Abstract
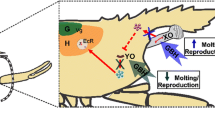
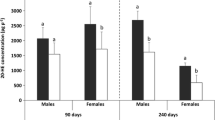
The endocrine system of crustaceans regulates the molt cycle with ecdysteroid hormones, mainly the 20-hydroxyecdysone (20-HE). Moreover, the molt process requires the action of chitinolytic enzymes (e.g., chitinase, chitobiase) to break down the old cuticle. However, endocrine disrupting compounds (EDC) are capable of altering their normal functioning. Glyphosate-based herbicides (GBH), such as Roundup®, the most widely used herbicides, are found in freshwater environments and have been considered EDC for many aquatic organisms. Therefore, this study examined the effects of environmentally relevant GBH concentrations (0.0065, 0.065, and 0.28 mg L−1) on the 20-HE concentration and chitobiase activity in the decapod prawn Macrobrachium potiuna exposed for 14 days. Additionally, lipid peroxidation, a biomarker of membrane lipid degradation, was evaluated in hepatopancreas to assess cellular damage. Results showed that GBH decreased the 20-HE concentration in females at the two highest concentrations tested, while an increase was observed in males exposed to the highest GBH concentration. In addition, GBH also decreased chitobiase activity in males (all concentrations) and females (the two highest concentrations). Finally, GBH caused increased lipid peroxidation in males, indicating cellular damage in the hepatopancreas. In conclusion, this work suggests that GBH is an EDC for crustaceans by disrupting molting, which could lead to altered reproduction and thus population dynamics.

Decrease in the 20-HE concentration and chitobiase activity in muscle of males and females of the freshwater prawn Macrobrachium potiuna exposed to the herbicide Roundup® for 14 days



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annett R, Habibi HR, Hontela A (2014) Impact of glyphosate and glyphosate-based herbicides on the freshwater environment. J Appl Toxicol 34:458–479. https://doi.org/10.1002/jat.2997
Avigliano E, Schenone NF (2015) Human health risk assessment and environmental distribution of trace elements, glyphosate, fecal coliform and total coliform in Atlantic Rainforest mountain rivers (South America). Microchem J 122:149–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2015.05.004
Bauer RT (1996) A test of hypothesis on male mating systems and female molting in decapod shrimp, using Sicyonia dorsalis (Decapoda: Penaeoidea). J Crustac Biol 16:429–436
Benbrook CM (2016) Trends in glyphosate herbicide use in the United States and globally. Environ Sci Eur 28:15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12302-016-0070-0
Bond G, Buckup L (1983) O cultivo de Macrobrachium borellii (Nobili, 1896) e de Macrobrachium potiuna (Müller, 1880) em laboratório (Crustacea, Decapoda, Palaemonidae). Rev Bras Biol 43:177–190
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 52:302–309
Chen H, Gu X, Zeng Q, Mao Z, Liang X, Martyniuk CJ (2019) Carbamazepine disrupts molting hormone signaling and inhibits molting and growth of Eriocheir sinensis at environmentally relevant concentrations. Aquat Toxicol 208:138–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.01.010
CONAMA (2005) Conselho Nacional Do Meio Ambiente. Resolução número 357. Accessed in 03/04/2018. Available in:. http://www.mma.gov.br/port/conama/legiabre.cfm?codlegi-459
Duchet C, Inafuku MM, Caquet T, Larroque M, Franquet E, Lagneau C, Lagadic L (2011) Chitobiase activity as an indicator of altered survival, growth and reproduction in Daphnia pulex and Daphnia magna (Crustacea: Cladocera) exposed to spinosad and diflubenzuron. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:800–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.11.001
Dutra BK, Fernandes FA, Failace DM, Oliveira GT (2011) Effect of roundup® (glyphosate formulation) in the energy metabolism and reproductive traits of Hyalella castroi (Crustacea, Amphipoda, Dogielinotidae). Ecotoxicology 20:255–263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-010-0577-x
Espie PJ, Roff JC (1995) Characterization of chitobiase from Daphnia magna and its relation to chitin flux. Physiol Zool 68:727–748
Freire R, Schneider RM, Freitas FH, Bonifácio CM, Tavares CRG (2012) Monitoring of toxic chemical in the basin of Maringá stream. Acta Sci Technol 34:295–302. https://doi.org/10.4025/actascitechnol.v34i3.10302
Gasnier C, Dumont C, Benachour N, Clair E, Chagnon MC, Séralini GE (2009) Glyphosate-based herbicides are toxic and endocrine disruptors in human cell lines. Toxicology 262:184–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2009.06.006
Gismondi E (2018) Identification of molt-inhibiting hormone and ecdysteroid receptor cDNA sequences in Gammarus pulex, and variations after endocrine disruptor exposures. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 158:9–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.04.017
Gismondi E, Cossu-Leguille C, Beisel J (2013) Do male and female gammarids defend themselves differently during chemical stress? Aquat Toxicol 140–141:432–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2013.07.006
Horion S, Thomé JP, Gismondi É (2015) Changes in antitoxic defense systems of the freshwater amphipod Gammarus pulex exposed to BDE-47 and BDE-99. Ecotoxicology 24:959–966. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-015-1438-4
Lafontaine A, Gismondi E, Boulangé-Lecomte C, Geraudie P, Dodet N, Caupos F, Lemoine S, Lagadic L, Thomé JP, Forget-Leray J (2016) Effects of chlordecone on 20-hydroxyecdysone concentration and chitobiase activity in a decapod crustacean, Macrobrachium rosenbergii. Aquat Toxicol 176:53–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2016.04.006
Le TH, Lim ES, Lee SK, Choi YW, Kim YH, Min J (2010) Effects of glyphosate and methidathion on the expression of the Dhb, Vtg, Arnt, CYP4 and CYP314 in Daphnia magna. Chemosphere 79:67–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2009.12.067
LeBlanc GA (2007) Crustacean endocrine toxicology: a review. Ecotoxicology 16:61–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10646-006-0115-z
Malik Z, Jones CJP, Connock MJ (1987) Assay and subcellular localization of H2O2 generating mannitol oxidase in the terrestrial slug Arion ater. J Exp Zool 242:9–15. https://doi.org/10.1002/jez.1402420103
Melo MS, Santos TPG, Jaramillo M, Nezzi L, Müller YMR, Nazari EM (2019a) Histopathological and ultrastructural indices for the assessment of glyphosate-based herbicide cytotoxicity in decapod crustacean hepatopancreas. Aquat Toxicol 210:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2019.03.007
Melo MS, Nazari EM, Joaquim-Justo C, Müller YMR, Gismondi E (2019b) Effects of low glyphosate-based herbicide concentrations on endocrine-related gene expression in the decapoda Macrobrachium potiuna. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:21535–21545
Melo MS, Nazari EM, Müller YMR, Gismondi E (2020) Modulation of antioxidant gene expressions by Roundup® exposure in the decapod Macrobrachium potiuna. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 190:110086. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.110086
Mensah PK, Muller WJ, Palmer CG (2012) Using growth measures in the freshwater shrimp Caridina nilotica as biomarkers of Roundup® pollution of South African freshwater systems. Phys Chem Earth 50–52:262–268. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pce.2012.08.003
Mensah PK, Palmer CG, Odume ON (2015) Ecotoxicology of glyphosate and glyphosate-based herbicides — toxicity to wildlife and humans. In: Larramendy ML, Soloneski S (eds) Toxicity and Hazard of agrochemicals. IntechOpen, Croatia, pp 281–304. https://doi.org/10.5772/60767
Mykles DL (2011) Ecdysteroid metabolism in crustaceans. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 127:196–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsbmb.2010.09.001
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Okada E, Pérez D, Gerónimo E, Aparicio V, Massone H, Costa JL (2018) Non-point source pollution of glyphosate and AMPA in a rural basin from the southeast Pampas, Argentina. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:15120–15132
Omran NE, Salama WM (2013) The endocrine disruptor effect of the herbicides atrazine and glyphosate on Biomphalaria alexandrina snails. Toxicol Ind Health 32:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1177/0748233713506959
Peruzzo PJ, Porta AA, Ronco AE (2008) Levels of glyphosate in surface waters, sediments and soils associated with direct sowing soybean cultivation in north pampasic region of Argentina. Environ Pollut 156:61–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2008.01.015
Reynolds SE, Samuel RI (1996) Physiology and biochemistry of insect moulting fluid. Adv In Insect Phys 26:157–222
Richard S, Moslemi S, Sipahutar H, Benachour N, Seralini GE (2005) Differential effects of glyphosate and roundup on human placental cells and aromatase. Environ Health Perspect 716:716–720. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.7728
Rodríguez EM, Medesani D, Fingerman M (2007) Endocrine disruption in crustaceans due to pollutants: a review. Comp Biochem Physiol - A Mol Integr Physiol 146:661–671. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2006.04.030
Sinhorin VDG, Sinhorin AP, dos Teixeira JM, S, Miléski KML, Hansen PC, PSA M, Kawahita NH, Baviera AM, Loro VL (2014) Effects of the acute exposition to glyphosate-based herbicide on oxidative stress parameters and antioxidant responses in a hybrid Amazon fish surubim (Pseudoplatystoma sp). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 106:181–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.04.040
Song Y, Evenseth LM, Iguchi T, Tollefsen KE (2017) Release of chitobiase as an indicator of potential molting disruption in juvenile Daphnia magna exposed to the ecdysone receptor agonist 20-hydroxyecdysone. J Toxicol Environ Heal Part A 80:954–962. https://doi.org/10.1080/15287394.2017.1352215
Tillmann M, Schulte-oehlmann U, Duft M (2001) Effects of endocrine disruptors on prosobranch snails (Mollusca: Gastropoda) in the laboratory. Part III: cyproterone acetate and vinclozolin as antiandrogens. Ecotoxicology 10:373–388
US EPA (2009) United States Environmental Protection Agency, National Primary Drinking Water Regulation, EPA 816-F-09- 0042009. (Washington)
Vijayavel K, Gomathi RD, Durgabhavani K, Balasubramanian MP (2004) Sublethal effect of naphthalene on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant status in the edible marine crab Scylla serrata. Mar Pollut Bull 48:429–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.marpolbul.2003.08.017
Walsh LP, Mccormick C, Martin C, Stocco DM (2000) Roundup inhibits steroidogenesis by disrupting steroidogenic acute regulatory (StAR) protein expression. Environ Health Perspect 108:769–776
World Health Organization. Promotion of Chemical Safety Unit & Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (1996). WHO/FAO Data sheet on pesticides. no. 91, Glyphosate. World Health Organization. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/63290
Xuereb B, Chaumot A, Mons R, Garric J, Geffard O (2009) Acetylcholinesterase activity in Gammarus fossarum (Crustacea Amphipoda) intrinsic variability, reference levels, and a reliable tool for field surveys. Aquat Toxicol 93:225–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquatox.2009.05.006
Zou E, Fingerman M (1999) Patterns of N-acetyl-B-glucosaminidase isoenzymes in the epidermis and hepatopancreas and induction of N-acetyl-B-glucosaminidase activity by 20-hydroxyecdysone in the fiddler crab, Uca pugilator. Comp Biochem Physiol Part C 124:345–349
Funding
This work was conducted during a scholarship supported by the Programa de Doutorado Sanduíche no Exterior from the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior to MSM (CAPES/PDSE 47/2017).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Philippe Garrigues
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 18 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Melo, M.S., Nazari, E.M., Müller, Y.M.R. et al. Roundup® disrupts chitinolytic enzyme activity and ecdysteroid concentration in Macrobrachium potiuna. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27, 43396–43402 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11025-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-11025-2