Abstract
Scientists use the Earth as a tool for astrobiology by analyzing planetary field analogues (i.e. terrestrial samples and field sites that resemble planetary bodies in our Solar System). In addition, they expose the selected planetary field analogues in simulation chambers to conditions that mimic the ones of planets, moons and Low Earth Orbit (LEO) space conditions, as well as the chemistry occurring in interstellar and cometary ices. This paper reviews the ways the Earth is used by astrobiologists: (i) by conducting planetary field analogue studies to investigate extant life from extreme environments, its metabolisms, adaptation strategies and modern biosignatures; (ii) by conducting planetary field analogue studies to investigate extinct life from the oldest rocks on our planet and its biosignatures; (iii) by exposing terrestrial samples to simulated space or planetary environments and producing a sample analogue to investigate changes in minerals, biosignatures and microorganisms. The European Space Agency (ESA) created a topical team in 2011 to investigate recent activities using the Earth as a tool for astrobiology and to formulate recommendations and scientific needs to improve ground-based astrobiological research. Space is an important tool for astrobiology (see Horneck et al. in Astrobiology, 16:201–243, 2016; Cottin et al., 2017), but access to space is limited. Complementing research on Earth provides fast access, more replications and higher sample throughput. The major conclusions of the topical team and suggestions for the future include more scientifically qualified calls for field campaigns with planetary analogy, and a centralized point of contact at ESA or the EU for the organization of a survey of such expeditions. An improvement of the coordinated logistics, infrastructures and funding system supporting the combination of field work with planetary simulation investigations, as well as an optimization of the scientific return and data processing, data storage and data distribution is also needed. Finally, a coordinated EU or ESA education and outreach program would improve the participation of the public in the astrobiological activities.
Similar content being viewed by others
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
One of the key goals of astrobiology is to explore planetary bodies of our solar system in order to determine their potential for habitability and extra-terrestrial life. This is achieved by partly analyzing materials from specific environments on Earth that exhibit similar conditions as planets and moons in our Solar System (i.e. planetary field analogues), and by using laboratory set-ups that mimic planetary and deep space conditions (i.e. laboratory analogues).
There are many planetary field analogue environments on Earth with extreme ranges of temperature, salinity, mineral content, pH, pressure, and water availability (Marlow et al. 2011). This diversity mimics in parts various extra-terrestrial environments that are of interest to astrobiologists, such as the terrestrial planets (Venus and Mars), the Jovian moons (e.g. Europa), and the Saturn moons (Titan and Enceladus) (Preston and Dartnell 2014). Planetary field analogues are used to (i) perform in-situ measurements during field campaigns, allowing to test methodologies, protocols, and technologies, and (ii) collect samples, both biotic (extant and extinct or fossilized) and abiotic for analyses by state-of-the-art methods in the laboratory, e.g. to investigate the relationship between biosignatures and their rock/mineral context, and to identify microorganisms from extreme environments. These kinds of activities inform astrobiologists about habitability and biosignatures present on Earth and elsewhere, planetary processes, the most appropriate life-detection methods and techniques, validation of space mission instrumentation and payload testing, selection of the best landing sites for future life-detection missions, and finally, the mobility of rovers on representative terrains.
Laboratory analogues on Earth provide laboratory access to selected parameters of extra-terrestrial environments for a wide variety of experiments, e.g. the formation and preservation of biosignatures, the alteration of minerals and rocks, physical and chemical processes or the survival and adaptation mechanisms of microorganisms, as well as their interaction under simulated atmospheric composition, pressure, temperature and radiation of the space environment of interest. In addition, simulation facilities are important tools for necessary space hardware tests (e.g. Motamedi 2013).
The European Space Agency (ESA) funded a Topical Team in 2011 to summarize the most recent achievements in the field of astrobiology (Cottin et al. 2015). Reviews on experimental studies of space as a tool for astrobiology (Cottin et al. 2017) and on the Earth as a tool for astrobiology (current manuscript) have also been compiled. The present manuscript is a review of recent activities using Earth as a tool for astrobiology, reporting on planetary field analogues sites on Earth (Sect. 2), field test campaigns (Sect. 3), and simulation facilities in Earth laboratories (Sect. 4). A synthesis of all relevant information, as well as recommendations from the Topical Team to ESA is also presented (Sect. 5). This study thus perfectly complements the EU-funded Astrobiology Roadmap, a very broad overview of the state of the art of, and challenges for, astrobiology in general (Horneck et al. 2016).
2 Planetary Field Analogue Environments on Earth
Planetary field analogue environments are places on Earth with geological or environmental conditions that are similar to those that exist on an extra-terrestrial planetary body (Léveillé 2009). They do not replicate all the conditions of another planetary body, but instead mimic specific parameter(s) (Marlow et al. 2008, 2011). The purpose of using terrestrial analogue sites for planetary missions can be divided into five categories: (i) learning about planetary processes (both geological and biological) on Earth and elsewhere; (ii) testing protocols, strategies, methodologies, operations, technologies, and payload instrumentation; (iii) training highly-qualified personnel (e.g. PhD students and engineers), as well as science and operation teams; (iv) engaging the public, space agencies, media, and educators; and (v) defining detectable biosignatures from extant/extinct life, the limits of life and habitability on Earth (Lee 2007; Léveillé 2009). There are currently a few on-line databases for planetary field analogue rocks and sites, such as:
-
(i)
the International Space Analogue Rockstore (ISAR), which is a collection of well-characterized rocks used for testing and calibrating instruments to be flown on space missions (Bost et al. 2013) (http://www.isar.cnrs-orleans.fr/isar/). The ISAR is located in the Centre de Biophysique Moléculaire (CBM) of the Centre National de la Recherche Scientifique (CNRS) in Orléans, and is supported by the Observatoire des Sciences de l’Univers en Région Centre (OSUC), the Centre National d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES), and ESA;
-
(ii)
the Concepts for Activities in the Field for Exploration (CAFE), which was commissioned by ESA (Preston et al. 2013a), and resulted in a catalogue of all planetary field analogue sites used and currently in use (Preston et al. 2013b). This catalogue describes in detail each of these field sites (e.g. location, geological and environmental information) and is the most extensive and up-to-date catalogue available;
-
(iii)
the Europlanet Planetary Field Analogues (PFA), which offers access to five well-characterized terrestrial field sites (http://www.europlanet-2020-ri.eu/research-infrastructure/field-lab-visits/ta1-pfa). The PFA has been selected to provide the most realistic analogues of the surfaces of Mars, Europa and Titan. Access is provided for scientists to perform high quality scientific research and test instrumentation for space missions under realistic planetary conditions and undertake comparative planetology research.
The Committee on Space Research (COSPAR) Panel on Exploration (PEX) in cooperation with the European Science Foundation (ESF) has elaborated a report on an “International Earth-based research program as a stepping stone for global space exploration—Earth-X” (Ehrenfreund et al. 2011). Analogue research is an international endeavor since the sites of interest are distributed around the globe, and potential technology and scientific developments are of interest to many fields of study and within many areas of exploration both on the Earth and in space.
In 2003 the ESF initiated a new research support activity called Investigating Life in Extreme Environments (ILEE). This initiative showed the need for a coordinated, interdisciplinary approach to improve future opportunities for funding research on “Life in extreme environments” (LEXEN). The coordination action for research on study of life in extreme environments (CAREX) was a Seventh Framework Programme (FP7) project funded by the European Commission (EC) and coordinated by the British Antarctic Survey and the Natural Environment Research Council (NERC). The project operated from 1 January 2008 to 30 June 2011 and addressed the enhanced coordination of LEXEN research in Europe by providing networking and exchange of knowledge opportunities to the scientific community. It was an interdisciplinary initiative covering all life forms existing in extreme environments on Earth, as well as addressing the use of extreme environments as planetary field analogues in the search for extra-terrestrial life. The four priority areas identified in the CAREX strategic roadmap included: (1) contributions of life in extreme environments (LEXEN) to biogeochemical cycles and responses to environmental change, (2) stressful environments—responses, adaptation and evolution, (3) biodiversity, bioenergetics and interactions in extreme environments, and (4) life and habitability (final CAREX report summary available at http://cordis.europa.eu/result/rcn/55055_en.html). The resulting strategic roadmap for European research on LEXEN is a basis for strategic programme planning for science organizations such as the EC, COSPAR, and other institutions outside Europe such as the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Astrobiology Institute and the Japan Agency for Marine-Earth Science and Technology (JAMSTEC). One example of a European follow-on research project funded by the EC in the Framework Program 7 is the Mars Analogues for Space Exploration (MASE, 2014–2017, http://mase.esf.org/). It has the aim (i) to isolate and characterise anaerobic microorganisms from selected sites that closely match environmental conditions that might have been habitable on early Mars, (ii) to study their responses to realistic combined environmental stresses that might have been experienced in habitable environments on Mars, and (iii) to investigate their potential for fossilization on Mars and their detectability by carrying out a systematic study of the detectability of artificially fossilized organisms exposed to known stresses.
The selection of astrobiologically-relevant field sites is most often dependent on environmental conditions that favor our current understanding of the limits of life and that could support metabolic activity and growth, either currently or in the geologic past (see Cottin et al. 2017). One example used in ecological field campaigns are the measurements on metabolic activity such as measuring methane production by methanogens (Wagner et al. 2005, 2007) or photosynthetic activity by phototrophs like cyanobacteria, alga and lichens (Lange 1969; Lange et al. 1970; Schroeter et al. 1994; Schroeter and Scheidegger 1995; Pannewitz et al. 2003). Also, reproduction expressed by the growth rate may be recorded, which might take several years of continuously monitoring the selected field sites in order to obtain measurement results over longer time scales. This time-consuming observation is necessary because of the dominance of very slow growing species present, for example, in extreme Mars-analogue field sites. In parallel, measurements on irradiation, temperature, relative humidity, methane/\(\mbox{CO}_{2}\) production or consumption and oxygen production are also performed (Lange et al. 1970, 1996). Such investigation on planetary analogue field sites on Earth provides fundamental information on life’s behavior and its capacity to influence or change its environment. The interchange between the environment and the life forms might also provide insight into search strategies and objectives for the search for life on other planets or moons. The amount of measured gases released by microorganisms might serve as references for potential gas traces produced by life on another planet. In addition, bio-leaching of rocks and soils (Cockell 2010) due to metabolic activity and release of acidic substances as well as possible deposits of secondary metabolites can change mineral composition or enrich soil with organic material. The analysis of such environmental patterns as a biosignature of life can be studied in the field as well as in the laboratory, which would lead to the identification of fossilization processes on Earth and support the search for extinct life on other planets (Orange et al. 2011; Westall et al. 2011, 2015a, 2015b).
Terrestrial microorganisms adapted to the most extreme environments on Earth (i.e. extremophiles) are potential models for understanding long-term survival in specific extra-terrestrial conditions, in particular in the Martian surface/subsurface, and in the icy moons of Jupiter and Saturn surface/subsurface environments. Environmental conditions, such as extremes of dry, cold, with relatively high radiation background and weak seasonal fluctuations (e.g. in the planetary field analogue environment of permafrost in Antarctica), extreme dry and relatively hot or cold (e.g. in the planetary field analogue environments of the Atacama Desert in Chile, and the Antarctic Dry Valleys), extreme pH conditions (e.g. in the planetary field analogue environment of the Río Tinto), and extreme salinity (e.g. in the planetary field analogue environment of the saturated salt areas of the Dead Sea), make these environments similar to space- and planetary environments. Prokaryotes (e.g. bacteria, bacterial spores, cyanobacteria) have been studied in such extreme planetary field analogue environments due to the fact that early life forms on Earth were prokaryotes and the assumption that if any extra-terrestrial life exists in the Solar System, it must be simple cellular organisms (Hansen 2007; Westall et al. 2015a, 2015b). For example, microbial cryptoendolithic communities that colonize the pore spaces of sedimentary rocks in Antarctica and other deserts to avoid stressful environmental conditions (e.g. ultraviolet (UV) radiation, very low or very high temperatures and very dry conditions) have been studied (Friedmann and Ocampo 1976; Friedmann 1982; Jänchen et al. 2014; de Vera et al. 2014a). Eukaryotes (e.g. lichens, microcolonial fungi and tardigrades) have also been studied, and shown a high resistance against the extreme conditions (Meeßen et al. 2015; Jänchen et al. 2015, Onofri et al. 2004, 2008, 2012, 2015, Sancho et al. 2007, de la Torre et al. 2010, de Vera et al. 2010, 2014b). In addition, fossil traces of primitive prokaryotes in well-preserved rocks from the early Earth constitute ideal analogues for potential primitive life forms on the early Mars (Westall et al. 2015a, 2015b).
Characterization of the ecosystems where extremophiles will be collected during field campaigns is necessary. Monitoring of the UV-climatology and microclimatology, as well as parallel physiological activity determination is a fundamental step to compare the seasonal adaptations of extremophile organisms to their natural habitat with the resistance to simulated space- and planetary conditions (de la Torre 2002, de la Torre et al. 2004, de Vera et al. 2014b). Community studies are performed by in situ exposure of the microbial population in environmental samples (e.g. rock or soil; Olsson-Francis and Cockell 2010). The community is characterized before exposure, which may include constructing a 16S rRNA gene library and culturing. Environmental samples are generally diverse, and thus the number of exposed species is much higher than that of pure cultures. Exposing the community will lead to the selection of microorganisms that are resistant. This will give information regarding the physiological requirements of microbial survival in the conditions examined. In addition, the incubation of the microbial community in situ does not involve culturing the microorganisms in the laboratory prior to exposure. Lichens have also been studied as they have multiple protective mechanisms. These allow lichens to grow in some of the most extreme environments on Earth (de Vera et al. 2004, 2008, 2010, 2014b). Using field campaigns, lichens are collected as “fresh samples” directly from their natural habitat. For example, samples of the lichen Pleopsidium chlorophanum and Buelia frigida were collected in Mars-analogue dry, cold and UV-irradiated environments in the North Victoria Land Mountains in Antarctica (de Vera et al. 2014b, Meeßen et al. 2015), or the vagrant lichen, such as Circinaria fruticulosa originally from continental deserts and arid areas of Middle Asia, Eurasia, North America and Northern Africa, and thus well adapted to harsh environmental conditions (e.g. heat, drought, and high levels of solar UV radiation) have been collected on clayey soils in continental high basins of Central Spain. After collection, they were kept dry and protected from light under dark conditions for several months before the tests (Sancho et al. 2000). In the next sub-section, we highlight diverse planetary field analogue sites.
2.1 Planetary Field Analogues Sites
Space missions to planetary bodies in our solar system are expensive and time-consuming, taking decades to reach their target. In the meantime, and in order to prepare for these space missions, scientists use locations on Earth that mimic some characteristics of those solar system locations. The terrestrial materials used as planetary analogues provide a preview of the properties of the solar system location they best mimic (e.g. Marlow et al. 2008, 2011):
-
Compositional analogues include properties such mineralogy, elemental abundances, volatile content (water and dissolved gases), and organic content.
-
Electrochemical analogues include similarities in terms of chemical properties such as dielectric constant, redox potential, pH, water activity, and magnetism.
-
Environmental analogues mimic the temperature, aridity, wind and radiation, or the conditions existing on the early planets and moons in the Solar System.
-
Physical analogues comprise thermo-physical (e.g. albedo and thermal inertia), mechanical (e.g. bearing strength, cohesive strength, and the angle of internal friction), and bulk physical characteristics (e.g. particle size distribution, particle shape, density, and porosity).
An ideal analogue would mimic all the required compositional, electrochemical, physical and environmental properties of a specific solar system location. Note that some environmental conditions cannot be found on Earth (e.g. high levels of unfiltered UV radiation, altered gravity, different atmospheres/atmospheric composition, very low pressure) (Rettberg et al. 2004; Prinn and Fegley 1987). While no present terrestrial analogue mimics all properties, they play a crucial role in preparing for different aspects of future space missions. On the other hand, rocks from the early Earth record the corresponding environmental conditions and are thus highly valuable samples.
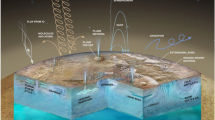
A summary of the representative locations studied as terrestrial analogue sites is present in Fig. 1, and in the text below (Marlow et al. 2008, 2011; Preston and Dartnell 2014). Representative terrestrial analogue sites used internationally are shown and supplemented by terrestrial analogues used by ESA-member states for astrobiological studies. Some are funded by the EU (e.g. the CAFE study), while some are funded nationally (e.g. the GANOVEX-expedition).
Global map of the Earth with 33 analogue sites identified (adapted from Preston and Dartnell 2014). The map includes sites used by ESA state members and also the international community. Identification is as follow: Site 1—High-altitude atmosphere; 2—Yilgarn Craton (Western Australia); 3—Rio Tinto (Spain); 4—The Golden Deposit (Canadian High Arctic); 5—Yellowstone National Park (USA); 6—Haughton Impact Structure (Devon Island); 7—Dongwanzi Ophiolite Complex (China); 8—Axel Heiberg Island (Canadian High Arctic); 9—The Antarctic Dry Valleys (Antarctica); 10—Antarctic North Victoria Land Mountains 11—Sub-glacial Volcanism (Iceland); 12—Kamchatka (Russian Federation); 13—Bockfjord Volcanic Complex (Svalbard); 14—Kilimanjaro (Tanzania, Africa); 15—Atacama (South America); 16—The Mojave Desert (USA); 17—Namib Desert (Namibia, Africa); 18—Ibn Battuta Centre Sites (Morocco); 19—Qaidam Basin (Tibetan Plateau); 20—caves in Sardinia; 21—caves in Tenerife and Lanzarote; 22—Lake Vostok (Antarctica); 23—Permafrost (Multiple Sites); 24—The Borup Fiord Pass (Ellesmere Island); 25—Lake Tirez (Spain); 26—Orca Basin (Gulf of Mexico); 27—Mono Lake (California, USA); 28—The Dead Sea (Israel); 29—Lost City (Mid-Atlantic Ridge); 30—The Mariana Trench (Pacific Ocean); 31—Lidy Hot Springs (USA); 32—The Columbia River Basalts (USA); 33—Pitch Lake (Trinidad and Tobago); 34—Rancho La Brea Tar Pits (California, USA); 35—Alaskan Oil Fields (USA); 36—Pilbara (north of Western Australia); 37—Barberton (South Africa). Number 1 broadly corresponds to high-altitude atmospheric analogues for Venus, numbers 2 to 21 are analogue sites for Mars, numbers 22 to 32 are analogue site for Europa and Enceladus, numbers 33 to 35 are analogue site for Titan, and numbers 36 to 37 are analogue sites for the early Earth
Acid-Saline Lakes of Western Australia
The acid-saline lakes of the Yilgarn Craton in Western Australia were considered to have the most similar bulk physical and mineralogical content to the Meridiani Planum on Mars (Grotzinger et al. 2005, Benison and Bowen 2006, Bowen et al. 2008). In addition, microorganisms were found in the surface of the acid-saline lakes (Hong et al. 2006; Mormile et al. 2007, 2009).
Antarctic and Artic Ices
A diverse set of microorganisms has been detected in the ice-sheet of the Lake Vostok in Antarctica (Priscu et al. 1999; Karl et al. 1999; Shtarkman et al. 2013). The Artic permafrost has also a high content of microorganisms (Jakosky et al. 2003; Gilichinsky et al. 2003; Rivkina et al. 2000; Vorobyova et al. 1997; Vishnivetskaya et al. 2006), making both environments good analogues for the icy Moons Europa, Enceladus and Ganymede. The Arctic ice may also be used as an analogue of Mars due to the observation by the Phoenix Lander of the water ice-Martian surface interface (Smith 2009; Smith et al. 2009), the low water activity and limited organic content (Deming 2002; Vishnivetskaya et al. 2006).
Antarctic McMurdo Dry Valleys
The McMurdo Dry Valleys, with a surface area of \(6861~\mbox{km}^{2}\) (Cary et al. 2010), are the largest ice-free area in Antarctica (Fig. 2) and the driest cold place on Earth (Marchant et al. 1996). The precipitation, exclusively snow is often less than 10 mm water-equivalent (weq) per year, ranging from 3 mm to less than 100 mm in the location closer to the sea (Fountain et al. 2009). The Dry Valleys are located within the Transantarctic Mountains in the Southern part of Victoria Land, close to the western coast of McMurdo Sound (between 160°E and 164°E longitude and 76°S and 78°S latitude). The winter air temperature fluctuates between −20 and −50°C (occasionally lower), rising to mean daily values of about −15°C in the summer, up to 15°C or higher values at ground surfaces. Surface soils seem sterile in large parts of the area, but rocks (Friedmann 1982), and permafrost (Gilichinsky et al. 2007) can be rich in microbial life; for instance, soils collected in the upper part of the Dry Valleys, such as the University Valley at 1700 m above sea level (mean annual air temperature −23°C, maximum −2.8°C), yielded only 6 heterotrophic isolates on over 1000 agar plates in 2 years (Goordial et al. 2016). Microbial diversity, investigated both by isolation cultural methods and by molecular analyses, resulted much higher in milder sites (Cary et al. 2010). In particular, molecular tools demonstrated a microbial diversity in soils higher than expected (Smith et al. 2006). Life in rocks is rich, mainly represented by cryptoendolithic communities, thriving in air-spaces within porous rocks (Friedmann 1982; Friedmann 1993), and biodiversity in cryptoendolithic communities has been studied also by molecular phylogenetic methods (de la Torre et al. 2003). Since the NASA Viking Mars exploration in 1976, Antarctic Dry Valleys has been considered the closest climatic terrestrial analogue of Mars (Horowitz et al. 1972; Wynn-Williams and Edwards 2000). In fact, numerous similarities have been highlighted between the hyper-arid cold desert Antarctic Dry Valleys microclimate zones and the latitudinal and local microclimate zones observed on Mars (Marchant and Head 2007).
Antarctic North Victoria Land Mountains
Like the Antarctic Dry Valleys, a number of small valleys within the Antarctic Mountains of North Victoria Land are considered to be Mars-analogue field sites. This is because of their isolated locations of about 100 to 300 km away from the coastline where the mountains form barriers against the humid air streams from the ocean. At altitudes of about 1500 to 2500 m high, the UV irradiation, very low temperatures and the extreme dryness act on a variety of microorganisms, in particular on lichens, microfungi and cyanobacteria (de Vera et al. 2014b; Meeßen et al. 2015). Since 2009 two Mars-analogue field campaigns were conducted in these areas during the German Antarctic North Victoria Land Expeditions (GANOVEX) 10 (2009/2010) and GANOVEX 11 (2015/2016), by the German Aerospace Center (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt e.V., DLR) in cooperation with the Federal Institute for Geosciences and Natural Resources (Bundesanstalt für Geowissenschaften und Rohstoffe, BGR), and with the logistic support of the Italian Antarctic Research Program (Programma Nazionale di Ricerche in Antartide, PNRA). Results obtained from Mars simulation experiments with samples collected in these habitats have shown that the organisms were able to retain water, survive and even be active in a Mars-like environment (de Vera et al. 2014b; Jänchen et al. 2015; Meeßen et al. 2015).
Atacama Desert
The Yungay (Chile) and Arequipa (Peru) regions of the Atacama Desert are the driest hot places on Earth, serving as a compositional Martian analogue because of its sulphate and perchlorate mineralogy and low organic content (Catling et al. 2010; Peeters et al. 2009; Buch et al. 2006; Amashukeli et al. 2007; Meunier et al. 2007; Skelley et al. 2007). This is suggested to be the result of the highly oxidizing composition of the Atacama Desert soil (Sutter et al. 2005; Ewing et al. 2006; Navarro-González et al. 2003; Quinn et al. 2005; Lester et al. 2007).
Deep Sea Vents
Extreme life forms live on Earth in the vicinity of deep sea hydrothermal vents, where no sunlight reaches, using, for example, sulphur compounds as source of energy. In addition, lithoautotrophic methanogenesis (i.e. the conversion of \(\mbox{CO}_{2}\) and \(\mbox{H}_{2}\) to methane) can be a source of metabolic energy for the production of biomass at hydrothermal systems (McCollom 1999). Similar environments might exist on Europa or Enceladus, which have icy crusts and possibly liquid oceans beneath. In fact, magnesium sulphate salts have been detected in Europa’s ice surface using the Keck II telescope, possibly providing a sample of the ocean underneath (Brown and Hand 2013) and in the plumes of Enceladus (Bouquet et al. 2015).
Early Archaean Terrains
The early Earth represents an ideal environmental and microbial analogue for early habitable bodies in the Solar System. The early Earth was a volcanically and hydrothermally active ocean planet, while Mars was basically a land-locked volcanic planet with isolated pockets of habitability (Westall 2012; Westall et al. 2015a), and the now icy moons (Enceladus, possibly Titan, Europa, and Callisto) of the outer Solar System could have been or are still similar. The reason for this is that, despite the great distances of the various bodies from the early, fainter Sun, they all underwent melting, fractionation and cooling. At a certain critical moment during their geological evolution, these bodies would have had liquid water in contact with hot rock and hydrothermal edifices, while there is indication that Enceladus has ongoing hydrothermal activity (Hsu et al. 2015) and more recently, evidence of aqueous geysers has been observed on Europa (Roth et al. 2014). Hypothesizing that carbon-water-based life had a hydrothermal origin (Russell and Hall 1997; Martin et al. 2008), life could have appeared on any of them, including Mars. Another important analogy is that the early Earth was anaerobic, as would have been (and still are) the other bodies.
Although tectonic recycling has destroyed terrestrial rocks of Hadean age (4.5–4.0 Ga) that could have recorded the transition from prebiotic chemistry into biological chemistry, there are two enclaves on Earth where well-preserved rocks dating back to 3.5 billion years (Ga) are preserved. These locations are the Pilbara in Western Australia and the Barberton Greenstone Belt in eastern South Africa (Fig. 3). Volcanoclastic sediments deposited in shallow water—at depths similar to those of crater lakes on Mars—and hosting abundant hydrothermal vents contain the remains of early, anaerobic life forms (Westall et al. 2011, 2015a, 2015b). Both chemotrophic and phototrophic colonies are preserved in the strongly hydrothermally-influenced sediments. Thus, the local environmental conditions, volcanic sediment type, hydrothermal environment, and the early life forms and their exceptional preservation, make the rocks of the Early Archaean terrains in the Pilbara and Barberton ideal analogues for extra-terrestrial life, especially on Mars. On the other hand, Deamer and colleague argue that the origin of life occurred in an evaporite pond in a prebiotic environment (Deamer 2014). According to these authors, in such geothermal setting organic compounds would have interacted with mineral surfaces to promote self-assembly and polymerization reactions.
Lava Tubes and Caves
Lava tubes and caves are useful analogue sites since they provide both geological and biological data on subsurface environments. In particular, microbial metabolisms and biosignatures of organisms that persist independent of surface photosynthesis such as methanogens and chemolithotrophs can be examined (Fernández-Remolar et al. 2008). The deleterious surface of present-Mars has long since been recognized as a reason why habitable conditions, if they exist on Mars today, are likely to be localized to the deep subsurface (Boston et al. 1992). Today, the largest quantities of water are found in the subsurface (e.g. Holt et al. 2008). The specific interest in lava tubes on Earth is motivated by their presence in volcanic, basaltic environments analogous to the geological context of lava tubes on Mars (Cushing et al. 2007; Williams et al. 2010). On Mars, lava tubes provide a natural way to access the deep subsurface. As caves can potentially occur in any type of geological environment, understanding their geology and biota provides a comprehensive understanding of near-surface habitability of a diversity of planetary materials that can be applied to understanding extra-terrestrial subsurface habitability (Abbey et al. 2005).
Pitch Lake
Pitch Lake on the Caribbean island of Trinidad and Tobago may be used as an analogue of the methane lakes of Titan (Schulze-Makuch et al. 2011). The Pitch Lake has very low water activity, being filled with hot asphalt, and bubbling hydrocarbon gases (such as methane). It has been shown that active microorganisms survive on its extreme conditions (Schulze-Makuch et al. 2011).
Rio Tinto
Rio Tinto in southern Spain is an analogue for rivers present on early Mars. It is characterized by acidic headwaters (pH value of 2.3) due to oxidation of sulphide ore deposits in this region (Bigham and Nordstrom 2000; Fernández-Remolar et al. 2005), and also a very high concentration of iron (Amils et al. 2007). Despite all these extreme conditions, microbiological communities thrive. This makes Rio Tinto a good electrochemical and compositional analogue of early Mars, in particular to study the possible role of microorganisms on the formation of iron oxide and sulphate deposits on the planet (Amils et al. 2007).
Salten Skov
Salten Skov is a Martian analogue collected from Jutland (Denmark). It contains high concentrations of iron oxides, and has been used for its similar bulk physical and magnetic properties to Mars (Gunnlaugsson et al. 2002; Merrison et al. 2004; Nørnberg et al. 2004, 2008). Just like JSC Mars-1, Salten Skov has a high microbiological and organic content, and therefore is not the best Mars soil analogue from the organic point of view (Hansen et al. 2005; Garry et al. 2006; Peeters et al. 2009; Chan et al. 2012).
Utah Desert
The Utah Desert has a mineral composition similar to Mars (Borst et al. 2010), with sedimentary deposits of sands, evaporites, clays and gypsum (Kotler et al. 2011). The microbiological and organic content are very heterogeneous; amino acids range from non-detectable to several thousand parts-per-billion (ppb), while an extraordinary variety of putative extremophiles was observed (Ehrenfreund et al. 2011; Direito et al. 2011; Martins et al. 2011).
3 Field Test Campaigns
3.1 Semi-permanent Field-Testing Bases
Semi-permanent field testing campaigns with permanent infrastructure have been established to carry out multidisciplinary research for mission and technology development and definition. Although not their core business, scientific campaigns can be carried here out as well (Ansdell et al. 2011). Two of these sites are centered around underwater activities, the Aquarius Undersea Research Station at the Florida Keys, USA, a site to study coral reefs (Todd and Reagan 2004) and the Pavilion Lake Research Project (PLRP) that aims to explain the origin of freshwater microbiolites (Lim and Brady 2011). The Boulby International Subsurface Astrobiology Laboratory (BISAL, UK) is the world’s first permanent subsurface astrobiology laboratory. It explores instrument testing for robotic and human planetary missions, as well as deep subsurface evaporate geochemistry and biology (Cockell et al. 2013; Payler et al. 2017). Most of the sites focus on developing Mars exploration scenarios, sometimes combined with Moon activities. These include the Haughton Mars Project (HMP) Research Station at Devon Island, Canada (Lee and Osinski 2005, http://marsonearth.org/), the McGill Arctic Research Station (MARS) at Axel Heiberg Island (Pollard et al. 2009), the Pacific International Space Center for Exploration Systems (PISCES) at Hawaii (Schowengerdt et al. 2007; Duke et al. 2007), and the Ibn Battuta Centre for exploration and field activities in Morocco, established in 2006 http://www.ibnbattutacentre.org/).
3.2 Long-Term Field-Testing Campaigns
Long-term field testing campaigns are used to test for planetary instruments and missions (Ansdell et al. 2011). Examples include the Arctic Mars Analog Svalbard Expedition (AMASE), the Desert Research and Technology Studies (Desert RATS), and the NASA Extreme Environments Mission Operations (NEEMO) campaigns. The AMASE is a campaign focused on science and technology, in which technology is tested in support of the science, and it took place on Svalbard, Norway (Steele et al. 2007). The Desert RATS field-testing campaigns support future manned mission scenarios, including technology related testing (Ross et al. 2013) (http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/desertrats/). They have taken place in various locations in the United States, including Mauna Kea (Hawaii) (ten Kate et al. 2013), and Black Point Lava Flow (Arizona), which were selected based on their physical resemblance to the lunar and Martian surface. The scope of these campaigns includes testing single space suit configurations and multi-day integrated mission scenarios (Ross et al. 2013), as well as integrating science into the technology-driven scenarios and communication between scientists and engineers (Yingst et al. 2015). The NEEMO campaigns are technology and mission oriented, and use the Aquarius Station, which provide a convincing analogue for space exploration (Thirsk et al. 2007) (http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/NEEMO/).
Field research at Mars analogue sites, such as desert environments can provide important constraints for instrument calibration and landing site strategies of robotic exploration missions to Mars that will investigate habitability and life beyond Earth during the next decade. Terrestrial analogue studies are used to better understand the nature, the process and the utilization of geological processes and resource utilization on Earth in order to interpret and validate information from orbiting or surface missions on extra-terrestrial bodies (Foing et al. 2011). In this analogue context, all the mission aspects are simulated to perform fieldwork as a test of human factors procedures. The Mars Desert Research Station (MDRS) in southern Utah (USA) is an analogue site where human space mission simulations are performed in order to investigate all possible factors that may interact to affect mission success, such as human factors and geological in-situ resource exploration (Schlacht et al. 2010; Direito et al. 2011; Ehrenfreund et al. 2011; Foing et al. 2011, 2013, 2014; Kotler et al. 2011; Martins et al. 2011; Orzechowska et al. 2011; Thiel et al. 2011). Every two weeks, exchange crews of six members come to the station to perform a new mission to establish the knowledge of, and to test the equipment necessary for future successful planetary exploration, also from a human factors perspective. An illustration of the kind of scientific results that were obtained includes data relevant for habitability and astrobiology. Astrobiology field research from the MDRS was conducted during the EuroGeoMars 2009 campaign. EuroGeoMars 2009 was an example of a Moon-Mars field research campaign dedicated to the demonstration of astrobiology instruments and a specific methodology of comprehensive measurements from selected sampling sites (Foing et al. 2011). Special emphasis was given to sample collection and pre-screening using in-situ portable instruments. A comprehensive analysis was applied to a set of selected samples from different geological formations including Mancos Shale, Morrison, and Dakota Formation as well as a variety of locations (surface, subsurface and cliffs) partly in-situ in the habitat or in a post-analysis cycle. Individual technical laboratory analysis studies were compiled and correlations were investigated of environmental parameters, minerals, organic markers and biota. The results were interpreted in the context of future missions that target the identification of organic molecules and biomarkers on Mars. Results showed that the Utah desert has a mineral composition similar to Mars (Borst et al. 2010), with sedimentary deposits of sands, evaporites, clays and gypsum (Kotler et al. 2011). The microbiological and organic content are very heterogeneous, with amino acids ranging from non-detectable to several thousand parts-per-billion (ppb), while an extraordinary variety of putative extremophiles was observed (Ehrenfreund et al. 2011; Direito et al. 2011; Martins et al. 2011).
Several field campaigns (e.g. EuroGeoMars2009 and Drilling on the Moon and Mars in Human Exploration/International Lunar Exploration Working Group (DOMMEX/ILEWG) Euro-MoonMars) have been conducted at the MDRS. Most of the information we have from the surface of the Moon and Mars comes from satellite observations. Satellite images of high resolution are very important to achieve a successful selection of landing sites and planning of traverses on unfamiliar planetary sites. In order to help in the interpretation of Mars missions’ measurements from orbit (Mars Express, MRO) or from the surface (MSL Curiosity) at Gale crater, several field research campaigns (e.g. ILEWG EuroMoonMars) were performed in the extreme conditions of the Utah desert. These provided data analysis relevant to Mars geology at multiple scales. The goal of ILEWG EuroMoonMars project (2013) was to conduct field studies to identify environments analogous to those that Curiosity has been studying at Gale crater. Therefore, a comparative study was made between satellite images with a spatial resolution of 50–60 cm per pixel. This is comparable to the resolution of MRO HiRise on Mars. Traverses at MDRS similar to geomorphological features seen at the Gale crater were planned as possible and implemented using a rover, drone and Extravehicular Activity (EVA) simulation walks, before taking rocks and soil samples (Figs. 4 and 5). The usability of a drone for imaging reconnaissance was tested, and experiences and lessons learnt were assessed concerning geological traverse planning based on high resolution satellite images (Foing et al. 2014).
Map of geological features and inverted riverbeds around MDRS, Utah showing areas explored by traverses and EVAs, and through samples (Foing et al. 2014)
(Left) Concretions in Utah Brushy Basin Member of the Morrison Formation within a cross-bedded sandstone, compared to (right) similar concretions, cross-bedding and veins apparent in Curiosity camera color images (Foing et al. 2014)
4 Laboratory Analogues
4.1 Planetary and Low Earth Orbit (LEO) Space Simulation Facilities
Planetary and Low Earth Orbit (LEO) space simulation facilities are designed to reproduce a wide range of conditions of space, as the ones accessible in LEO (i.e. on satellites or the International Space Station (ISS)), or of a specific planet or moon, including vacuum or the relevant atmospheric pressure and composition, UV radiation, and (surface) temperature. Laboratory planetary analogues allow exposure to conditions which cannot be found in analogue field sites. Indeed, they provide the means to investigate the effect of extra-terrestrial environmental parameter on biological, chemical and material samples in the laboratory, and the basis for space experiments including the selection of best landing areas for possible life detection. All planetary and LEO space simulation facilities are technically limited. Nevertheless, according to their individual focus, they provide valuable research opportunities with the advantage of fast and easy access and capacity for more or bigger experiments when compared to space research facilities.
Simulation facilities at the various locations are usually divided into those used for organic chemistry experiments only, and those that are also used for biological experiments or hardware tests. The required simulated environmental parameters of low temperatures, low pressure and short wavelength UV are of interest for biological and chemical experiments and hardware tests. In contrast, cleanliness of the facility, in particular with respect to organic compounds is of great importance to organic chemical experiments and—depending on its destination—for final flight hardware. Cleanliness with respect to organisms is absolutely necessary for biological experiments, but with the insertion of biology into any facility, cleanliness of the facility with respect to organic compounds can no longer be insured. Therefore, experiments with biological material as test objects often are not consistent with the performance of organic chemical experiments in the same facilities. Exceptions are compartmentalizations and separation of the experiments, as in the EXPOSE ground simulations. For most biological exposure experiments, the required conditions at a sample site are (i) simulated temperature ranges from at least −25°C up to a maximum of 120°C, as this is the range where life can exist in a dormant, viable or reproductive and metabolically active state (Price and Sowers 2004; Junge et al. 2006; Kashefi and Lovley 2003; Schwartzman and Lineweaver 2004), (ii) irradiation with different spectral ranges, in particular with respect to the short wavelength cut off, (iii) high or low pressure regimes including vacuum as in LEO, (iv) high or low relative humidity and (v) different atmospheric compositions. Damage induction, repair capacities, adaptation and adaptation strategies, hence the overall influence on cell functions of the applied parameter or combinations, are investigated for different species. Passive exposure experiments performed in these chambers only allow the comparison of samples before and after the simulation experiments to evaluate the effect of the applied parameters. In this case, biological samples are prepared from inactive forms of selected organisms, i.e. spores, cysts, or organisms in hibernation mode, where metabolism, growth or any other vitality parameters are not detectable with current methods. After exposure, the revival of the organisms and their metabolic resumption and growth is analyzed in comparison with the pre-exposure base data to better understand the effect of the individual applied parameter. Molecular analysis e.g. of DNA damages and repair mechanisms increase our knowledge on the underlying reactions. In particular, organisms that are derived from extreme terrestrial environments are of high interest to better understand their adaptation strategies. They are selected from terrestrial environments that differ from standardized lab conditions, i.e. 1013.25 hPa, 293.15 K (20°C) and the terrestrial atmospheric composition of about 78% \(\mbox{N}_{2}\) and 20% \(\mbox{O}_{2}\), often from the above presented analogues. Water availability is the major necessity for active life as we know it from Earth. Wherever water is available in the simulated extra-terrestrial environment, active instruments that detect metabolic activity or growth during the exposure experiment complete the simulation facility design.
Currently, one of the main astrobiological focuses is the question of extinct or extant life and corresponding signatures on Mars. The possible transport of viable organisms to Mars, accidentally by spacecraft and their survival capacities are of interest for Planetary Protection means. Indeed, the prevention of any contamination of Mars by Earth organisms is the major topic of Planetary Protection regulations. Therefore, most simulation facilities have been designed to simulate either LEO space or Mars surface conditions. The aim of LEO space simulation facilities is to approach as much as possible LEO pressure of down to \(10^{-7}~\mbox{Pa}\) and, in particular the short wavelength solar UV and vacuum UV (VUV) radiation non-attenuated by an Earth ozone layer. For Mars, simulation temperatures between 198 K (−75°C) and 293 K (20° C) are applied (de Vera et al. 2010, 2014a, 2014b; Krala et al. 2011; Schuerger et al. 2013; Martin and Cockell 2015), approaching temperatures observed in equatorial to mid-latitudes on Mars (McEwen et al. 2011; Head et al. 2003). In parallel, atmospheric pressure of about 600 to 800 Pa with a Mars-like atmospheric composition of about 95% \(\mbox{CO}_{2}\), 2.7% \(\mbox{N}_{2}\), and 1% \(\mbox{O}_{2}\) and traces of water is obtained. The need of adequate radiation spectra approximating the solar UV regimes is mainly achieved using specific solar UV lamps (Rabbow et al. 2012; Lorek and Koncz 2013; de Vera et al. 2014a, 2014b). A special type of Mars simulation facility are wind tunnels for the simulation of Martian dust devils and dust storms to investigate correlated effects, in particular on landers and rovers hardware, but also for a better understanding of their effect on the Martian environment itself.
Several laboratory setups have been devoted to the study of the evolution of potential biological records (mainly organic matter such amino acids, carboxylic acids, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, nucleobases, etc.) under simulated Martian surface conditions (Fig. 6). Initially, these experiments were focused on the impact of UV radiation and oxidation processes. Table 1 highlights some key parameters of some laboratory simulations submitting pure or mixed organic molecules to simulated Martian UV sources (Hintze et al. 2010; Johnson and Pratt 2010; Oro and Holzer 1979; Poch et al. 2013, 2014, 2015; Schuerger et al. 2008; Stalport et al. 2008, 2009, 2010; Stoker and Bullock 1997; ten Kate et al. 2005, 2006). Among these parameters, the use of a Xenon arc lamp as the radiation source has proven to better reproduce the energy and relative abundance of the UV photons (190 to 400 nm) supposed to reach the surface of Mars (Schuerger et al. 2003). Moreover, temperature and pressure should also be representative of the Martian ones for several reasons: First, because temperature can influence the kinetics of the chemical reactions occurring in the simulation reactor (ten Kate et al. 2006), as pressure may also do (Keppler et al. 2012). Second, because the chemical stability and physical state (solid or gas) of the products is largely dependent of these parameters. Thus, when possible, analysis should be made in situ during the simulation at constant environmental conditions in order to retrieve information on both the kinetics of transformation and the nature of the products. With some of these setups, the influence of a mineral matrix has also been investigated such as in clays (montmorillonite, saponite, nontronite) (Poch et al. 2015; dos Santos et al. 2016), in sulfates (gypsum, jarosite) (dos Santos et al. 2016), in minerals containing ferrous iron (augite, enstatite and basaltic lava) (dos Santos et al. 2016), and in the Mars soil analogues JSC-Mars 1 (Garry et al. 2006; Stalport et al. 2010), Salten Skov (Garry et al. 2006; Peeters et al. 2009), and Atacama (Peeters et al. 2009). Note that the source for JSC Mars-1 is the ash from the Pu’u Nene cinder cone on Hawaii. Analyzed at the Johnson Space Center, it mimics the composition and physical properties of Mars (Allen et al. 1998a; Allen et al. 1998b; Perko et al. 2006). However, the very high organic content of JSC Mars-1 precludes it as a good analogue regarding organic material (Garry et al. 2006). Finally, some studies have investigated the influence of energetic particles on the evolution of organics at the surface of Mars (Kminek and Bada 2006; Gerakines and Hudson 2013; Mate et al. 2015). The results show that this type of radiation can cause the degradation of simple organic molecules (glycine) on a timescale of hundreds of millions of years. On the other hand, UV radiation acts on a much shorter timescale (several days to months) (see for example Poch et al. 2014). Furthermore, higher-energy radiation can penetrate deeper into the soil (up to around 2 m) than UV radiation (up to a few microns or millimeters), potentially leading to inactive bacteria or spores due to accumulating radiation damage (Dartnell et al. 2007).
A large number of simulation facilities (\({>}50\)) worldwide are capable of mimicking general planetary surfaces and space conditions to some extent. Only a limited number of the available simulation facilities in Europe is listed below to show typical examples of the various approaches to simulating space and planetary environments in the laboratory. Facilities restricted to abiotic (non-biological) simulations only are indicated. Three sub-sections are also included to describe specific types of simulation facilities: 4.1.1 biologically relevant accessories for in situ analysis in simulation facilities; 4.1.2 Mars wind tunnels; and 4.1.3 simulation facilities for organic aerosols in planetary atmospheres.
Mars Organic Molecule Irradiation and Evolution (MOMIE), LISA, Paris, France
The MOMIE experimental set-up allows investigators to simulate the in-situ Mars-like UV irradiation (Fig. 6A; Poch et al. 2013). It uses Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy to monitor the sample, at a temperature (2–218 K) and pressure (1–6 mbar) representative of the mean conditions at the Martian surface. The setup is composed of a reactor (Fig. 6A—section A) housing the sample (on an \(\mbox{MgF}_{2}\) window, in green) which is maintained at 6 mbar, thanks to gas circulation system (Fig. 6A—section B), and 218 K using a cryothermostat (Fig. 6A—section C). The irradiation source is a Xenon arc lamp (Fig. 6A—section D), and a mobile mirror enables to switch between irradiation or analysis phases via FT-IR spectroscopy (Fig. 6A—section E). A glove compartment (Fig. 6A—section F) filled with \(\mbox{N}_{2}\) contains the entire device. The work in this chamber has focused on photochemistry of organic molecules and the effect of the mineral matrix (Stalport et al. 2008; Poch et al. 2013, 2014, 2015)
The Planetary Atmospheres Simulation Chamber (PASC), The Centre for Astrobiology Research (CAB), Madrid, Spain
The PASC reproduces atmospheric compositions and surface temperatures for most planetary objects (Fig. 6B; Mateo-Martí et al. 2006). Temperatures can be set from −269 to 52°C, pressures from 5 to \(5\times10^{-9}~\mbox{mbar}\). A residual gas analyzer regulates the required atmospheric composition with ppm precision, while a combination of a deuterium lamp and a noble-gas discharge lamp provides the required UV spectrum. PASC has already been used to study the UV-absorbing properties of a Martian analogue (basaltic dust) as a function of its thickness and mass (Muñoz-Caro et al. 2006), the stability of saline water under Mars conditions (Zorzano et al. 2009), the survival of chemolithoautotrophic bacteria and resistance of the lichen Circinaria gyrosa exposed to simulated Mars conditions (Gomez et al. 2010; Sánchez Iñigo et al. 2012), and the photostability of nucleobases and peptide biomolecules under UV irradiation (Mateo-Martí et al. 2009; Mateo-Martí and Pradier 2013).
Mars Simulation Facilities, The Open University (OU), UK
Two chambers comprise the Mars simulation facilities at the Open University. The large chamber provides pressure and temperature conditions representative of the surface of Mars (Fig. 6C). This chamber has the capability to incorporate large-scale regolith experiments. The small Mars chamber has a solar illumination facility designed for instrument qualification and astrobiology experiments, which allows an automated variation of the environment (e.g. thermal diurnal cycling; Patel et al. 2010). These simulation chambers have been used, for example to study the degradation of microbial fluorescence biosignatures by solar ultraviolet radiation on Mars (Dartnell and Patel 2013), the influence of mineralogy on the preservation of amino acids under simulated Mars conditions (dos Santos et al. 2016), and the potential of interlayer regions of silicate sheets as a favorable habitat for endolithic microorganisms (Kapitulčinová et al. 2015).
Mars Environmental Simulation Chamber (MESCH), Aarhus University, Denmark
MESCH is a double-walled cylindrical Mars simulation facility comprised of a cryogenic environmental chamber, an atmospheric gas analyzer, and a xenon/mercury discharge source to generate UV radiation (Fig. 6D). The double wall functions as a cooling mantle through circulation of liquid \(\mbox{N}_{2}\). A carousel controlled by an external motor holds up to 10 samples. Exchange of the samples without changing the environment of the chamber is achieved due to a load-lock system, which has a small pressure-exchange chamber. Data such as temperature, pressure, and UV exposure time are used in automated feedback mechanisms, allowing a wide variety of experiments (Jensen et al. 2008).
Planetary Environmental Liquid Simulator (PELS), University of Edinburgh, UK
The PELS chamber at the University of Edinburgh is designed for examining extra-terrestrial aqueous environmental conditions (Fig. 6F). The front door has a glass view port in the center, so samples and manipulations can be easily viewed. For liquid input/output, vacuum flanges have been modified with bored-through steel bulkheads, through which polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) tubing has been attached to give a corrosion-resistant wetted flow path and vacuum seal. The facility, containing six separate sample vessels, allows for statistical replication of samples. Control of pressure, gas composition, UV irradiation conditions and temperature allows for the precise replication of aqueous conditions, including sub-zero brines under Martian atmospheric conditions. A sample acquisition system allows for the collection of both liquid and solid samples from within the chamber without breaking the atmospheric conditions, enabling detailed studies of the geochemical evolution and geomicrobiological habitability of past and present extra-terrestrial environments (Martin and Cockell 2015).
Planetary Analogues Laboratory for Light, Atmosphere, and Surface Simulations (PALLAS), Utrecht University, The Netherlands
PALLAS is a planetary surface simulation facility at Utrecht University (Fig. 6F). Variable parameters include the atmospheric composition and pressure (\(10^{-7}\)–900 mbar), sample temperature (−80 to \(+60\)°C) and solar (UV-Visible) spectrum. The UV spectrum is generated with a combination of a Xenon solar simulator equipped with a water filter to remove residual heat (250–900 nm) and a deuterium light source (160–400 nm). Gases can be pre-mixed or mixed within the chamber to obtain a range of atmospheric conditions. Up to ten samples can be placed, either in the beam spot of the UV source or in the dark (as control) on a table that can be cooled to −80°C using a cooling bath. A quadrupole mass spectrometer is mounted onto the chamber, via a differentially pumped sampling volume, to sample and analyze the atmosphere during the experiments (ten Kate and Reuver 2015).
Planetary and Space Simulation Facilities at the DLR, Germany
There are three planetary simulation chambers in the Institute of Planetary Research at DLR Berlin which are operated by the Spectroscopy Laboratory Group and the Astrobiological Laboratories Group. One is a vacuum chamber (\(40 \times 30 \times 30~\mbox{cm}\)) which simulates conditions on Venus and Mercury. Samples can reach 500°C and beyond, while keeping the rest of the chamber relatively cold (Maturilli et al. 2010). The second chamber is a Mars Simulation Facility (MSF). The MSF laboratory consists of a cold chamber with a cooled volume of \(80 \times 60 \times 50~\mbox{cm}\). The effective operational experimental chamber, which is cooled within the cold chamber, is a cylinder with inner diameters of \(20.1 \times 32.4~\mbox{cm}\). This chamber operates at 6 mbar \(\mbox{CO}_{2}\) pressure at −75°C. The solar spectra range as it appears on Mars can be simulated by the use of a Xe-lamp and the applied above mentioned environmental parameters as well as the humidity can be varied according to the programed daily cycles. It can be used in non-biological simulation experiments (in different disciplines such as planetary geology, astrobiology, environmental chemistry and materials science and sensor testing), and for biologically relevant experiments by using hardware, which performs in situ measurements during the simulation experiments (de Vera et al. 2010, 2014a, 2014b see Sect. 4.1.1 of the present manuscript). The third simulation chamber is a micro-version of the second simulation facility, which can be connected to a cryostate and can even simulate the temperature conditions of the icy moons and deep space (down to 4 K). It is adapted to be placed under a microscope and Raman spectroscope, allowing measurements under simulated planetary conditions testing the influence of environmental conditions on the measurement operations. The use of this facility will be of significant support for the approved future ESA BioSigN exposure experiment in LEO. By using ocean and deep sea material it will simulate and approach the conditions which space exposed plume ejecta of the icy moons might face to. In parallel it will investigate the degree of biosignature detection by spectroscopy under these extreme icy moon-related space conditions.
The astrobiology group of the Radiation Biology Department at the DLR Institute of Aerospace Medicine operates a total of seven modular Planetary and Space Simulation Facilities (PSI) in Cologne. A full description of the facilities, their operational parameters and space experiments performed in these facilities was published by Rabbow et al. (2016) (http://www.dlr.de/spacesim). The facilities differ with respect to size, provide simulated space vacuum or planetary atmospheres, are temperature controlled and are equipped with optical windows and a variety of solar simulators for UV-irradiation. The facilities were repeatedly used for space mission preparation and reference experiments.
Space environment simulation is realized by combining vacuum, down to \(10^{-9}\) Pa with Ion getter pumps are connected (“Deep Space” facilities PSI 3, 6 and 9), temperature oscillation at sample site and short wavelength UV irradiation as experienced outside the Earth Ozone layer. This setup complemented space mission experiments, as e.g. on the Long Duration Exposure Facility (LDEF) from April 7th 1984 to January 11th 1990, in ERA on EURECA from August 2nd 1992 to June 24th 1993 and several Biopan experiments on Foton satellites.
Material tests were performed in the big sized facilities, which can be used for Life Science and Human Flight operations and also for Astrobiology tasks. They are connected to computer controlled temperature regulation, solar simulators and providing space vacuum or Mars atmosphere with respect to pressure and gas composition. They performed the space experiment pre-flight test and mission parallel ground experiments for all three long-term ESA multiuser exposure facilities EXPOSE-E from February 7th 2008 to September 12th 2009, EXPOSE-R from November 26th 2008 to March 9th 2011, and EXPOSE-R2 from July 23rd 2014 to June 5th 2016.
While simulation of space and Mars surface environment was the main focus in the past and is adapted for anaerobic organisms in preparation of the ESA MEXEM experiment, the facilities are upgraded now also for the simulation of the icy moon Europa ocean conditions in preparation of the ESA IceCold active exposure experiment featuring in situ life measurements. Recently, the stationary vacuum facilities were complemented by small transport and exposure boxes (TRex-Box) and the option for additional ionizing irradiation in an x-ray facility under defined vacuum or planetary atmospheric conditions.
These past and current ground based experiments performed in simulation facilities cannot substitute space experiments that use space as a tool for astrobiology to investigate the effect of the unique combination of environmental parameters on life. Simulation of space parameters and their combination are technically limited. In particular, short UV with wavelength <200 nm and the complex ionizing radiation field of space can only be approximately simulated. But in contrast to space, Earth bound facilities used as tools for astrobiological investigations provide easy and fast access and more experimental space, an important feature in particular for the preparation of astrobiological space experiments.
In order to allow the exposure of a wide variety of scientifically interesting biological organisms, the complete DLR laboratory housing the simulation facilities is announced as Genetic laboratory safety level 1 for the use of genetically modified organisms, and as Biosafety level 2 laboratory according to German law.
4.1.1 Biologically Relevant Accessories for “in situ” Analysis in Simulation Facilities
In analogy to the recommendations in “Space as tool for astrobiology” for advanced astrobiological space hardware (Cottin et al. 2017), in situ measurements during ground based simulation experiments are of prime importance. The activity of tested samples can be measured in situ by specific sensor hardware applied during the simulation experiments in addition to the sensors, which are measuring the environmental conditions during the simulation experiments. For example, the degree of photosynthetic activity can be monitored and recorded during simulation conditions by a planetary and Mars adapted measurement device named Mini-PAM (Walz 1999; Lorek and Koncz 2013, de Vera et al. 2010, 2014a, 2014b). Methane production of methanogens can be observed during Mars simulation experiments due to the use of specific optical hardware like laser spectroscopy and gives indirectly information on growth rates of methanogens during simulation experiments (Schirmack et al. 2014). Biological activity during the simulation experiments may be observed by many other ways: (i) pH-changing of soil where bio-samples are embedded, (ii) camera based observations of bleaching effects of soil and rocks and (iii) use of isotopes in atmospheric gases and use of isotope detecting hardware for check of consumption or production of gases due to biological activity, or optical density variations measured by photometers.
4.1.2 Mars Wind Tunnels
Dust devils and dust storms occur frequently on the Martian surface (Greely et al. 1977). Both slow and fast moving dust interacts with its environment, with abrading effects on landers and rovers, and also on mineralogy (Merrison et al. 2010). In terrestrial dust storms the interaction of dust particles leads to the generation of an electric field (e.g. Freier 1960), a process which on Mars has been related to oxygen enhancement (Atreya et al. 2006) and methane destruction in the atmosphere (Farrell et al. 2006). To study the effects of the moving dust, several wind tunnel facilities have been established. A selection of Mars wind tunnels available on the USA is described below.
The Mars Surface Wind Tunnel (MARSWIT), NASA Ames Research Center, USA
MARSWIT, the first Mars wind tunnel was established in the 1960s at NASA Ames Research Center (Greeley et al. 1977, 1980, 2000; Greeley 2002). This pentagon-shaped chamber, a 30 m high concrete tower, can be evacuated to a minimum pressure of 3.8 mbar. Large experimental apparatus can be placed inside the chamber. High-pressure air (up to \(9.86~\mbox{kg}/\mbox{cm}^{2}\)) is introduced into the tunnel to induce the flow of air. At these pressures a maximum free-stream airspeed of 180 m/s can be achieved at Mars-like pressures of 5 mbar (500 Pa) (Greeley et al. 1977).
The Arizona State University Vortex Generator (ASUVG), USA
As dust devils have entirely different dynamics than dust flows and storms, ASUVG was built specifically to simulate dust devils. It consists of three components: the frame, the vortex generator, and the test table. The vortex generator includes a cylinder with a “bell mouth” to alleviate boundary effects at the edge of the cylinder, a motor drive, and a fan blade system. The dust is placed on a test table that can be raised, lowered, or moved laterally to simulate different motions of a dust devil During the tests, the ambient temperature, relative humidity, wind speeds, and surface pressures on the test bed beneath the vortex can be measured (Greeley et al. 2003; Greeley 2002; Neakrase et al. 2006; Neakrase and Greeley 2010).
The Aarhus Wind Tunnel Simulator (AWTS), University of Aarhus, Denmark
The AWTS facility was specifically built to reproduce wind conditions on the Martian surface and to study the transport of airborne dust. To do so, a re-circulating wind tunnel is housed within an environmental chamber that operates at the atmospheric pressure (6–10 mbar), composition and temperature of Mars. An axially mounted fan driven by an electric motor draws gas down the central wind tunnel and returns it in an outer cylindrical cavity. This design has been chosen to maximize the available open wind tunnel area (cross section) while maintaining smooth fluid flow given the limited environmental chamber dimensions. It is of importance when utilizing the recirculating system that the area of the return flow is comparable (if not greater than) to that of the wind tunnel in order to minimize turbulence and irregularities in the wind stream. Fins are used to minimize rotation effects on the wind by the fan (Merrison et al. 2002, 2004, 2007, 2008, 2010, 2012).
4.1.3 Simulation Facilities for Organic Aerosols in Planetary Atmospheres
Experimental setups are developed in planetary science to simulate the production of organic aerosols in planetary atmospheres. These laboratory analogues are often named “tholins” in the literature since the seminal work by Sagan and Khare in 1979 (Sagan and Khare 1979). The abundance, the prebiotic interest as extra-terrestrial nitrogen-rich organic matter, and the poor knowledge of their chemical composition make Titan’s atmospheric aerosols one of the most studied objects through laboratory simulation. However, tholins have also been produced to investigate the formation and/or evolution of aerosols in other atmospheres such as the early Earth’s atmosphere (Trainer et al. 2004), the Jovian atmosphere (McDonald et al. 1991; Sagan et al. 1993), and Triton’s atmosphere (McDonald et al. 1994).
The main principle of these experiments is to couple an energy source to a gas mixture composed of the main atmospheric components in order to mimic the initiation of the complex chemical networks taking place in the given atmosphere and leading to the production of organic aerosols. The energy sources used in the laboratory are proxies for the solar irradiation and the precipitation of magnetospheric electrons. Those natural sources are reproduced in the laboratory by UV photon fluxes (Carrasco et al. 2014; Imanaka and Smith 2010; Trainer et al. 2012; Tran et al. 2008; Trainer et al. 2006) and/or by plasma discharges (Somogyi et al. 2005; Coll et al. 1999; Horvath et al. 2009; Imanaka et al. 2004; Sciamma-O’Brien et al. 2010; Hörst and Tolbert 2013). Pressure and temperature are strongly dependent on the experiments, and can hardly reproduce the whole range and extreme conditions occurring in real atmospheres. As developed in (Carrasco et al. 2013a, 2013b), wall effects can be encountered at low pressure conditions, when the mean free path exceeds the typical dimensions of the photo-reactor. Considering these constraints, it is important to propose and develop various and complementary experiments. The larger the set of conditions is explored, the better our knowledge on the sensitivity enables to extrapolate the analogues properties to the atmospheric aerosols properties. A complementary approach consists in targeting an organic growth mechanism by initiating the polymerization of a specific molecule, minor in the atmospheric composition but expected as a possible precursor of the aerosol nucleation process. Thus, tholins of interest for Titan were synthesized by polymerization of HCN (Vuitton et al. 2010) and \(\mbox{C}_{4}\mbox{N}_{2}\) molecules (Couturier-Tamburelli et al. 2014). Organic growth processes through negative ion chemistry was also investigated between \(\mbox{CN}^{-}\) ions and \(\mbox{HC}_{3}\mbox{N}\) molecules (Žabka et al. 2012).
The first aim of these laboratory experiments is to address the question of how atmospheric chemistry can sustain the formation of complex organic matter and possibly prebiotic buildings blocks in a planetary system (Raulin et al. 2012). This laboratory approach focuses on the chemical processes. Firstly, the chemistry is decoupled from the complex transport occurring in an atmosphere, and submitting aerosols to the large variety of physical conditions encountered on the global scale. Secondly, the chemical kinetics is accelerated to give access to long time-scale processes, which are hardly accessible from direct observations. Laboratory studies have been used for example to investigate Titan’s aerosol chemical composition through geological time-scale (Mahjoub et al. 2012), and the low isotopic nitrogen fractionation of the Archean organic matter on the early Earth (Kuga et al. 2014). And thirdly, analogues can be analyzed with highly efficient analytical techniques yet out of reach in space, providing unique information on the chemical composition and formation processes of the organic aerosols: Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) (Derenne et al. 2012; He and Smith 2014), high resolution mass spectrometry (Gautier et al. 2014; Pernot et al. 2010; Somogyi et al. 2005) or thermal characterization (He et al. 2014; Nna-Mvondo et al. 2013).
The second aim of these laboratory experiments is to support space missions giving rise to useful collaborations between laboratory, modelling and observation studies. These collaborations involve both the preparation of new missions and the exploitation of on-going and past missions. Planetary atmospheres are complex systems coupling chemical, dynamical and radiative processes. The observation data reflect all this complexity and can be difficult to interpret. The chemical and physical properties of the laboratory analogues provide access to essential parameters for de-convoluting atmospheric data measurements. Laboratory analogues are extensively used for example as a support of interpretation for the Cassini-Huygens space mission (Fig. 7). Optical refractive indices of laboratory analogues were used to interpret the light-scattering properties by Titan’s aerosols from the Descent imager/spectral radiometer (DISR) instrument (Hadamcik et al. 2009; Hadamcik et al. 2013). Mid- and far-IR absorption properties of Titan’s aerosol analogues helped to identify and confirm aerosols signatures obtained by the Visible and Infrared Mapping Spectrometer (VIMS) and the Composite Infrared Spectrograph (CIRS) instruments (Gautier et al. 2012; Sebree et al. 2014), but also identified some limitations of the laboratory approach through discrepancies between laboratory analogues and Titan’s aerosols signatures (Gautier et al. 2012; Imanaka et al. 2012; Kim et al. 2011). Mass analysis at high resolution of laboratory analogues also provided some leads on the chemical composition of the large species detected in Titan’s ionosphere by the Cassini Plasma Spectrometer (CAPS) instrument at low mass resolution (Carrasco et al. 2013a, 2013b). Moreover, laboratory analogues are used as model organic matter to calibrate and optimize space instrumentation for future space missions in order to detect and analyze organics in space. Analogues of Titan’s atmospheric aerosols have for example been used to improve the analysis of organics in space by pyrolysis-Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (pyr-GC-MS) (He et al. 2014; Morisson et al. 2016).
One of the difficulties encountered when simulating the synthesis of organic aerosols is to prevent samples from air contamination when collecting them and bringing them to external analytical devices (Cable et al. 2012). Without any specific precaution the analogues adsorb and react on their surface with oxygen, leading to a few percent of oxygen in their elemental composition (Fleury et al. 2014). This issue becomes a critical interference when studying the primordial incorporation of oxygen in the aerosols in planetary conditions (Hörst et al. 2012). Some efforts can be made to collect the analogues in oxygen free gloves boxes, but this caution is not enough. A total oxygen-free chain would be required to transport the samples from their site of synthesis to their site of analysis. This is to date hardly achievable and remains a strong limitation to simulate in the laboratory analogues of planetary organic aerosols with a controlled content of oxygen.
4.2 Interstellar and Cometary Organic Chemistry Simulation Facilities
Numerous laboratory experiments have been developed to study the complex organic chemistry occurring in interstellar and cometary ices (Allamandola et al. 1988; Palumbo et al. 2004; Briani et al. 2013; Kobayashi et al. 1995; Moore and Hudson 2005; Meinert et al. 2012; Danger et al. 2013). The principle of such experiments is the following; from observations of the most abundant species present in the ices in late stages of the molecular clouds (out of which stars and planetary systems form), together with some comparison with cometary atmospheres, one can built templates of ices to study their evolution in the laboratory. The templates consist in the deposition of a gaseous mixture representative of cosmic ices molecules in a high vacuum chamber and on a cold (10–80 K) inert window. At this stage, the main analytical tool is infrared spectroscopy because, historically, this method was used to understand the composition and behavior of such ices in space (d’Hendecourt et al. 1996). Since cosmic ices can be subjected to various energetic processes (VUV irradiation, cosmic-rays, and thermal heating), all these processes are straightforward to produce in the laboratory to study the ice chemistry that progressively forms complex organic molecules and actual organic matter. Globally these processes are templates of the general evolution of the ices, from molecular clouds to their incorporation in comets and other minor bodies in the solar (or any planetary) system. For astrobiological purposes, the philosophy of such experiments is linked to the possible generation of so-called prebiotic molecules that can be found in these ices and/or organic residues. Indeed, one can note that when the sample is warmed up to room temperature for further analysis using more precise and sophisticated tools, a refractory organic residue always remains on the substrate as the volatiles sublime (Fig. 8). Mayo Greenberg, who was the first to conceive such an experimental approach called this residue “Yellow Stuff” (Greenberg 1982) because of its light-yellow color. The necessity to proceed to such experimental simulations is dictated by the fact that the very high level of complexity obtained from solid state reactions within the bulk of the ices generates a very large number of products. Therefore, it would be impossible to predict the issue of such non-directed Miller-type experiments using an ab-initio model implying thousands of species and reaction channels.
A typical experimental setup allowing the photolysis of cometary ice analogues made by deposition of a gas mixture on a cold sample carrier and cooled down to 10 K in a cryostat (the UV lamp can be replaced in some setups by an ion or an electron gun). The ice evolution can be analyzed in situ by IR spectroscopy. The room temperature residue can then be collected for further analysis such as GC-MS, High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and Very High Mass Resolution Spectrometry (VHRMS). Schematic of the experimental set-up from Briani et al. 2013
The diversity of organic compounds synthesized during such laboratory simulations is remarkable but their identification is not always evident (Colangeli et al. 2004; Cottin et al. 1999; Danger et al. 2013), and depends on the various analytical methods and protocols used in the procedure. Surprisingly, if templates of abundant interstellar ices are considered, essentially containing H, C, O and N roughly in cosmic abundances, the nature of the complex molecules tends not to depend too much on the ice composition (Muñoz Caro and Schutte 2003). Similarly, the nature of the energy sources, either VUV photons or fast energetic particles (including heavy swift high energy ions) leads, at least to the first order to similar radical-molecule reactions giving very similar organic residues (Muñoz-Caro et al. 2014). This is due to the nature of the solid-state chemistry which is generated by the irradiation process, and by further warming-up of the sample. This chemistry is basically dictated by diffusion of reactants and radical-molecule recombination, which appear to be a somewhat random process. The chemistry considered and simulated in these laboratory experiments can occur to ice mixtures either on icy coated dust grains in interstellar clouds (potentially pre-cometary ices), or within the Solar Nebula during the accretion of icy planetesimals, or in the outer layers of comet ices in the Solar system. The fact that these simulations do lead to a rather unique class of organic materials that may share some similarities with chondritic organic matter is a good argument in favor of the validity of this approach, which can be considered as a systemic one, and ultimately allows for the build-up of an astrophysical scenario for the origin of the organic matter in the solar system (or any forming planetary system). This organic matter may later be involved (or not) in prebiotic processes that may be at work on telluric planets in presence of the right environmental conditions, mainly liquid water and a free energy source (UV-visible photons being the most probable one because of entropy considerations). Indeed, the full nature of this astrophysical scenario is highly convoluted and these simulations must be considered as templates that are able to reproduce some of the organic complexity observed in meteorites, and further on may suggest prebiotic routes for the emergence of life by the delivery of exogenous organic matter on the early Earth. One does not need to fully reproduce all the aspects of the true historical scenario (indeed an impossible task), but instead highlight the main points and bottlenecks that such a scenario may encounter. Direct implication on astrobiology, as far as the habitability of a planet, the subsequent prebiotic activity in a given environment and the emergence of life in the form of autocatalytic chemical networks are considered, is central to this type of laboratory studies and further potential and expected developments.
For direct relevance to astrobiology, it must be noted that a great number of amino acids (such as glycine, alanine, sarcosine, valine, proline, serine, etc.) are reported in residues obtained after UV irradiation of ice mixtures containing molecules such as of \(\mbox{H}_{2}\mbox{O}\), \(\mbox{NH}_{3}\), \(\mbox{CH}_{3}\mbox{OH}\), HCN, CO and \(\mbox{CO}_{2} \) (Bernstein et al. 2002; Muñoz-Caro et al. 2002; Meinert et al. 2012). Those are detected using classical GC-MS techniques, sometimes with very high sensitivity and separation properties such as in the case of bi-dimensional GC-MS. In some experiments, contrary to what can be done in the analysis of meteorites, labelling of the carbon used in the experiments (i.e. using \({}^{13}\mbox{C}\)) leads to results in which potential terrestrial contaminations issues can be fully discarded. Analytical protocols require usually the dissolution in water of the soluble organic matter present in the residues, followed by acid hydrolysis (for the liberation of amino acids often trapped in some form of macromolecular material), as well as derivatization methods in order to allow the use of the GC technique, which requires the compounds to be volatile. Although somewhat controversial, non-hydrolysed samples versus hydrolysed ones do show very similar composition in amino acids, the hydrolysed fraction showing usually a larger abundance (Nuevo et al. 2008). Nevertheless, free amino acids do exist in the residues, as in primitive carbonaceous meteorites (Martins et al. 2015). It is a matter of debate whether hydrolysis of the synthetic organic matter present in these residues is relevant to what could have occurred on the primitive Earth. It is however expected that organic matter exogenously delivered to our primitive planet was mixed to an ocean of liquid water, and that similar chemistry occurred. Many other potentially prebiotic molecules are present in these residues. Sugars were detected in the same suite of experiments using strictly the same methodology (but not the same extraction and detection protocol due to the different chemical properties of the searched target molecules). Glycolaldehyde and glyceraldehyde, two molecules suspected to be important for the formation of ribonucleotides in a particularly primitive Earth-like environment (Powner et al. 2009), were found (de Marcellus et al. 2015). More recently, the detection of the aldopentose ribose together with a full family of structurally related sugar molecules have been reported in quite high abundances in the same laboratory ices (Meinert et al. 2016). One may also note that nucleobases are suspected to be present in the residue. Indeed, the detection of uracil, and in only one case cytosine was achieved (Nuevo et al. 2009, 2014). Up to this moment no other nucleobases have been identified, but a systematic search is underway in some laboratories.
The issue of chirality is also being investigated through laboratory simulations. It has been reported that an asymmetric (i.e. a chiral electromagnetic field) vacuum UV photolysis of a racemic mixture of leucine in the solid-state results in the production of an enantiomeric excess of one of the forms of the amino acid (Meierhenrich et al. 2005). Moreover, enantiomeric excesses can be detected when amino acids are directly synthesized within an achiral ice mixture under circularly polarized light (CPL), with an enantiomeric excess of up to 2.54% (de Marcellus et al. 2011; Modica et al. 2014). In this case, the evolution of the ice under VUV light does produce chiral precursors of organic compounds. If the VUV light is generated as circularly polarized light using a synchrotron light source such as the SOLEIL (Source Optimisée de Lumière d’Énergie Intermédiaire du Laboratoire pour l’utilisation du rayonnement électromagnétique) in France, on a line dedicated to the production of chiral photons, enantiomeric excesses can be generated and observed within the same organic residues formed in the warming-up process. Remarkably Modica et al. (2014) found that five different amino acids present the same (L- or D-) excesses in the experiment, depending on the helicity of the CPL used. When no CPL is used (e.g. in the linear polarization irradiation regime), a racemic sample is obtained.
4.3 Instrument Testing Facilities
Before deployment on a mission, instruments need to reach a certain technical readiness level (TRL). This TRL can be reached by testing the instrument both in the field (as described earlier) and in the lab under realistic planetary conditions. Several chambers have been developed specifically for instrument testing.
Chemistry and Camera (ChemCam) Environmental Chamber
The ChemCam Environmental Chamber was developed at the University of Toulouse, France to test the first Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy instrument under simulated Martian environment (pressure and composition). The instrument was part of ChemCam on the Curiosity Rover (Cousins and Crawford 2011). In each experiment, five samples are placed in the chamber (kept at room temperature) and the ChemCam instrument is installed 3 meters from the sample (Cremers and Radziemski 2006).
Sample Analysis at Mars (SAM) Environmental Chamber
The SAM environmental chamber was developed at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, USA to mimic the thermal conditions in a rover on the surface of Mars, allowing simultaneous instrument suite qualification The SAM chamber consists of six independent thermal zones, in which the temperature can be cycled between −40°C and \(+50\)°C, and the pressure varied from \(10^{-6}\) to 1000 mbar (Mahaffy et al. 2012).
5 Conclusions and Recommendations
Over the past few decades, the role of the Earth as a tool for Astrobiology has been emphasized by establishing a wide range of planetary analogue field sites and simulation facilities in the laboratory. But these existing infrastructures and logistics are still unknown to the broader community and often could complement each other. The first activities, such as the EU supported EUROPLANET or CAFE, have just started to coordinate systematic interactions and common projects combing planetary field site research with planetary simulation experiments. The goal is to achieve as many investigations as possible on the origins of life and habitability of Mars and other planets or moons by experiments in the field combined with planetary simulations in the lab. But further work and synergistic cooperation is needed. A number of different national Polar Expeditions, Desert research projects and Deep sea missions are often organized field campaigns with the topic of “climate change” or “environmental issues”, and offer in parallel to researchers of other disciplines opportunities to participate. These are opportunities to cooperate and to share also results, which might be of significant relevance either for astrobiology and Earth sciences researchers. To further enhance the utilization of the Earth and Earth-based systems as a tool for Astrobiology with emphasis on synergistic cooperation we propose the following recommendations to ESA.
5.1 Analogue Studies, Field Work and Laboratory Simulations
-
Obtain more calls for opportunities for field test campaigns in environments that are similar to solar system bodies. To facilitate these field campaigns, a central point of contact (potentially hosted at ESA) could be established to help organize campaigns, to keep an oversight of the conditions on the field sites, and to work together with the local responsible parties. One of its responsibilities would be to oversee the remote monitoring of the field sites, through satellite data or ground stations for field sensors.
-
Establish an EU or ESA supported international survey of all expeditions performing scientific work in planetary field analogue sites, which could provide logistics and infrastructure, enabling an interdisciplinary scientific cooperation. This can minimize the costs, and also allow astrobiologists to learn methods, operations and strategies from other scientific communities. In this way scientists share their own knowledge and results for general and common use.
-
Improvement of infrastructures and resources to undertaking astrobiological research is necessary. This means that the combination of field work and planetary simulation investigations is not sufficiently developed at present. For example, support is needed for the scientific community involved in the study of biosignatures and life detection, as well as for future space missions dedicated to the search for life on other planets and moons. A systematic approach with tests on instruments under simulated planetary and space conditions as well as tests on the operation capacity in the field is needed.
-
Support the use of simulation facilities, which is currently covered in the ESA-member states by national or international cooperation agreements. In addition, the planetary field analogue projects should be supported by ESA like it is accomplished by NASA in the United States.
-
A European Astrobiology Platform (or Institute) should be implemented to optimize the scientific return by using a coordinated infrastructure and funding system. This is in agreement with recent recommendations by the AstRoMap European Astrobiology Roadmap, which was supported by the European Commission Seventh Framework Programme (Horneck et al. 2016)
-
Data obtained on astrobiological research should be shared with the scientific community through an open access database. Coordinated funding must insure the ability to establish this database.
-
Develop a coordinated EU or ESA program of opportunities for public education and outreach, including training for scientists, and information to the public about the state of the art in Astrobiology.
5.2 ESA Field Campaign Facilities
General Curation Facility
It would be beneficial for the community to develop a common sampling protocol, and a tool for packing and transporting the samples in oxygen-free conditions, to be able to share the analogues within the community without altering them in the transport. In the same way, the PFA and ISAR should be expanded in order to contribute meaningfully with the proposed European/ESA curation facility (n.b. not country specific) to host planetary field analogue samples. In fact, the ISAR is being transferred to the ESA facility under construction at Harwell in the UK for this purpose. There should be a interaction with the European curation of astromaterials received by a sample return mission from future space exploration programs (e.g. the requirements for such facility are being defined by the EC Horizon 2020 project EURO-CARES, http://www.euro-cares.eu/), in order to have a parallel between planetary field analogue samples and actual collected samples from the sample return missions as foreseen within the Solar System exploration program to asteroids, Mars, the Moon, and comets. Whether or not both sets of samples should be placed at the European Sample Curation Facility (ESCF) is still to be discussed.
Analytical Facilities
An ESA supported User Analytical Facility Network should be established to facilitate uniformity in analyses and therefore allowing the different campaigns to be compared to each other. This User Analytical Facility Network could be comprised of instrumentation at associated institutions as well as instrumentation at ESA centers available for this purpose. The aim of this network would be to enable all participating scientists to make use of the most sophisticated instrumentation around. The network should include instrumentation for ultra-trace sample analysis, such as High-Resolution MS facilities (ToF-SIMS, NanoSIMS, LA-ICPMS), Microscopy facilities (CLSM, AFM, SEM, TEM, FIB), Spectroscopy facilities (Infrared, Raman, Fluorescence, NMR) and Analytical chemistry facilities (LC-ToF-MS, GC-MS).
ESA Archiving Facilities
An archiving facility should be built, consisting of two parts. A Ground Reference Sample Storage, where samples collected on the field testing campaigns will be stored for future reference, and an Electronic Database, where simulated planetary environment parameters and environmental field parameters are logged, field campaign data and laboratory data stored, and all these can be interconnected with existing databases.
References
W. Abbey, E. Salas, R. Bhartia, L.W. Beegle, The Mojave vadose zone: a subsurface biosphere analogue for Mars. Astrobiology 13, 637–646 (2005)
L.J. Allamandola, S.A. Sandford, G.J. Valero, Photochemical and thermal evolution of interstellar/precometary ice analogs. Icarus 76, 225–252 (1988)
C.C. Allen et al., Lunar and Planetary Science Conference XXXI Abstracts (1998a), p. 1287
C.C. Allen et al., Lunar and Planetary Science Conference XXIX Abstracts (1998b), p. 1690
X. Amashukeli et al., J. Geophys. Res. 112, G04S16 (2007)
R. Amils et al., Extreme environments as Mars terrestrial analogs: the Rio Tinto case. Planet. Space Sci. 55, 370–381 (2007)
M. Ansdell, P. Ehrenfreund, C. McKay, Stepping stones toward international space exploration. Acta Astronaut. 68, 2098–2113 (2011)
S.K. Atreya, A. Wong, N. Renno, W. Farrell, G. Delory, D. Sentman, S. Cummer, J. Marshall, S. Rafkin, D. Catling, Oxidant Enhancement in Martian Dust Devils and Storms: implications for Life and Habitability. Astrobiology 6, 439–450 (2006)
K.C. Benison, B.B. Bowen, Icarus 183, 225–229 (2006)
M.P. Bernstein, J.P. Dworkin, S.A. Sandford, G.W. Cooper, L.J. Allamandola, Racemic amino acids from the ultraviolet photolysis of interstellar ice analogues. Nature 416, 401–403 (2002)
D.A. Beysens, J.J.W.A. van Loon (eds.), Generations and Applications of Extraterrestrial Environments on Earth (River Publishers, Aalborg, 2015)
J.M. Bigham, D.K. Nordstrom, in Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, vol. 40 (2000), pp. 351–403
A. Borst et al., Lunar and Planetary Science Conference XLI Abstracts (2010), p. 2744
N. Bost, F. Westall, C. Ramboz, F. Foucher, D. Pullan, A. Meunier, S. Petit, I. Fleicher, G. Klingelhöfer, J. Vago, Missions to Mars: characterization of Mars analogue rocks for the International Space Analogue Rockstore (ISAR). Planet. Space Sci. 82, 113–127 (2013)
P.J. Boston, M.V. Ivanov, C.P. McKay, On the possibility of chemosynthetic ecosystems in subsurface habitats on Mars. Icarus 95, 300–308 (1992)
A. Bouquet, O. Mousis, J.H. Waite, S. Picaud, Possible evidence for a methane source in Enceladus’ ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 42, 1334–1339 (2015)
B.B. Bowen et al., Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 268, 52–63 (2008)
G. Briani, N. Fray, H. Cottin, Y. Benilan, M.-C. Gazeau, S. Perrier, HMT production and sublimation during thermal process of cometary organic analogs. Implications for its detection with the ROSETTA instruments. Icarus 226, 541–551 (2013)
M.E. Brown, K.P. Hand, Astron. J. 145, 1–7 (2013)
A. Buch et al., Planet. Space Sci. 54, 1592–1599 (2006)
M.L. Cable et al., Titan tholins: simulating titan organic chemistry in the Cassini-Huygens Era. Chem. Rev. 112, 1882–1909 (2012)
N. Carrasco, H. Cottin, M. Cloix, Y. Bénilan, P. Coll, M.-C. Gazeau, R. Raulin, K. Saiagh, C. Szopa, The AMINO experiment: methane photolysis under solar VUV irradiation. Int. J. Astrobiol. 14, 79–87 (2014)
N. Carrasco, A. Giuliani, J-J. Correia, G. Cernogora, VUV photochemistry simulation of planetary upper atmosphere using synchrotron radiation. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 20, 587–590 (2013a)
N. Carrasco, J. Westlake, P. Pernot, H. Waite Jr., Nitrogen in Titan’s atmospheric aerosol factory, in The Early Evolution of the Atmospheres of Terrestrial Planets (Springer, New York, 2013b)
S.C. Cary, I.R. McDonald, J.E. Barrett, D.A. Cowan, On the rocks: the microbiology of Antarctic Dry Valley soils. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 8, 129–138 (2010)
D.C. Catling, M.W. Claire, K.J. Zahnle, R.C. Quinn, B.C. Clark, M.H. Hecht, S. Kounaves, Atmospheric origins of perchlorate on Mars and in the Atacama. J. Geophys. Res. 115, E00E11 (2010)
H.-S. Chan et al., Planet. Space Sci. 68, 42–47 (2012)
C.S. Cockell, Geomicrobiology beyond Earth: microbe–mineral interactions in space exploration and settlement. Trends Microbiol. 18, 308–314 (2010)
C.S. Cockell, S. Payler, S. Paling, D. McLuckie, Boulby International Subsurface Astrobiology Laboratory. Astron. Geophys. 54, 2.25–2.27 (2013)
L. Colangeli, J.R. Brucato, A. Bar-Nun, R.L. Hudson, M.H. Moore, Laboratory experiments on cometary materials, in Comets II, ed. by M.C. Festou, H.U. Keller, H.A. Weaver (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 2004), pp. 695–717
P. Coll, D. Coscia, N. Smith, M.C. Gazeau, S.I. Ramirez, G. Cernogora, G. Israel, F. Raulin, Experimental laboratory simulation of Titan’s atmosphere: aerosols and gas phase. Planet. Space Sci. 47, 1331–1340 (1999)
H. Cottin, M.C. Gazeau, F. Raulin, Cometary organic chemistry: a review from observations, numerical and experimental simulations. Planet. Space Sci. 47, 1141–1162 (1999)
H. Cottin, J.M. Kotler, K. Bartik, H.J. Cleaves, C.S. Cockell, J-P.P. de Vera, P. Ehrenfreund, S. Leuko, I.L. ten Kate, Z. Martins, R. Pascal, R. Quinn, P. Rettberg, F. Westall, Astrobiology and the Possibility of Life on Earth and Elsewhere…. Space Sci. Rev. (2015). doi:10.1007/s11214-015-0196-1
H. Cottin, J.M. Kotler, C.S. Cockell, R. Demets, P. Ehrenfreund, A. Elsaesser, L. d’Hendecourt, J. van Loon, Z. Martins, S. Onofri, R. Quinn, E. Rabbow, P. Rettberg, A.J. Ricco, K. Slenzka, R. de la Torre, J.-P. de Vera, F. Westall, N. Carrasco, A. Fresneau, Y. Kawaguchi, Y. Kebukawa, D. Nguyen, O. Poch, K. Saiagh, F. Stalport, A. Yamagishi, H. Yano, B.A. Klamm, Space as a tool for astrobiology: review and recommendations for experimentations in Earth orbit and beyond. Space Sci. Rev. (2017). doi:10.1007/s11214-017-0365-5
C.R. Cousins, I.A. Crawford, Volcano-Ice Interaction as a Microbial Habitat on Earth and Mars. Astrobiology 11, 695–710 (2011)
I. Couturier-Tamburelli, M.S. Gudipati, A. Lignell, R. Jacovi, N. Piétri, Spectroscopic studies of non-volatile residue formed by photochemistry of solid C4N2: a model of condensed aerosol formation on Titan. Icarus 234, 81–90 (2014)
D. Cremers, L. Radziemski, History and fundamentals of LIBS, in Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy: Fundamentals and Applications (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2006), pp. 9–16. Chapter 1
G.E. Cushing, T.N. Titus, J.J. Wynne, P.R. Christensen, THEMIS observes possible cave skylights on Mars. Geophys. Res. Lett. 34, L17201 (2007)
G. Danger, F.R. Orthous-Daunay, P.D. Marcellus, P. Modica, V. Vuitton, F. Duvernay, L. Flandinet, L.L.S. d’Hendecourt, R. Thissen, T. Chiavassa, Characterization of laboratory analogs of interstellar/cometary organic residues using very high resolution mass spectrometry. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 118, 184–201 (2013)
L.R. Dartnell, L. Desorgher, J.M. Ward, A.J. Coates, Modelling the surface and subsurface Martian radiation environment: implications for astrobiology. Geophys. Res. Lett. 34, L02207 (2007)
L. Dartnell, M.R. Patel, Degradation of microbial fluorescence biosignatures by solar ultraviolet radiation on Mars. Int. J. Astrobiol. 13, 112–123 (2013)
R. de la Torre Noetzel, Estudio de los efectos de la radiación UV sobre ecosistemas epilíticos. Tesis Doctoral, Universidad Complutense de Madrid (2002)
J.R. de la Torre, B.M. Goebel, E.I. Friedmann, N.R. Pace, Microbial diversity of cryptoendolithic communities from the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69, 3858–3867 (2003)
R. de la Torre, G. Horneck, L.G. Sancho, A. Pintado, K. Scherer, R. Facius, U. Deutschmann, M. Reina, P. Baglioni, R. Demets, Studies of LICHENS from high mountain regions in outer space: the BIOPAN experiment, in Proceedings of the III European Workshop on Exo-Astrobiology, vol. 545 (2004), pp. 193–194
R. de la Torre, L.G. Sancho, G. Horneck, C. Ascaso, A. de los Ríos, K. Olsson-Francis, C.S. Cockell, P. Rettberg, T. Berger, J.P.P. de Vera, S. Ott, J.M. Frías, J. Wierzchos, M. Reina, A. Pintado, R. Demets, Survival of lichens and bacteria exposed to outer space conditions—results of the Lithopanspermia experiments. Icarus 208, 735–748 (2010)
P. de Marcellus, C. Meinert, M. Nuevo, J.J. Filippi, G. Danger, D. Deboffle, L. Nahon, L.L.S. d’Hendecourt, U.J. Meierhenrich, Non-racemic amino acid production by ultraviolet irradiation of achiral interstellar ice analogs with circularly polarized light. Astrophys. J. Lett. 727, L27 (2011)
P. de Marcellus, C. Meinert, I. Myrgorodska, L. Nahon, T. Buhse, L.L.S. d’Hendecourt, U.J. Meierhenrich, Aldehydes and sugars from evolved precometary ice analogs: importance of ices in astrochemical and prebiotic evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 112, 965–970 (2015)
L. d’Hendecourt, M. Jourdain de Muizon, E. Dartois, M. Breitfellner, P. Ehrenfreund, J. Benit, F. Boulanger, J.L. Puget, H.J. Habing, ISO-SWS observations of solid state features towards RAFGL 7009S. Astron. Astrophys. 315L, 365–369 (1996)
D. Deamer, The origin of life, in The Princeton Guide to Evolution (Princeton University Press, Princeton, 2014), pp. 121–126
J.W. Deming, Psychrophiles and polar regions. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 3, 301–309 (2002)
S. Derenne, C. Coelho, C. Anquetil, C. Szopa, A.S. Rahman, P.F. McMillan, F. Corà, C.J. Pickard, E. Quirico, C. Bonhomme, New insights into the structure and chemistry of Titan’s tholins via \({}^{13}\mbox{C}\) and \({}^{15}\mbox{N}\) solid state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Icarus 221, 844–853 (2012)
J.P. de Vera, D. Möhlmann, F. Butina, A. Lorek, R. Wernecke, S. Ott, Survival potential and photosynthetic activity of lichens under Mars-like conditions: a laboratory study. Astrobiology 10, 215–227 (2010)
J.-P. de Vera, S. Dulai, A. Kereszturi, A. Koncz, A. Lorek, D. Mohlmann, M. Marschall, T. Pocs, Results on the survival of cryptobiotic cyanobacteria samples after exposure to Mars-like environmental conditions. Int. J. Astrobiol. 13, 35–44 (2014a)
J.-P. de Vera, D. Schulze-Makuch, A. Khan, A. Lorek, A. Koncz, D. Möhlmann, T. Spohn, Adaptation of an Antarctic lichen to Martian niche conditions can occur within 34 days. Planet. Space Sci. 98, 182–190 (2014b)
J.-P. de Vera, G. Horneck, P. Rettberg, S. Ott, The potential of the lichen symbiosis to cope with the extreme conditions of outer space II: germination capacity of lichen ascospores in response to simulated space conditions. Adv. Space Res. 33, 1236–1243 (2004)
J.P. de Vera, P. Rettberg, S. Ott, Life at the limits: capacities of isolated and cultured lichen symbionts to resist extreme environmental stresses. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 38, 457–468 (2008)
S.O.L. Direito, P. Ehrenfreund, A. Marees, M. Staats, B. Foing, W. Röling, A wide variety of putative extremophiles and large beta-diversity at the Mars Desert Research Station (Utah). Int. J. Astrobiol. 10, 191–208 (2011)
R. dos Santos, M. Patel, J. Cuadros, Z. Martins, Influence of mineralogy on the preservation of amino acids under simulated Mars conditions. Icarus 277, 342–353 (2016)
M.B. Duke et al., PISCES: Hawaii facility for simulation and training, in Proc., 38th Lunar and Planetary Science Conf., Lunar and Planetary Institute (LPI), Houston 2007)
Ehrenfreund et al., Astrobiology and habitability studies in preparation for future Mars missions: trends from investigating minerals, organics and biota. Int. J. Astrobiol. 10, 239–254 (2011)
S.A. Ewing et al., Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 70, 5293–5322 (2006)
W. Farrell, G. Delory, S.K. Atreya, Martian dust storms as a possible sink of atmospheric methane. Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, L21203 (2006)
D.C. Fernandez-Remolar et al., Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 240, 149–167 (2005)
D.C. Fernández-Remolar, O. Prieto-Ballesteros, N. Rodriguez, F. Gómez, R. Amils, J. Gómez-Elvira, C.R. Stoker, Underground habitats in the Rio Tinto Basin: a model for subsurface life habitats on Mars. Astrobiology 8, 1023–1047 (2008)
B. Fleury, N. Carrasco, T. Gautier, A. Mahjoub, J. He, C. Szopa, E. Hadamcik, A. Buch, G. Cernogora, Influence of CO on Titan atmospheric reactivity. Icarus 238, 221–229 (2014)
B.H. Foing, C. Stoker, J. Zavaleta, P. Ehrenfreund, C. Thiel, P. Sarrazin, D. Blake, J. Page, V. Pletser, J. Hendrikse, S. Direito, J.M. Kotler, Z. Martins, G. Orzechowska, C. Gross, L. Wendt, J. Clarke, A.M. Borst, S.T.M. Peters, M.B. Wilhelm, G.R. Davies (ILEWG EuroGeoMars 2009 Team), Field astrobiology research in Moon–Mars analogue environments: instruments and methods. Int. J. Astrobiol. 10, 141–160 (2011)
B.H. Foing, C. Orgel, C. Stoker, P. Ehrenfreund et al., Gale crater analogue geology studies at multiple scales, in LPI, vol. 45 (2014), p. 2675
B.H. Foing, C. Stoker, L. Rodrigues, Å. Svendsen, I. Rammos et al., Astrobiology, geology and habitability field studies supporting Mars research, in LPI, vol. 44 (2013), p. 3057
A.G. Fountain, T.H. Nylen, A. Monaghan, H.J. Basagic, D. Bromwich, Snow in the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. Int. J. Climatol. 30, 633–642 (2009)
G. Freier, The electric field of a large dust devil. J. Geophys. Res. 65, 3504 (1960)
E.I. Friedmann, Ocampo, Endolithic blue-algae in the dry valleys: primary producers in the Antarctic desert ecosystem. Science 193, 1247–1249 (1976)
E.I. Friedmann, Endolithic microorganisms in the Antarctic cold desert. Science 215, 1045–1053 (1982)
E.I. Friedmann (ed.), Antarctic Microbiology (Wiley, New York, 1993)
J.R. Garry et al., Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 41, 391–405 (2006)
T. Gautier, N. Carrasco, A. Mahjoub, S. Vinatier, A. Giuliani, C. Szopa, C.M. Anderson, J.-J. Correia, P. Dumas, G. Cernogora, Mid- and far-infrared absorption spectroscopy of Titan’s aerosols analogues. Icarus 221, 320–327 (2012)
T. Gautier, N. Carrasco, I. Schmitz-Afonso, D. Touboul, C. Szopa, A. Buch, P. Pernot, Nitrogen incorporation in Titan’s tholins inferred by high resolution orbitrap mass spectrometry and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 404, 33–42 (2014)
P.A. Gerakines, R.L. Hudson, Glycine’s radiolytic destruction in ices: first in situ laboratory measurements for Mars. Astrobiology 13, 647–655 (2013)
D. Gilichinsky et al., Astrobiology 3, 331–341 (2003)
D.A. Gilichinsky et al., Astrobiology 7, 275–311 (2007)
F. Gomez, E. Mateo-Martí, O. Prieto-Ballesteros, J.A. Martín-Gago, R. Amils, Protection of chemolithoautotrophic bacteria exposed to simulated mars environmental conditions. Icarus 209, 482–487 (2010)
J. Goordial, A.F. Davila, D. Lacelle, W. Pollard, M. Marinova, C. Greer, J. DiRuggiero, C.P. McKay, L. Whyte, Nearing the cold-arid limits of microbial life in permafrost of an upper dry valley, Antarctica. ISME J. 10, 1613–1624 (2016)
R. Greeley, B.R. White, J.B. Pollack, J.D. Iversen, R.N. Leach, Dust storms on Mars: considerations and simulations. NASA Technical Memorandum 78423: 1–32 (1977)
R. Greeley, R. Leach, B. White, J. Iversen, J. Pollack, Threshold windspeeds for sand on Mars—wind-tunnel simulations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 7, 121–124 (1980)
R. Greeley, G. Wilson, R. Coquilla, B. White, R. Haberle, Wind-blown dust on Mars: laboratory simulations of flux as a function of surface roughness. Planet. Space Sci. 48, 1349–1355 (2000)
R. Greeley, Saltation impact as a means for raising dust on Mars. Planet. Space Sci. 50, 151–155 (2002)
R. Greeley, M.R. Balme, J.D. Iversen, M. Metzger, R. Mickelson, J. Phoreman, B. White, Martian dust devils: laboratory simulations of particle threshold. J. Geophys. Res. 108, 1–12 (2003)
J.M. Greenberg, What are comets made of? A model based on interstellar dust, in Comets, ed. by L.L. Wilkening (University of Arizona Press, Tucson, 1982), pp. 131–163
J.P. Grotzinger et al., Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 240, 11–72 (2005)
H.P. Gunnlaugsson et al., Hyperfine Interact. 144/145, 365–370 (2002)
E. Hadamcik, J.-B. Renard, A. Mahjoub, T. Gautier, N. Carrasco, G. Cernogora, C. Szopa, Optical properties of analogs of Titan’s aerosols produced by dusty plasma. Earth Planets Space 65, 1175–1184 (2013)
E. Hadamcik, J-B. Renard, G. Alcouffe, G. Cernogora, A-C. Levasseur-Regourd, C. Szopa, Light scattering measurements on Titan’s aerosols analogues produced by a dusty plasma. Planet. Space Sci. 57, 1631–1641 (2009)
Hansen, European Space Agency, ESA Communications SP-1299 (2007)
A. Hansen et al., Int. J. Astrobiol. 4, 135–144 (2005)
C. He, M.A. Smith, A comprehensive NMR structural study of Titan aerosol analogs: implications for Titan’s atmospheric chemistry. Icarus 243, 31–38 (2014)
J. He, A. Buch, N. Carrasco, C. Szopa, Thermal degradation of organics for pyrolysis in space: Titan’s atmospheric aerosol case study. Icarus 248, 205–212 (2014)
J.W. Head, J.F. Mustard, M.A. Kreslavsky, R.E. Milliken, D.R. Marchant, Recent ice ages on Mars. Nature 426, 797–802 (2003)
P.E. Hintze, C.R. Buhler, A.C. Schuerger, L.M. Calle, C.I. Calle, Alteration of five organic compounds by glow discharge plasma and UV light under simulated Mars conditions. Icarus 208, 749–757 (2010)
J.W. Holt, A. Safaeinili, J.J. Plaut, J.W. Head, R.J. Phillips, R. Seu, S.D. Kempf, P. Choudhary, D.A. Young, N.E. Putzig, D. Biccari, Y. Gim, Radar sounding evidence for buried glaciers in the southern mid-latitudes of Mars. Science 322, 1235–1238 (2008)
B. Hong et al., in Abstracts, American Society for Microbiology 106th General Meeting (2006), p. 388
G. Horneck et al., AstRoMap European Astrobiology Roadmap. Astrobiology 16, 201–243 (2016)
N.H. Horowitz, R.E. Cameron, J.S. Hubbard, Microbiology of the Dry Valleys of Antarctica. Science 193, 242–245 (1972)
S.M. Hörst, M.A. Tolbert, In situ measurements of the size and density of Titan aerosol analogs. Astrophys. J. Lett. 770, L10 (2013)
S. Hörst et al., Formation of amino acids and nucleotide bases in a Titan atmosphere simulation experiment. Astrobiology 12, 809–817 (2012)
G. Horvath, J.D. Skalny, N.J. Mason, M. Klas, M. Zahoran, R. Vladoiu, M. Manole, Corona discharge experiments in admixtures of \(\mbox{N}_{2}\) and \(\mbox{CH}_{4}\): a laboratory simulation of Titan’s atmosphere. Plasma Sources Sci. Technol. 18, 034016 (2009)
H.-W. Hsu et al., Ongoing hydrothermal activities within Enceladus. Nature 519, 207–210 (2015)
H. Imanaka, B.N. Khare, J.E. Elsila, E.L.O. Bakes, C.P. McKay, D.P. Cruikshank, S. Sugita, T. Matsui, R.N. Zare, Laboratory experiments of Titan next term tholin formed in cold plasma at various pressures: implications for nitrogen-containing polycyclic aromatic compounds in previous termTitan next term haze. Icarus 168, 344–366 (2004)
H. Imanaka, P. Dale Cruikshank, B.N. Khare, C.P. McKay, Optical constants of Titan tholins at mid-infrared wavelengths (2.5–25 μm) and the possible chemical nature of Titan’s haze particles. Icarus 218, 247–261 (2012)
H. Imanaka, M.A. Smith, Formation of nitrogenated organic aerosols in the Titan upper atmosphere. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 107, 12423–12428 (2010)
J. Jänchen, J. Meeßen, T.H. Herzog, M. Feist, R. de la Torre, J.-P.P. de Vera, Humidity interaction of lichens under astrobiological aspects: the impact of UVC exposure on their water retention properties. Int. J. Astrobiol. 14, 445–456 (2015)
J. Jänchen, A. Bauermeister, N. Feyh, J.-P. de Vera, P. Rettberg, H.-C. Flemming, U. Szewzyk, Water retention of selected microorganisms and Martian soil simulants under close to Martian environmental conditions. Planet. Space Sci. 98, 163–168 (2014)
B. Jakosky et al., Astrobiology 3, 343–350 (2003)
L.L. Jensen, J. Merrison, A.A. Hansen, K.A. Mikkelsen, T. Kristoffersen, P. Nørnberg, B.A. Lomstein, K. Finster, A facility for long-term Mars simulation experiments: the Mars Environmental Simulation Chamber (MESCH). Astrobiology 8, 537–548 (2008)
A.P. Johnson, L.M. Pratt, Metal-catalyzed degradation and racemization of amino acids in iron sulfate brines under simulated Martian surface conditions. Icarus 207, 124–132 (2010)
K. Junge, H. Eicken, B.D. Swanson, J.W. Deming, Bacterial incorporation of leucine into protein down to \(-20^{\circ}\mbox{C}\) with evidence for potential activity in sub-eutectic saline ice formations. Cryobiology 52, 417–429 (2006)
D. Kapitulčinová et al., The interlayer regions of sheet silicates as a favorable habitat for endolithic microorganisms. Geomicrobiol. J. 32, 530–537 (2015)
D.M. Karl et al., Science 286, 2144–2147 (1999)
K. Kashefi, D.R. Lovley, Science 301, 934 (2003)
F. Keppler, I. Vigano, A. McLeod, U. Ott, M. Früchtl, T. Röckmann, Ultraviolet-radiation-induced methane emissions from meteorites and the Martian atmosphere. Nature 486, 93–96 (2012)
S.J. Kim, A. Jung, C.K. Sim, R. Courtin, A. Bellucci, B. Sicardy, I.O. Song, Y.C. Minh, Retrieval and tentative identification of the 3 μm spectral feature in Titan’s haze. Planet. Space Sci. 59, 699–704 (2011)
G. Kminek, J.L. Bada, The effect of ionizing radiation on the preservation of amino acids on Mars. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 245, 1–5 (2006)
K. Kobayashi, T. Kasamatsu, T. Kaneko, J. Koike, T. Oshima, T. Saito, T. Yamamoto, H. Yanagawa, Formation of amino acid precursors in cometary ice environments by cosmic radiation. Adv. Space Res. 16, 21–26 (1995)
Kotler, R.C. Quinn, Z. Martins, B.H. Foing, P. Ehrenfreund, Analysis of mineral matrices of planetary soils analogs from the Utah Desert. Int. J. Astrobiol. 10, 221–230 (2011)
T.A. Krala, T.S. Altheide, A.E. Lueders, A.C. Schuerger, Low pressure and desiccation effects on methanogens: implications for life on Mars. Planet. Space Sci. 59, 264–270 (2011)
M. Kuga, N. Carrasco, B. Marty, Y. Marrocchi, S. Bernard, T. Rigaudier, B. Fleury, L. Tissandier, Nitrogen isotopic fractionation during abiotic synthesis of organic solid particles. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 393, 2–13 (2014)
O.L. Lange, \(\mbox{CO}_{2}\)-Gaswechsel von Moosen nach Wasserdampfaufnahme aus dem Luftraum. Planta 89, 90–94 (1969)
O.L. Lange, E.-D. Schulze, W. Koch, Experimentell-ökologische Untersuchungen an Flechten der Negev-Wüste. III. \(\mbox{CO}_{2}\)-Gaswechsel und Wasserhaushalt von Krusten- und Blattflechten am natürlichen Standort während der sommerlichen Trockenperiode. Flora 12, 525–538 (1970)
O.L. Lange, T.G.A. Green, H. Reichenberger, A. Meyer, Photosynthetic depression at high thallus water contents in lichens: concurrent use of gas exchange and fluorescence techniques with a cyanobacterial and a green algal Peltigera species. Bot. Acta, Ber. Dtsch. Bot. Gesellschaft 109, 43–50 (1996)
P. Lee, Haughton-Mars Project 1997–2007: a decade of Mars analog science and exploration research at Haughton Crater, Devon Island, High Arctic, in Proc., 2nd Int. Workshop on Exploring Mars and its Earth Analogs International Research School of Planetary Sciences (IRSPS), Pescara, Italy (2007)
P. Lee, G.R. Osinski, The Haughton-Mars Project: overview of science investigations at the Haughton impact structure and surrounding terrains, and relevance to planetary studies. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 40, 1755–1758 (2005)
E. Lester et al., Soil Biol. Biochem. 39, 704–708 (2007)
R. Léveillé, Validation of astrobiology technologies and instrument operations in terrestrial analogue environments. C. R., Palévol 8, 637–648 (2009)
D.S.S. Lim, A.L. Brady (Pavilion Lake Research Project (PLRP) Team), A historical overview of the Pavilion Lake Research Project—analog science and exploration in an underwater environment, in Special Paper Geological Society of America, vol. 483 (2011), pp. 85–116
A. Lorek, A. Koncz, Simulation and measurement of extraterrestrial conditions for experiments on habitability with respect to Mars, in Habitability of other Planets and Satellites, Cellular Origin, Life in Extreme Habitats and Astrobiology, vol. 18, ed. by J.P. de Vera, J. Seckbach (2013), pp. 145–162
P.R. Mahaffy et al., The sample analysis at Mars investigation and instrument suite. Space Sci. Rev. 170, 401–478 (2012)
A. Mahjoub, N. Carrasco, P.-R. Dahoo, T. Gautier, C. Szopa, G. Cernogora, Influence of methane concentration on the optical indices of Titan’s aerosols analogues. Icarus 221, 670–677 (2012)
D. Marchant, G.H. Denton, C.C. Swisher III., N. Potter Jr., Late Cenozoic Antarctic paleoclimate reconstructed from volcanic ashes in the Dry Valleys region of southern Victoria Land. Bull. Geol. Soc. Am. 108, 181–194 (1996)
D.R. Marchant, J.W. Head, Antarctic dry valleys: microclimate zonation, variable geomorphic processes, and implications for assessing climate change on Mars. Icarus 192, 187–222 (2007)
J.J. Marlow et al., Astron. Geophys. 49, 2.2–2.5 (2008)
J.J. Marlow et al., Int. J. Astrobiol. 10, 31–44 (2011)
D. Martin, C.S. Cockell, PELS (Planetary Environmental Liquid Simulator): a new type of simulation facility to study extraterrestrial aqueous environments. Astrobiology 15, 111–118 (2015)
W. Martin et al., Hydrothermal vents and the origin of life. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6, 805–814 (2008)
Z. Martins, M.A. Sephton, B.H. Foing, P. Ehrenfreund, Extraction of amino acids from soils close to the Mars Desert Research Station (MDRS), Utah. Int. J. Astrobiol. 10, 231–238 (2011)
Z. Martins, P. Modica, B. Zanda, L.L.L.S. D’Hendecourt, The amino acid and hydrocarbon contents of the Paris meteorite: insights into the most primitive CM chondrite. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. J. 50, 926–943 (2015)
B. Maté, I. Tanarro, R. Escribano, M.A. Moreno, V.J. Herrero, Stability of extraterrestrial glycine under energetic particle radiation estimated from 2 keV electron bombardment experiments. Astrophys. J. 806, 151 (2015)
E. Mateo-Martí, O. Prieto-Ballesteros, J.M. Sobrado, J. Gómez-Elvira, J.A. Martín-Gago, A chamber for studying planetary environments and its applications to astrobiology. Meas. Sci. Technol. 17, 2274–2280 (2006)
E. Mateo-Martí, C.M. Pradier, J.A. Martín-Gago, UV-Photostability of adenine on gold and silicon surfaces. Astrobiology 9, 573–579 (2009)
E. Mateo-Martí, C.M. Pradier, UV irradiation study of a tripeptide isolated in an argon matrix: a tautomerism process evidenced by infrared and X-ray photoemission spectroscopies. Spectrochim. Acta, Part A, Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 109, 247–252 (2013)
A. Maturilli, J. Helbert, M. D’Amore, Dehydration of phyllosilicates under low temperatures: an application to Mars, in 41st Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, abstract 1533 (2010), p. 1299
T.M. McCollom, J. Geophys. Res. 104, 30729–30742 (1999)
G.D. McDonald, B.N. Khare, W.R. Thompson, C. Sagan, CH4/NH3/H2O spark tholin: chemical analysis and interaction with Jovian aqueous clouds. Icarus 94, 354–367 (1991)
G.D. McDonald, W.R. Thompson, M. Heinrich, B.N. Khare, C. Sagan, Chemical investigation of Titan and Triton tholins. Icarus 108, 137–145 (1994)
A.S. McEwen et al., Seasonal flows on warm Martian slopes. Science 333, 740–743 (2011)
J. Meeßen, P. Wuthenow, P. Schille, E. Rabbow, J.-P.P. de Vera, S. Ott, Resistance of the Lichen Buellia frigida to simulated space conditions during the preflight tests for BIOMEX—viability assay and morphological stability. Astrobiology 15, 601–615 (2015)
U.J. Meierhenrich, L. Nahon, C. Alcaraz, J.H. Bredehoft, S.V. Hoffmann, B. Barbier, A. Brack, Asymmetric vacuum UV photolysis of the amino acid leucine in the solid state. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. Engl. 44, 5630–5634 (2005)
C. Meinert, J.-J. Filippi, P.D. Marcellus, L.L.S. d’Hendecourt, U.J. Meierhenrich, N-(2-Aminoethyl)glycine and amino acids from interstellar ice analogues. ChemPlusChem 77, 186–191 (2012)
C. Meinert, I. Myrgorodska, P. de Marcellus, T. Buhse, L. Nahon, S.V. Hoffmann, L.L.S. d’Hendecourt, U.J. Meierhenrich, Ribose and related sugars from ultraviolet irradiation of interstellar ice analogs. Science 352, 208–213 (2016)
J.P. Merrison, P. Bertelsen, C. Frandsen, P. Gunnlaugsson, J.M. Knudsen, S. Lunt, M.B. Madsen, L.A. Mossin, J. Nielsen, P. Nørnberg, K.R. Rasmussen, E. Uggerhoj, Simulation of the Martian dust aerosol at low wind speeds. J. Geophys. Res., Planets 107, 5133 (2002)
J. Merrison, J. Jensen, K. Kinch, R. Mugford, P. Nørnberg, The electrical properties of Mars analogue dust. Planet. Space Sci. 52, 279–290 (2004)
J.P. Merrison, H. Gunnlaugsson, P. Nørnberg, A. Jensen, K. Rasmussen, Determination of the wind induced detachment threshold for granular material on Mars using wind tunnel simulations. Icarus 191(2), 568–580 (2007)
J.P. Merrison, H. Bechtold, H. Gunnlaugsson, A. Jensen, K. Kinch, P. Nørnberg, K. Rasmussen, An environmental simulation wind tunnel for studying aeolian transport on Mars. Planet. Space Sci. 56, 426–437 (2008)
J.P. Merrison, H.P. Gunnlaugsson, S. Knak Jensen, P. Nørnberg, Mineral alteration induced by sand transport: a source for the reddish color of Martian dust. Icarus 205(2), 716–718 (2010)
J.P. Merrison, H.P. Gunnlaugsson, M.R. Hogg, M. Jensen, J.M. Lykke, M. Bo Madsen, M.B. Nielsen, P. Nørnberg, T.A. Ottosen, R.T. Pedersen, S. Pedersen, A.V. Sørensen, Factors affecting the electrification of wind-driven dust studied with laboratory simulations. Planet. Space Sci. 60, 328–335 (2012)
D. Meunier et al., Adv. Space Res. 39, 337–344 (2007)
P. Modica, C. Meinert, P.D. Marcellus, L. Nahon, U.J. Meierhenrich, L.L.S. d’Hendecour, Enantiomeric excesses induced in amino acids by ultraviolet circularly polarized light irradiation of extraterrestrial ice analogs: a possible source of asymmetry for prebiotic chemistry. Astrophys. J. 788, 79 (2014)
M.H. Moore, R.L. Hudson, Production of complex molecules in astrophysical ices, in Astrochemistry: Recent Successes and Current Challenges. Proceedings IAU Sym., vol. 231 (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2005), pp. 247–260
M.R. Mormile et al., Instruments, methods, and missions for astrobiology, in Proceedings of the SPIE Annual Meeting, vol. 33 (2007), p. 6694
M.R. Mormile et al., Astrobiology 9, 919–930 (2009)
M. Morisson, C. Szopa, N. Carrasco, A. Buch, T. Gautier, Titan’s organic aerosols: molecular composition and structure of laboratory analogues inferred from systematic pyrolysis gas chromatography mass spectrometry analysis. Icarus 277, 442–454 (2016)
K. Motamedi, Validating the performance of a Raman laser spectrometer (RLS) instrument under Martian conditions. PhD thesis, VU University, Amsterdam, The Netherlands (2013)
G.M. Muñoz-Caro, U.J. Meierhenrich, W.A. Schutte, B. Barbier, A. Arcones Segovia, H. Rosenbauer, W.H.-P. Thiemann, A. Brack, J.M. Greenberg, Amino acids from ultraviolet irradiation of interstellar ice analogues. Nature 416, 403–406 (2002)
G.M. Muñoz Caro, W.A. Schutte, UV-photoprocessing of interstellar ice analogs: new infrared spectroscopic results. Astron. Astrophys. 412, 121–132 (2003)
G.M. Muñoz-Caro, E. Mateo-Martí, J. Martínez-Frías, Near-UV transmittance of basalt dust as an analog of the Martian regolith: implications for sensor calibration and astrobiology. Sensors 6, 688–696 (2006)
G.M. Muñoz-Caro, E. Dartois, P. Boduch, H. Rothard, A. Domaracka, A. Jiménez-Escobar, Comparison of UV and high-energy ion irradiation of methanol: ammonia ice. Astron. Astrophys. 566, 93–99 (2014)
R. Navarro-González et al., Mars-like soils in the Atacama desert, Chile, and the dry limit of microbial life. Science 302, 1018–1021 (2003)
L.D.V. Neakrase, R. Greeley, J.D. Iversen, M.R. Balme, E.E. Eddlemon, Dust flux within dust devils: preliminary laboratory simulations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 33, L19S09 (2006)
L.D.V. Neakrase, R. Greeley, Dust devil sediment flux on and Mars: laboratory simulations. Icarus 206, 306–318 (2010)
D. Nna-Mvondo, J.L. de la Fuente, M. Ruiz-Bermejo, B. Khare, C.P. McKay, Thermal characterization of Titan’s tholins by simultaneous TG–MS, DTA, DSC analysis. Planet. Space Sci. 85, 279–288 (2013)
P. Nørnberg, H.P. Gunnlaugsson, J.P. Merrison, A.L. Vendelboe, Planet. Space Sci. 57, 628–631 (2008)
P. Nørnberg, U. Schwertmann, H. Stanjek, T. Anderson, H.P. Gunnlaugsson, Clay Miner. 39, 85–98 (2004)
M. Nuevo, G. Auger, D. Blanot, L. D’Hendecourt, A detailed study of the amino acids produced from the vacuum UV irradiation of interstellar ice analogs. Orig. Life Evol. Biosph. 38, 37–56 (2008)
M. Nuevo, S.N. Milam, S.A. Sandford, J.E. Elsila, J.P. Dworkin, Formation of uracil from the ultraviolet photo-irradiation of pyrimidine in pure \(\mbox{H}_{2}\mbox{O}\) ices. Astrobiology 9, 683–695 (2009)
M. Nuevo, C. Materese, S.A. Sandford, Photochemistry of pyrimidine in realistic astrophysical ices and the production of nucleobases. Astrophys. J. 793, 125–132 (2014)
K. Olsson-Francis, C. Cockell, Experimental methods for studying microbial survival in extraterrestrial environments. J. Microbiol. Methods 80, 1–13 (2010)
S. Onofri, L. Selbmann, L. Zucconi, S. Pagano, Antarctic microfungi as models for exobiology. Planet. Space Sci. 52, 229–237 (2004)
S. Onofri, D. Barreca, L. Selbmann, D. Isola, E. Rabbow, G. Horneck, J.-P.P. de Vera, J. Hatton, L. Zucconi, Resistance of Antarctic black fungi and cryptoendolithic communities to simulated space and Mars conditions. Stud. Mycol. 61, 99–109 (2008)
S. Onofri, R. de la Torre, J.-P. de Vera, S. Ott, L. Zucconi, L. Selbmann, G. Scalzi, K. Venkateswaran, E. Rabbow, F.J. Sánchez Inigo, G. Horneck, Survival of rock-colonizing organisms after 1.5 years in outer space. Astrobiology 12, 508–516 (2012)
S. Onofri, J.-P. de Vera, L. Zucconi, L. Selbmann, G. Scalzi, K.J. Venkateswaran, E. Rabbow, R. de la Torre, G. Horneck, Survival of Antarctic cryptoendolithic fungi in simulated Martian conditions on board the international space station. Astrobiology 15, 1052–1059 (2015)
F. Orange, A. Chabin, A. Gorlas, S. Lucas-Staat, C. Geslin, M. Le Romancer, D. Prangishvili, P. Forterre, F. Westall, Experimental fossilisation of viruses from extremophilic Archaea. Biogeosciences 8, 1465–1475 (2011)
J. Oro, G. Holzer, The photolytic degradation and oxidation of organic compounds under simulated Martian conditions. J. Mol. Evol. 14, 153–160 (1979)
G. Orzechowska, R.D. Kidd, B.H. Foing, I. Kanik, C. Stoker, P. Ehrenfreund, Analysis of Mars analog soil samples using solid phase microextraction, organic solvent extraction and gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Int. J. Astrobiol. 10, 209–220 (2011)
M.E. Palumbo, G. Ferini, G.A. Baratta, Infrared and Raman spectroscopy of refractory residues left over after ion irradiation of nitrogen bearing icy mixtures. Adv. Space Res. 33, 49–56 (2004)
S. Pannewitz, M. Schlensog, T.G.A. Green, L.G. Sancho, B. Schroeter, Are lichens active under snow in continental Antarctica. Oecologia 135, 30–38 (2003)
M.R. Patel, K. Miljkovic, T.J. Ringrose, M.R. Leese, The hypervelocity impact facility and environmental simulation at the Open University, in European Planetary Science Congress, vol. 5, EPSC (2010), p. 655
S.J. Payler et al., Planetary science and exploration in the deep subsurface: results from the MINAR Program, Boulby Mine, UK. Int. J. Astrobiol. 16, 114–129 (2017)
Z. Peeters et al., Int. J. Astrobiol. 8, 301–315 (2009)
H. Perko et al., J. Aerosp. Eng. 19, 169–176 (2006)
P. Pernot, N. Carrasco, R. Thissen, I. Schmitz-Afonso, Tholinomics-chemical analysis of nitrogen-rich polymers. Anal. Chem. 82, 1371–1380 (2010)
O. Poch, A. Noblet, F. Stalport, J.J. Correia, N. Grand, C. Szopa, P. Coll, Chemical evolution of organic molecules under Mars-like UV radiation conditions simulated in the laboratory with the “Mars Organic Molecule Irradiation and Evolution” (MOMIE) setup. Planet. Space Sci. 85, 188–197 (2013)
O. Poch, S. Kaci, F. Stalport, C. Szopa, P. Coll, Laboratory insights into the chemical and kinetic evolution of several organic molecules under simulated Mars surface UV radiation conditions. Icarus 242, 50–63 (2014)
O. Poch, M. Jaber, F. Stalport, S. Nowak, T. Georgelin, J.F. Lambert, C. Szopa, P. Coll, Effect of nontronite smectite clay on the chemical evolution of several organic molecules under simulated Martian surface ultraviolet radiation conditions. Astrobiology 15, 221–237 (2015)
W. Pollard, T. Haltigin, L. Whyte, T. Niederberger, D. Andersen, C. Omelon, J. Nadeau, M. Ecclestone, M. Lebeuf, Overview of analogue science activities at the McGill Arctic Research Station, Axel Heiberg Island, Canadian High Arctic. Planet. Space Sci. 57, 646–659 (2009)
M.W. Powner, B. Gerland, J.D. Sutherland, Synthesis of activated pyrimidine ribonucleotides in prebiotically plausible conditions. Nature 459, 239–242 (2009)
L.J. Preston, L.R. Dartnell, Planetary habitability: lessons learned from terrestrial analogues. Int. J. Astrobiol. 13, 81–98 (2014)
L.J. Preston, S. Barber, M. Grady, CAFE—Concepts for Activities in the Field for Exploration—Executive summary report. ESA Contract #4000104716/11/NL/AF. http://esamultimedia.esa.int/docs/gsp/C4000104716ExS.pdf (last visited on Nov. 15, 2013)
L.J. Preston, S. Barber, M. Grady, CAFE—Concepts for Activities in the Field for Exploration—TN2: the Catalogue of Planetary Analogues. http://esamultimedia.esa.int/docs/gsp/The_Catalogue_of_Planetary_Analogues.pdf (last visited on Nov. 15, 2013)
P.B. Price, T. Sowers, Temperature dependence of metabolic rates for microbial growth, maintenance, and survival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 101, 4631–4636 (2004)
R.G. Prinn, B. Fegley, The atmosphere of Venus, Earth, and Mars: a critical comparison. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 15, 171–212 (1987)
J.C. Priscu et al., Science 286, 2141–2144 (1999)
R. Quinn et al., Planet. Space Sci. 53, 1376–1388 (2005)
F. Raulin, C. Brasse, O. Poch, P. Coll, Prebiotic-like chemistry on Titan. Chem. Soc. Rev. 41, 5380–5393 (2012)
E. Rabbow, P. Rettberg, S. Barczyk, M. Bohmeier, A. Parpart, C. Panitz, G. Horneck, R. von Heise-Rotenburg, T. Hoppenbrouwers, R. Willnecker, P. Baglioni, R. Demets, J. Dettmann, G. Reitz, Astrobiology 12, 374–386 (2012)
E. Rabbow, A. Parpart, G. Reitz, The planetary and space simulation facilities at DLR cologne. Microgravity Sci. Technol. 28, 215–229 (2016)
P. Rettberg, E. Rabbow, C. Panitz, G. Horneck, Biological space experiments for the simulation of Martian conditions: UV radiation and Martian soil analogues. Adv. Space Res. 33, 1294–1301 (2004)
E.M. Rivkina et al., Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66, 3230–3233 (2000)
A. Ross, J. Kosmo, B. Janoiko, Historical synopses of Desert RATS 1997–2010 and a preview of desert RATS 2011. Acta Astronaut. 90, 182–202 (2013)
L. Roth, J. Saur, K.D. Retherford, D.F. Strobel, P.D. Feldman, M.A. McGrath, F. Nimmo, Transient water vapor at Europa’s south pole. Science 343, 171–174 (2014)
M.J. Russell, A.J. Hall, The emergence of life from iron monosulphide bubbles at a submarine hydrothermal redox and pH front. J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 154, 377–402 (1997)
C. Sagan, B.N. Khare, Tholins: organic chemistry of interstellar grains and gas. Nature 277, 102 (1979)
C. Sagan, B.N. Khare, W.R. Thompson, G.D. McDonald, M.R. Wing, J.L. Bada, T. Vo-Dinh, E.T. Arakawa, Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the atmospheres of Titan and Jupiter. Astrophys. J. 414, 399–405 (1993)
F.J. Sánchez Iñigo, E. Mateo-Marti, J. Raggio, J. Meeßen, J. Martínez-Frías, L.G. Sancho, S. Ott, R. de la Torre, The resistance of the lichen Circinaria gyrosa (nom. provis.) towards simulated Mars conditions—a model test for the survival capacity of an eukaryotic extremophile. Planet. Space Sci. 72, 102–110 (2012)
L.G. Sancho, B. Schroeter, R. Del-Prado, Ecophysiology and morphology of the globular erratic lichen Aspicilia fruticulosa (Evers.) Flag. from Central Spain. Bibl. Lichenol. 75, 137–147 (2000)
L.G. Sancho, R. de la Torre, G. Horneck, C. Ascaso, A. de Los Rios, A. Pintado, J. Wierzchos, M. Schuster, Lichens survive in space: results from the 2005 LICHENS experiment. Astrobiology 7, 443–454 (2007)
J. Schirmack, M. Böhm, C. Brauer, H.-G. Löhmannsröben, J.-P. de Vera, D. Möhlmann, D. Wagner, Laser spectroscopic real time measurements of methanogenic activity under simulated Martian subsurface analogue conditions. Planet. Space Sci. 98, 198–204 (2014)
F. Schowengerdt, R. Fox, M. Duke, N. Marzwell, B. McKnight, PISCES: developing technologies for sustained human presence on the Moon and Mars, in Proc., 3rd AIAA Space Conf. and Exposition, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA), Reston, VA (2007), pp. 3029–3038
B. Schroeter, T.G.A. Green, L. Kappen, R.D. Seppelt, Carbon dioxide exchange at subzero temperatures. Field measurements on “Umbilicaria aprina” in Antarctica. Cryptogam. Bot. 4, 233–241 (1994)
A.C. Schuerger, R.L. Mancinelli, R.G. Kern, L.J. Rothschild, C.P. McKay, Survival of endospores of Bacillus subtilis on spacecraft surfaces under simulated Martian environments: implications for the forward contamination of Mars. Icarus 165, 253–276 (2003)
A.C. Schuerger, P. Fajardo-Cavazos, C.A. Clausen, J.E. Moores, P.H. Smith, W.L. Nicholson, Slow degradation of ATP in simulated Martian environments suggests long residence times for the biosignature molecule on spacecraft surfaces on Mars. Icarus 194, 86–100 (2008)
A.C. Schuerger, R. Ulrich, B.J. Berry, W.L. Nicholson, Growth of Serratia liquefaciens under 7 mbar, 0°C, and \(\mbox{CO}_{2}\)-enriched anoxic atmospheres. Astrobiology 13, 115–131 (2013)
D.W. Schwartzman, C.H. Lineweaver, The hyperthermophilic origin of life revisited. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 32, 168–171 (2004)
E. Sciamma-O’Brien, N. Carrasco, C. Szopa, A. Buch, G. Cernogora, Titan’s atmosphere: an optimal gas mixture for aerosol production? Icarus 209, 704–714 (2010)
J.A. Sebree, M.G. Trainer, M.J. Loeffler, C.M. Anderson, Titan aerosol analog absorption features produced from aromatics in the far infrared. Icarus 236, 146–152 (2014)
I.L. Schlacht, S. Voute, S. Irwin, M. Mikolajczak, B. Foing, A. Westenberg, C. Stoker, M. Masali, M. Rötting (Crew 91 & Mission Support), Moon-Mars Analogue Mission at the MDRS. EuroMoonMars-1 Mission, in IAC GLUC Global Lunar Conference 2010, Beijing (2010)
B. Schroeter, C. Scheidegger, Water relations in lichens at subzero temperatures: structural changes and carbon dioxide exchange in the lichen “Umbilicaria aprina” from continental Antarctica. New Phytol. 131, 273–285 (1995)
D. Schulze-Makuch et al., Astrobiology 11, 241–258 (2011)
I.A. Shkrob, S.D. Chemerisov, T.W. Marin, Photocatalytic decomposition of carboxylated molecules on light-exposed Martian regolith and its relation to methane production on Mars. Astrobiology 10, 425–436 (2010)
Y.M. Shtarkman et al., PLoS ONE 8, e67221 (2013)
A. Skelley et al., J. Geophys. Res. 112, G04S11 (2007)
J.J. Smith, L.A. Tow, W. Stafford, C. Cary, D.A. Cowan, Bacterial diversity in three different Antarctic cold desert mineral soils. Microb. Ecol. 51, 413–421 (2006)
P. Smith, in American Astronomical Society, AAS Meeting (2009), p. 213
P. Smith et al., Science 325, 58–61 (2009)
A. Somogyi, C-H. Oh, M.A. Smith, J.I. Lunine, Organic environments on Saturn’s Moon, Titan: simulating chemical reactions and analyzing products by FT-ICR and ion-trap mass spectrometry. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 16, 850–859 (2005)
F. Stalport, P. Coll, C. Szopa, F. Raulin, Search for organic molecules at the Mars surface: the “Martian Organic Material Irradiation and Evolution” (MOMIE) project. Adv. Space Res. 42, 2014–2018 (2008)
F. Stalport, P. Coll, C. Szopa, F. Raulin, Investigating the photostability of carboxylic acids exposed to Mars surface radiation conditions. Astrobiology 9, 543–549 (2009)
F. Stalport, Y.Y. Guan, P. Coll, C. Szopa, F. Macari, F. Raulin, D. Chaput, H. Cottin, UVolution, a photochemistry experiment in low Earth orbit: investigation of the photostability of carboxylic acids exposed to Mars surface UV radiation conditions. Astrobiology 10, 449–461 (2010)
A. Steele, H.E.F. Amundsen (AMASE 07 Team), Arctic Mars Analog Svalbard Expedition 2007, in Proc., 38th Lunar and Planetary Science Conf., Lunar and Planetary Institute (LPI), Houston (2007)
C.R. Stoker, M.A. Bullock, Organic degradation under simulated Martian conditions. J. Geophys. Res. 102, 10881–10888 (1997)
B. Sutter et al., Lunar and Planetary Science Conference XXXVI Abstracts (2005), p. 2182
C. Szopa, G. Cernogora, L. Boufendi, J-J. Correia, P. Coll, PAMPRE: a dusty plasma experiment for Titan’s tholins production and study. Planet. Space Sci. 54, 394–404 (2006)
I.L. ten Kate, M. Reuver, PALLAS: Planetary Analogues Laboratory for Light, Atmosphere, and Surface Simulations. Neth. J. Geosci. 95, 183–189 (2015)
I.L. ten Kate, J.R.C. Garry, Z. Peeters, R. Quinn, B. Foing, P. Ehrenfreund, Amino acid photostability on the Martian surface. Meteorit. Planet. Sci. 40, 1185–1193 (2005)
I.L. ten Kate, J.R.C. Garry, Z. Peeters, B. Foing, P. Ehrenfreund, The effects of Martian near surface conditions on the photochemistry of amino acids. Planet. Space Sci. 54, 296–302 (2006)
I.L. ten Kate, R. Armstrong, B. Bernhardt, M. Blumers, J. Craft, D. Boucher, E. Caillibot, J. Captain, G.M.T. D’Eleuterio, J.D. Farmer, D.P. Glavin, T. Graff, J.C. Hamilton, G. Klingelhöfer, R.V. Morris, J.I. Nuñez, J.W. Quinn, G.B. Sanders, R.G. Sellar, L. Sigurdson, R. Taylor, K. Zacny, Mauna Kea, Hawaii, as an analogue site for future planetary resource exploration: results from the 2010 ILSO-ISRU field-testing campaign. J. Aerosp. Eng. 26, 183–196 (2013)
Thiel, P. Ehrenfreund, B. Foing, V. Pletser, O. Ullrich, PCR-based analysis of microbial communities during the EuroGeoMars campaign at Mars Desert Research Station, Utah. Int. J. Astrobiol. 10, 177–190 (2011)
R. Thirsk, D. Williams, M. Anvari, NEEMO 7 undersea mission. Acta Astronaut. 60, 512–517 (2007)
B. Todd, M. Reagan, The NEEMO Project: A Report on How NASA Utilizes the “Aquarius” Undersea Habitat as an Analog for Long-Duration Space Flight. Engineering, Construction, and Operations in Challenging Environments, pp. 751–758 (2004). doi:10.1061/40722(153)103
M.G. Trainer, J.L. Jimenez, Y.L. Yung, O.B. Toon, M.A. Tolbert, Nitrogen incorporation in CH(4)-N(2) photochemical aerosol produced by far ultraviolet irradiation. Astrobiology 12, 315–326 (2012)
M.G. Trainer, A.A. Pavlov, D.B. Curtis, C.P. McKay, D. Worsnop, A.E. Delia, D.W. Toohey, O.B. Toon, M.A. Tolbert, Haze aerosols in the atmosphere of early Earth: manna from Heaven. Astrobiology 4, 409–419 (2004)
M.G. Trainer, A.A. Pavlov, H. Langley DeWitt, J.L. Jimenez, C.P. McKay, O.B. Toon, M.A. Tolbert, Organic haze on Titan and the early Earth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 103, 18035–18042 (2006)
B.N. Tran, M. Force, R.G. Briggs, J.P. Ferris, P. Persans, J.J. Chera, Titan’s atmospheric chemistry: photolysis of gas mixtures containing hydrogen cyanide and carbon monoxide at 185 and 254 nm. Icarus 193, 224–232 (2008)
T.A. Vishnivetskaya et al., Astrobiology 6, 400–414 (2006)
E. Vorobyova et al., FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 20, 277–290 (1997)
V. Vuitton, J.Y. Bonnet, M. Frisari, R. Thissen, E. Quirico, O. Dutuit, B. Schmitt, L. Le Roy, N. Fray, H. Cottin, E. Sciamma-O’Brien, N. Carrasco, C. Szopa, Very high resolution mass spectrometry of HCN polymers and tholins. Faraday Discuss. 147, 495–508 (2010)
D. Wagner, A. Lipski, A. Embacher, A. Gattinger, Methane fluxes in permafrost habitats of the Lena Delta: effects of microbial community structure and organic matter quality. Environ. Microbiol. 7, 1582–1592 (2005)
D. Wagner, A. Gattinger, A. Embacher, E.-M. Pfeiffer, M. Schloter, A. Lipinski, Methanogenic activity and biomass in Holocene permafrost deposits of the Lena Delta, Siberian Arctic and its implication for the global methane budget. Glob. Change Biol. 13, 1089–1099 (2007)
H. Walz, Photosynthesis yield analyzer mini-PAM, in Handbook of Operation 2nd edn. (Heinz-Walz GmbH, Effeltrich, 1999)
F. Westall, The Early Earth, in Frontiers of Astrobiology, ed. by C. Impey, J. Lunine, J. Funes (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2012), pp. 89–114
F. Westall, F. Foucher, B. Cavalazzi, S.T. de Vries, W. Nijman, V. Pearson, J. Watson, A. Verchovsky, I. Wright, J.N. Rouzaud, D. Marchesini, S. Anne, Early life on Earth and Mars: a case study from \(\sim3.5~\mbox{Ga}\)-old rocks from the Pilbara, Australia. Planet. Space Sci. 59, 1093–1106 (2011)
F. Westall, F. Foucher, N. Bost, M. Bertrand, D. Loizeau, J.L. Vago, G. Kminek, F. Gaboyer, K.A. Campbell, J-B. Bréhéret, P. Gautret, C.S. Cockell, Biosignatures on Mars: what, where and how? Implications for the search for Martian life. Astrobiology 15, 998–1029 (2015a)
F. Westall, K.A. Campbell, J.G. Bréhéret, F. Foucher, P. Gautret, A. Hubert, S. Sorieul, N. Grassineau, D.M. Guido, Archean (3.33 Ga) microbe-sediment systems were diverse and flourished in a hydrothermal context. Geology 43, 615–618 (2015b)
K.E. Williams, C.P. McKay, O.B. Toon, J.W. Head, Do ice caves exist on Mars? Icarus 209, 358–368 (2010)
D.D. Wynn-Williams, H.G.M. Edwards, Antarctic ecosystems as models for extraterrestrial surface habitats. Planet. Space Sci. 48, 1065–1075 (2000)
R.A. Yingst, P. Russell, I.L. ten Kate, S. Noble, T. Graff, L.D. Graham, D. Eppler, Designing remote operations strategies to optimize science mission goals: lessons learned from the Moon Mars Analog Mission Activities Mauna Kea 2012 field test. Acta Astronaut. 113, 120–131 (2015)
J. Žabka, C. Romanzin, C. Alcaraz, M. Polášek, Anion chemistry on Titan: a possible route to large N-bearing hydrocarbons. Icarus 219, 161–167 (2012)
M.P. Zorzano, E. Mateo-Martí, O. Prieto-Ballesteros, S. Osuna, N. Renno, The stability of liquid saline water on present day Mars. Geophys. Res. Lett. 36, L20201 (2009)
Acknowledgements
This work has been supported by ESA, through a Topical Team grant from 2011 to 2016. We are grateful to Oliver Angerer, Jason Hatton and René Demets from ESA for their help and support. UPEC and LISA provided important administrative help (Mireille Paul, Sabrina Hammache, Valérie Simard, Nicolas Vautrin). Zita Martins is funded by a Royal Society University Research Fellowship (grant UF080820 and grant UF130324). Nathalie Carrasco acknowledges the financial support of the European Research Council (ERC Starting Grant PRIMCHEM, grant agreement no. 636829). Pascale Ehrenfreund acknowledges support from the NASA Astrobiology Institute. Louis d’Hendecourt acknowledges support from the French Space Agency (CNES) Exobiology Group. Silvano Onofri acknowledges the Italian Space Agency (ASI) for financial support. Inge Loes ten Kate acknowledges the Netherlands Space Office (NSO), the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (NWO) and Raheleh Motamedi for fruitful discussions. Jean-Pierre de Vera acknowledges the Helmholtz-Gemeinschaft for financial support through the Helmholtz-Alliance Planetary Evolution and Life. Frances Westall acknowledge support from the French Space Agency (CNES), the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (ANR), the Centre national de la recherche scientifique (CNRS-MI-2014), the MASE project (supported by European Community’s Seventh Framework Programme (FP7/2007-2013) under Grant Agreement no. 607297), and the H2020 EUROCARES programme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Note by the editor: This is a Special Communication, supplementing the paper by Cottin et al. on “Astrobiology and the Possibility of Life on Earth and Elsewhere…”, 2015, Space Science Reviews, doi:10.1007/s11214-015-0196-1 and Cottin et al. on “Space as a Tool for Astrobiology: Review and Recommendations for Experimentations in Earth Orbit and Beyond”, 2017, Space Science Reviews, doi:10.1007/s11214-017-0365-5.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made.
About this article
Cite this article
Martins, Z., Cottin, H., Kotler, J.M. et al. Earth as a Tool for Astrobiology—A European Perspective. Space Sci Rev 209, 43–81 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-017-0369-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11214-017-0369-1