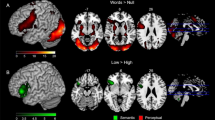
Abstract
Strategy effects on word searching in the Japanese letter fluency test were investigated using the Near-infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS). Participants were given a Japanese letter fluency test and they were classified into two types of strategy users, based on analysis of their recorded verbal responses. One group, AIUEO-order strategy users, employed sequential word searching based upon the imagery of the AIUEO-table which they mastered when young, and the other group, semantic strategy users, searched for the next word mainly based on semantic relations. The blood-flow volumes (OxyHb) measured of the AIUEO-order strategy users were greater than for the semantic strategy users in the frontal parts of the brain, and the blood-flow was more active in the right than in the left part of the brain. These different activation patterns suggest that the NIRS might be useful new brain imaging technique for examination of psychological process in verbal behavior.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez, J. A., & Emory, E. (2006). Executive function and the frontal lobes: A meta-analytic review. Neuropsychology Review, 16, 17–42.
Baldo, J. V., Schwartz, S., Wilkins, D., & Dronkers, N. F. (2006). Role of frontal versus temporal cortex in verbal fluency as revealed by voxel-based lesion symptom mapping. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 12, 896–900.
Brysbeart, M. (1995). Arabic number reading: On the nature of the numerical scale and the origin of phonological recording. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 124, 434–452.
Cai, Q., Lavidor, M., Brysbeart, M., Pauligan, Y., & Nazir, T. A. (2008). Cerebral lateralization of frontal lobe language processes and lateralization of the posterior visual word processing system. Journal of Cognitive Neurosciences, 20, 372–381.
Charlot, V., Tzourio, N., Zilbovicious, M., & Mazoyer, B. M. (1992). Different mental imagery abilities result in different regional cerebral blood flow activation patterns during cognitive tasks. Neuropsychologia, 30, 565–580.
Dehaene, S., & Akhavein, R. (1995). Attention, automaticity, and levels of representation in number processing. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Human Perception and Performance, 16, 626–641.
Farah, M. J. (1984). The neural basis of mental imagery: A componential analysis. Cognition, 18, 245–272.
Farah, M. J. (1995). The neural basis of mental imagery. In M. Gazzaniga (Ed.), Cognitive neuroscience (pp. 963–975). Cambridge: MA: MIT Press.
Fossati, P., Harvey, P. O., Le Bastard, G., Ergis, A. M., Jouvent, R., & Allilaire, J. F. (2003). Qualitative analysis of verbal fluency in depression. Psychiatry Research, 117, 17–24.
Frost, J. A., Binder, J. R., Springer, J. A., Hammeke, T. A., Bellgowan, P. S. F., Rao, S. M., et al. (1999). Language processing is strongly left lateralized in both sexes: Evidence from functional MRI. Brain, 122, 199–208.
Gourpvitch, M. L., Kirkby, B. S., Goldberg, T. E., Weinberger, D. R., Gold, J. M., Esposito, G., et al. (2000). A comparison of rCBF patterns during letter and semantic fluency. Neuropsychology, 14, 353–360.
Hatta, T. (1978). Visual field differences in a mental transformation task. Neuropsychologia, 16, 637–641.
Hatta, T., Koike, M., & Langman, P. (1994). Laterality of mental imagery generation and operation: Tests with brain-damaged patients and normal adults. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 16, 577–588.
Herrmann, M. J., Ehlis, A.-C., & Fallgatter, A. J. (2003). Frontal activation during a verbal-fluency task as measured by near-infrared spectroscopy. Brain Research Bulletin, 61, 51–56.
Hirshorn, E. A., & Thompson-Schill, S. L. (2006). Role of the left inferior frontal gyrus in covert word retrieval: Neural correlates of switching during verbal fluency. Neuropsychologia, 44, 2547–2557.
Hoshi, Y., Oda, I., Wada, Y., Ito, Y., Yamashita, Y., Oda, M., et al. (2000). Visuospatial imagery is a fruitful strategy for the digit span backward task: A study with near-infrared optical tomography. Cognitive Brain Research, 9, 339–342.
Hoshi, Y., & Tamura, M. (1997). Near-infrared optical detection of sequential brain activation in the prefrontal cortex during mental tasks. NeuroImage, 5, 292–297.
Ito, E., & Hatta, T. (2002). Development of the verbal fluency test for Japanese. Studies in Informatics and Sciences, 15, 81–96.
Ito, Y., & Hatta, T. (2003). Semantic processing of Arabic, Kanji, and Kana numbers: Evidence from interference in physical and numerical size judgments. Memory and Cognition, 31, 360–368.
Ito, Y., & Hatta, T. (2004). Spatial structure of quantitative representation of numbers: Evidence from SNARC effect. Memory and Cognition, 32, 662–673.
Jobsis, F. F. (1977). Noninvasive, infrared monitoring of cerebral and myocardial oxygen sufficiency and circulatory parameters. Science, 198, 1264–1274.
Kanari, A., & Hatta, T. (2007). Mechanisms of word generation in the Japanese letter fluency test: Does Japanese employ a specific strategy? Journal of Human Environmental Studies, 5, 7–12.
Kosslyn, S. M. (1996). Image and brain (pp. 315–317). Cambridge: MIT Press.
Landman, C., Dehaene, S., Pappata, S., Jobert, A., Bottelaneder, M., Roumenov, D., et al. (2007). Dynamics of prefrontal and cingulate activity during a reward-based logical deduction task. Cerebral Cortex, 17, 749–759.
Lezak, M. D. (2004). Neuropsychological assessment (4th ed.). New York: Oxford University Press.
Mummery, C. J., Patterson, K., Hodges, J. R., & Wise, R. J. (1996). Generating ‘tiger’ as an animal name or a word beginning with T: Differences in brain activation. Proceedings of Biological Sciences/The Royal Society, 263, 989–995.
Phelps, E. A., Hyder, F., Blamire, A. M., & Shulman, R. G. (1997). FMRI of the prefrontal cortex during overt verbal fluency. Neuroreport, 8, 561–565.
Piazza, M., & Dehaene, S. (2004). From number neurons to mental arithmetic: The cognitive neuroscience of number senses. In M. Gazzaniga (Ed.), The cognitive neurosciences (pp. 865–875). Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Pujol, J., Vendrell, P., Deus, J., Kulisevsky, J., et al. (1996). Frontal lobe activation during word generation studied by functional MRI. Acta Neurologica Scandinavica, 93, 403–410.
Raskin, S. A., Sliwinski, M., & Borod, J. C. (1992). Clustering strategies on tasks of verbal fluency in Parkinson’s disease. Nuropsychologia, 30, 95–99.
Rende, B., Ramsberger, G., & Miyake, A. (2002). Commonalities and differences in the working memory components underlying letter and category fluency tasks: A dual-task investigation. Neuropsychology, 16, 309–321.
Robert, P. H., Lafont, V., Medecin, I., Berthet, L., Thauby, S., Baudu, C., et al. (1998). Clustering and switching strategies in verbal fluency tasks: Comparison between schizophrenics and healthy adults. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 4, 539–546.
Ruff, R. M., Light, R. H., Parker, S. B., & Levin, H. S. (1997). The psychological construct of word fluency. Brain and Language, 57, 394–405.
Saito, K., & Watanabe, S. (2006). Spatial memory activation of the parietal cortex measured with near-infrared spectroscopic imaging in the finger-maze of the Morris water maze analogue for humans. Reviews in the Neurosciences, 17, 227–238.
Schlosser, R., Hutchinson, M., Joseffer, S., Rusinek, H., Saarimaki, A., Stevenson, J., et al. (1998). Functional magnetic resonance imaging of human brain activity in a verbal fluency task. Journal of Neurology and Neurosurgical Psychiatry, 64, 492–498.
Schroeter, M. L., Zysset, S., Wahl, M., & von Cramon, D. Y. (2004). Prefrontal activation due to Stroop interference increases during development – An event-related fNIRS study. Neuroimage, 23, 1317–1325.
Schwartz, S., Baldo, J., Graves, R. E., & Brugger, P. (2003). Pervasive influence of semantics in letter and category fluency: A multidimensional approach. Brain and Language, 87, 400–411.
Spreen, O., & Strauss, E. A. (1998). Compendium of neuropsychological tests (2nd ed.). New York: Oxford University Press.
Troyer, A. K. (2000). Normative data for clustering and switching on verbal fluency tasks. Journal of Clinical and Experimental Neuropsychology, 22, 370–378.
Troyer, A. K., Moscovitch, M., & Winocur, G. (1997). Clustering and switching as two components of verbal fluency: Evidence from younger and older healthy adults. Neuropsychology, 11, 138–146.
Villringer, A., & Chance, B. (1997). Non-invasive optical spectroscopy and imaging of human brain function. Trends in Cognitive Neurosciences, 20, 435–442.
Weiss, E. M., Hofer, A., Golaszewski, S., Siedentopf, C., Brinkhoff, C., Kremser, C., et al. (2004). Brain activation patterns during a verbal fluency test – A functional MRI study in healthy volunteers and patients with schizophrenia. Schizophrenia Research, 70, 287–291.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
Japanese syllabary table
ん (nn) | わ (wa) | ら (ra) | や (ya) | ま (ma) | は (ha) | な (na) | た (ta) | さ (sa) | か (ka) | あ (a) |
り (r i) | み (mi) | ひ (hi) | に (ni) | ち (t i) | し (si) | き (ki) | い (i) | |||
る (ru) | ゆ (yu) | む (mu) | ふ (hu) | ぬ (nu) | つ (tu) | す (su) | く (ku) | う (u) | ||
れ (re) | め (me) | へ (he) | ね (ne) | て (t e) | せ (se) | け (ke) | え (e) | |||
を (wo) | ろ (ro) | よ (yo) | も (mo) | ほ (ho) | の (no) | と (to) | そ (so) | こ (ko) | お (o) |
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hatta, T., Kanari, A., Mase, M. et al. Strategy effects on word searching in Japanese letter fluency tests: evidence from the NIRS findings. Read Writ 22, 1041–1052 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-008-9143-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11145-008-9143-9