Abstract
Purpose
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) measures water diffusion in biological tissues. Cellular water transport depends on aquaporins (AQPs). The expression of aquaporins might differ in several pathologic disorders. Therefore, the aim of this study was to evaluate the associations between AQP4 expression and different DWI parameters in meningioma.
Procedures
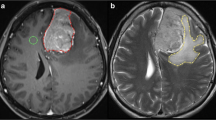
Twenty-three patients with meningioma grade I were included in this retrospective study. DWI was obtained with three b values (0; 500; 1000) using a 1.5-T device. ADCmean, ADCmin, ADCmax, and true diffusion coefficients (D) were obtained in every patient. Aquaporin 4 expression was quantified immunohistochemically in four immunoreactivity levels.
Results
The estimated DWI parameters (mean value ± standard deviation, 10−3 mm2 s−1) of the tumors were as follows: ADCmin 0.67 ± 0.16, ADCmean 0.94 ± 0.23, ADCmax 1.29 ± 0.50, and D 0.65 ± 0.23. The mean level of the AQP4 expression was 2.02 ± 0.75 points. A statistically significant correlation between AQP4 expression and ADCmax was identified (r = 0.508, p = 0.013). No significant correlations between AQP4 and other DWI parameters were found.
Conclusions
A clear correlation between AQP4 expression and ADCmax values in grade I meningioma was identified. There were no significant correlations between AQP4 expression and other DWI parameters, such as ADCmin, ADCmean, and D.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Verkman AS (2011) Aquaporins in clinical medicine. Annu Rev Med 63:303–316
Gore JC, Xu J, Colvin DC, et al. (2010) Characterization of tissue structure at varying length scales using temporal diffusion spectroscopy. NMR Biomed 23:745–756
Papadopoulos MC, Saadoun S (2015) Key roles of aquaporins in tumor biology. Biochim Biophys Acta 1848:2576–2583
Chenevert TL, Sundgren PC, Ross BD (2005) Diffusion imaging: insight to cell status and cytoarchitecture. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 16:619–632
Saadoun S, Papadopoulos MC, Davies DC, et al. (2002) Aquaporin-4 expression is increased in oedematous human brain tumours. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 72:262–265
Schnapauff D, Zeile M, Ben Niederhagen M, et al. (2009) Diffusion-weighted echo-planar magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of tumor cellularity in patients with soft-tissue sarcomas. J Magn Reson Imaging 29:1355–1359
Wang P, Ni RY, Chen MN, et al. (2010) Expression of aquaporin-4 in human supratentorial meningiomas with peritumoral brain edema and correlation of VEGF with edema formation. Genet Mol Res 10:2165–2171
Ng WH, Hy JW, Tan WL, et al. (2009) Aquaporin-4 expression is increased in edematous meningiomas. J Clin Neurosci 16:441–443
Surov A, Gottschling S, Mawrin C, et al. (2015) Diffusion-weighted imaging in meningioma: prediction of tumor grade and association with histopathological parameters. Transl Oncol 8:517–523
Whittle IR, Smith C, Navoo P, Collie D (2004) Meningiomas. Lancet 363:1535–1543
Gibbs P, Liney GP, Pickles MD, et al. (2009) Correlation of ADC and T2 measurements with cell density in prostate cancer at 3.0 tesla. Investig Radiol 44:572–576
Dietrich O, Hubert A, Heiland S (2014) Imaging cell size and permeability in biological tissue using the diffusion-time dependence of the apparent diffusion coefficient. Phys Med Biol 59:3081–3096
Surov A, Ginat DT, Sanverdi E, et al. (2016) Use of diffusion weighted imaging in differentiating between maligant and benign meningiomas. A multicenter analysis. World Neurosurg 88:598–602
Coenegrachts K, Delanote J, Beek Ter L, et al. (2009) Evaluation of true diffusion, perfusion factor, and apparent diffusion coefficient in non-necrotic liver metastases and uncomplicated liver hemangiomas using black-blood echo planar imaging. Eur J Radiol 69:131–138
Armes JE, Trute L, White D, et al. (1999) Distinct molecular pathogeneses of early-onset breast cancers in BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutation carriers: a population-based study. Cancer Res 59:2011–2017
Quandt D, Fiedler E, Boettcher D, et al. (2011) B7-h4 expression in human melanoma: its association with patients’ survival and antitumor immune response. Clin Cancer Res 17:3100–3111
Sawada T, Kato Y, Kobayashi M (2006) Expression of aquaporine-4 in central nervous system tumors. Brain Tumor Pathol 24:81–84
Day RE, Kitchen P, Owen DS, et al. (2014) Human aquaporins: regulators of transcellular water flow. Biochim Biophys Acta 1840:1492–1506
Tourdias T, Dragonu I, Fushimi Y, et al. (2009) Aquaporin 4 correlates with apparent diffusion coefficient and hydrocephalus severity in the rat brain: a combined MRI–histological study. NeuroImage 47:659–666
Badaut JEROM, Ashwal S, Adami A, et al. (2010) Brain water mobility decreases after astrocytic aquaporin-4 inhibition using RNA interference. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 31:819–831
Driessen JP, Caldas-Magalhaes J, Janssen LM, et al. (2014) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in laryngeal and hypopharyngeal carcinoma: association between apparent diffusion coefficient and histologic findings. Radiology 272:456–463
Surov A, Caysa H, Wienke A, et al. (2015) Correlation between different ADC fractions, cell count, Ki-67, total nucleic areas and average nucleic areas in meningothelial meningiomas. Anticancer Res 35:6841–6846
Ginat DT, Mangla R, Yeaney G, Wang HZ (2010) Correlation of diffusion and perfusion MRI with Ki-67 in high-grade meningiomas. Am J Roentgenol 195:1391–1395
Sanverdi SE, Ozgen B, Oguz KK, et al. (2012) Is diffusion-weighted imaging useful in grading and differentiating histopathological subtypes of meningiomas? Eur J Radiol 81:2389–2395
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by the institutional review board.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding
None.
Additional information
Stefan Schob and Alexey Surov contributed equally to the paper
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schob, S., Surov, A., Wienke, A. et al. Correlation Between Aquaporin 4 Expression and Different DWI Parameters in Grade I Meningioma. Mol Imaging Biol 19, 138–142 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-016-0978-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-016-0978-1