Abstract
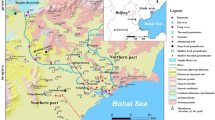
The health of near shore marine ecosystems has long been a concern because of its importance to coastal areas. Jiaozhou Bay (JZB) is one such marine ecosystem experiencing rapid water quality degradation in the last several decades. From the area surrounding the bay, the nutrients discharged into the bay through surface water and groundwater has been greatly changed. The thickness of the aquifers and the permeability is relatively high, the concentrations of nutrients in the groundwater are generally high, and so the groundwater discharged into JZB is very significant. However, no attempt has ever been made to evaluate the amount of nutrients discharged into the bay area via groundwater. In this study, the cross-section method and water balance method were used to estimate the amount of groundwater and nutrients discharged into JZB via the subsurface. Groundwater was monitored and sampled at aquifers surrounding the bay area, and some previously available data was also analyzed. The results indicated that groundwater from the Baisha Aquifer east of JZB now is the major source of nutrients (nitrate, dissolved SiO2) being discharged into the bay. The concentrations of nutrients in the groundwater have been increasing with intensive agricultural land use. However, Dagu Aquifer, the largest aquifer north of JZB, only provides limited nutrients to the bay area because of the construction of a low permeability subsurface dam. Historically, during the 1970s to the 1990s, the Baisha Aquifer experienced seawater intrusion due to excessive groundwater withdrawal. The same was true for the Dagu Aquifer from the 1980s to the 1990s. Because of this, no significant nutrients were discharged into the bay.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burnett, W. C., Bokuniewicz, H., Huettel, M., Moore, W. S., & Taniguchi, M. (2003). Groundwater and pore water inputs to the coastal zone. Biogeochemistry, 66, 3–33.
Cable, J. E., Burnett, W. C., Chanton, J. P., & Weatherly, G. L. (1996a). Estimating groundwater discharge into the northeastern Gulf of Mexico using radon-222. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 144, 591–604.
Cable, J. E., Bugnd, G. C., Burnett, W. C., & Chanton, J. P. (1996b). Application of 222Rn and CH4 for assessment of groundwater discharge to the coastal ocean. Limnology and Oceanography, 41(6), 1347–1353.
Cable, J. E., Burnett, W. C., Chanton, J. P., Corbett, D. R., & Cable, P. H. (1997a). Field evaluation of seepage meters in the coastal marine environment. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 45, 367–375.
Cable, J. E., Burnett, W. C., & Chanton, J. P. (1997b). Magnitude and variations of groundwater seepage along a Florida marine shoreline. Biogeochemistry, 38(2), 189–205.
Corbett, D. R., Chanton, J., Burnett, W. C., & Dillon, K. (1999). Patterns of groundwater discharge into Florida Bay. Limnology and Oceanography, 44(4), 1045–1055.
Corbett, D. R., Dillon, K., & Burnett, W. C. (2000). Tracing groundwater flow on a Barrier Island in the north-east Gulf of Mexico. Estuarine Coastal and Shelf Science, 51, 227–242.
Dong, Y. X., Gong, L. Z., Lei, J. G., Yin, L. Z., et al. (1989). Seawater intrusion report of Baishahe and Chengyanghe downstream area in Qingdao. Environmental and Hydrologic Central Station of Shandong Province (EHCS), 13–19, (in Chinese).
Gordeev, V. V., Dzhamalov, R. G., Zektser, I. S., Zhulidov, V. V., & Bryzgalo, V. A. (1999). Assessment of nutrient discharge with river and groundwater flow into marginal seas of the Russian Arctic regions. Vodnye Resursy, 26(2), 206–211.
Hydraulic Bureau of Laoshan District, Qingdao (1990). Water conservancy annals of Laoshan County.
Jiao, C. Y., Qiu, H. X., & Liu, G. Q. (1994). A numerical model for Dagu water source in Qingdao,. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao Vol.24 (supplement), 122–126, (in Chinese).
Johannes, R. E. (1980). The ecological significance of the submarine discharge of groundwater. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 3, 365–373.
Krupa, S. L., Belanger, T. V., Heck, H. H., Brock, J. T. & Jones, B. J. (1998). Krupaseep – The next generation seepage meter. Journal of Coastal Research SI, (26), 210–213.
Lambert, M. J., & Burnett, W. C.(2003). Submarine groundwater discharge estimates at a Florida coastal site based on continuous radon measurements. Biogeochemistry, 66, 55–73.
Lapointe, B. E., O’Connell, J. D., & Garrett, G. S. (1990). Nutrient couplings between on-site sewage disposal systems groundwaters and nearshore surface waters of the Florida Keys. Biogeochemistry, 10, 289–300.
Lee, D. R. (1977). A device for measuring seepage flux in lakes and estuaries. Limnology and Oceangraphy, 22, 140–147.
Liu, G. Q., & Qiu, H. X. (1994). Groundwater resources management model of Baishahe alluvial area. Journal of Ocean University of Qingdao Vol.24 (supplement), 101–106, (in Chinese).
Matson, B. A. (1993). Nutrient flux through soils and aquifers to the coastal zone of Guam (Mariana Islands). Limnology and Oceanography, 38(2), 361–371.
Millham, N. P., & Howes, B. L. (1994). Freshwater flow into a coastal embayment: Groundwater and surface water inputs. Limnology and Oceanography, 39(8), 1928–1944.
Moore, W. S. (1996). Large groundwater inputs to coastal waters revealed by (226) Ra enrichments. Nature, 380(6575), 612–614.
Moore, W. S. (1997). High fluxes of radium and barium from the mouth of the Ganges–Brahmaputra River during low river discharge suggest a large groundwater source. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 150(1–2), 141–150.
Moore, W. S. (2003). Sources and fluxes of submarine groundwater discharge delineated by radium isotopes. Biogeochemistry, 66, 75–93.
Paulsen, R. J., Smith, C. F., O’Rourke, D. E., & Wong, T. F. (2001). Development and evaluation of an ultrasonic groundwater seepage meter. Groundwater, 39(6), 904–911.
Poppe, L. J., & Moffett, A. M. (1993). Groundwater discharge and the related nutrient and trace metal fluxes into Quincy Bay, Massachusetts. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 25(1), 15–27.
Reay, W. G., Gallagher, D. L., & Simmons, G. M. (1992). Groundwater discharge and its impact on surface water quality in a Chesapeake Bay inlet. Water Research Bulletin, 28(6), 1121–1134.
Smith, L., & Zawadzki, W. (2003). A hydrogeologic model of submarine groundwater discharge: Florida intercomparison experiment. Biogeochemistry, 66, 95–110.
Simmons, G. M. Jr. (1992). Importance of submarine groundwater discharge (SGWD) and seawater cycling to material flux across sediment/water interfaces in marine environments. Marine Ecology Progress Series, 84, 173–184.
Sun, Y. P., Fu, Z. X., Wang, S. H., Gong, L. Z., et al. (1986). Dynamic monitoring report of groundwater exploitation tests in Dagu water source, Environmental and Hydrologic Central Station of Shandong Province (EHCS), 16–22, (in Chinese).
Sun, Y. P., Fu, Z. X., Wang, S. H., Gong, L. Z., et al. (1990). Investigation and research assessment of seawater intrusion in Qingdao. Environmental and Hydrologic Station of Qingdao, Shandong Province (EHS), 25–29, (in Chinese).
Taniguchi, M., & Fukuo, Y. (1993). Continuous measurements of groundwater seepage using an automatic seepage meter. Groundwater, 31, 675–679.
Taniguchi, M., Burnett, W. C., Smith, C. F., Paulsen, R. J., O’Rourke, D., Krupa, S. L., et al. (2003). Spatial and temporal distributions of submarine groundwater discharge rates obtained from various types of seepage meters at a site in the Northeastern Gulf of Mexico. Biogeochemistry, 66, 35–53.
Zhang, Q., Qiu, H., Zhu, C., & Yu, Z. (2002). Groundwater nitrate flux to Wanggezhuang Bay. Marine Environmental Sciences, 2: 14–18, (in Chinese).
Zhu, X., Liu, G. Q., Wang, S. Y., & Xiang, Y. Estimation of groundwater and nutrient flux from Baisha watershed into Jiaozhou Bay. Journal of Ocean University of China Vol. 35(1), 67–72, (in Chinese).
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Dr. J.X. Liu of the Environmental and Hydrogeologic Station of Qingdao, and Dr. G.F. Cheng of the Qingdao Hydraulic Bureau for providing surface water flux data and groundwater quality data. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation under Grant No. 40036010 and No. 40572171. The authors would like to thank the three anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments on the original manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, G.Q., Wang, S.Y., Zhu, X.J. et al. Groundwater and Nutrient Discharge into Jiaozhou Bay, North China. Water Air Soil Pollut: Focus 7, 593–605 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11267-007-9127-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11267-007-9127-9