electrodes [J]. Eur Polymer J 41(4):843–852
Liu Y, Yu D, Zeng C et al (2010) Biocompatible graphene oxide-based glucose biosensors [J]. Langmuir 26(9):6158–6160
Funding
This research work was supported by COMRA project (DY135-B2-17) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21273056).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nai, H., Cao, L., Sun, S. et al. Development and characterization of an ultrasensitive label-free electrochemical immunosensor for okadaic acid based on polydimer (p-aminobenzoic acid)-modified gold three-dimensional nanoelectrode ensembles. Ionics 27, 5323–5331 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-021-04252-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11581-021-04252-1